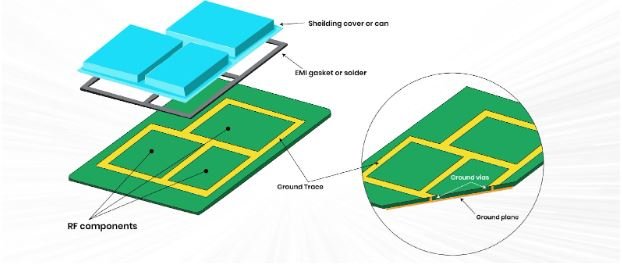
As in most industries, electronic markets require the PC board assembly to be as optimized as possible for cost, reliability, and overall production workflow. This is where the Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) principles kick in. DFMA is a systematic method that contains design instructions that guide the assembly of circuit boards and components in ways that minimize time and costs.
Integrating DFMA for PCBs enables designers and manufacturers to improve product quality while reducing assembly time and material costs. The idea is to achieve a balance between manufacturability, assemblability, functionality, and reliability. In this blog post, I will discuss the DFMA principles for PCBs, their influence on production, and the reasons why they are needed in optimized electronic products.
Defining DFMA in PCB Design
What does DFMA mean?
There are two key components of DFMA.
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM): Deals with the design approach toward multilayer PCBs and other board types to maximize ease of fabrication and minimize production costs.
- Design for Assembly (DFA): Deals with assembly-related issues where there is a large number of different parts by reducing the number of parts to be assembled, incorporating standardized components, and simplifying the layout of the wiring board.
With these two strategies combined, DFMA for PCBs will assist in eliminating manufacturing mistakes, shortening production times, and increasing product strength.
Important DFMA Considerations For PCBs
1. Optimization of the PCB Structure
Complex circuit board assemblies significantly increase cost and the possibility of defects. When optimizing PCB fabrication, designers should:
- Stand operate board shapes to eliminate additional material cutting and wasting.
- Eliminate unnecessary layers in multilayer PCBs.
- Organize and physically separate trace routing to aid in testing and debugging procedures.
- Eliminating features doesn’t add much to the overall cost of manufacturing and production time.
2. Utilize Appropriate Components and Materials
Using commercially available components can increase the efficiency of the PCBs remarkably. Using off-the-shelf items does have some limitations. Considerations include:
- Non-custom components that greatly reduce procurement expenses.
- Component footprints that do fit with standard DFMA when designing the PCB.
By using readily optimized materials and components, production time greatly increases since the risks are greatly mitigated.
3. Making PCB Layouts More Assembly Friendly
There is no doubt a good PCB layout will enhance the effectiveness of the pc board assembly. Here are some tips the designers can follow to achieve this:
- Position high-frequency components near the connectors in order to reduce interference.
- In multilayer PCBs, vias should be kept to a minimum to increase reliability.
- Allow sufficient spacing between components for automated assembly machines.
- Other activities like testing and troubleshooting become easy when the layout is optimized.
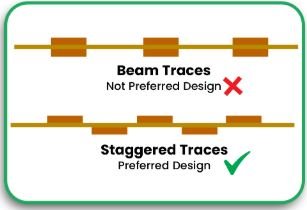
4. Cuts on Connected Flexible Parts
Flexible circuits do have their place within the industry, but an overabundance can hinder the ease of assembly when it comes to the printed circuit board. In order to promote reliability:
- Use rigid connectors in place of weak ribbon cables.
- Reduce interconnects and connectors to lower failure rates.
- Design the PCB to allow for surface-mount devices, which eases automated assembly.
- Incorporating single-sided PCBs for flexible areas while doing away with any fragile segments increases the durability of the end product.
PC Board DFMA Assembly, Making It More Efficient
1. PC Board Assembly Automation
A significant portion of assembly on a pc board is done automatically. DFMA for PCBs promotes the utilization of the following:
- “Pick-and-place” machines make the placement of board components both faster and more accurate.
- Reflow and wave soldering allows for automated soldering.
- Assembly defects are detected at an early stage with automated optical inspection (AOI).
The incorporation of automation during the PCB design process leads to increased consistency while lowering labor costs.
2. Proper Application of a Solder Mask
A solder mask on a PCB prevents the soldering-related bridges while at the same time protecting the copper traces from oxidation. When using the DFMA technique, it is best to remember the following:
- Select a solder mask material that can endure high temperatures, as well as chemical contact.
- Apply solder mask layers sufficiently to achieve proper coverage.
- Maintain spacing clearance between pads and apertures to enable zero short-circuit occurrences.
Performance and deterioration of the PCB can be enhanced by having a properly applied solder mask material.
3. Consolidating Assembly Operations
According to the DFMA rules, in order to increase efficiency of assembly operations:
- Eliminate components that are different in type to make stock control simpler, as well as to reduce manipulation.
- Employ similar standards in attaching equivalent components.
- Where feasible, incorporate parts to reduce the number of different assemblies.
Adhering to these steps leads to reduced production time, as well as lower economic costs.
Benefits of DFMA for PCB Manufacturers
-
Cost Savings
- Reducing unnecessary complexity in PCB design lowers production costs.
- Standardizing components allows for bulk purchasing and reduces expenses.
-
Improved Product Reliability
- Fewer interconnections and simpler layouts minimize potential failure points.
- Optimized solder mask material application enhances protection against environmental factors.
-
Faster Time-to-Market
- Streamlining manufacturing and assembly reduces production delays.
- Minimized revisions ensure that PCBs are ready for use more quickly.
-
Higher Manufacturing Efficiency
- Automated assembly compatibility speeds up the production process.
- Clear design guidelines reduce errors and improve consistency.
Best Practices of DFMA and Emerging Business Developments
The Growing Power of The Small Device
More powerful, smaller devices mean increased demand for higher performance and more compact multilayer PCBs.
The balance achieved between assembly ease and deep miniaturization exemplifies distinctions in DFMA principles.
An Increasing Need for Dependable Electronics
Automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors have more stringent designs for manufacture and assembly requirements for PCBs.
Quality control has become the number one priority for PCB circuit board manufacturers.
Expansion Tech of AI and Automation in Industry
In PCB design, AI-powered DFMA software adjusts the layout for speed and other factors.
Monitoring and testing become automated, removing the need for manual quality assurance.
Expert Insight
A review of 171 research articles highlights key aspects of DfMA, including its fundamental principles, its role in Dfab and DfAM, and its application in additive manufacturing (AM) assembly. Additionally, the potential of machine learning in optimizing DfMA processes has been explored, revealing significant opportunities for automation and efficiency.
Despite these advancements, there remain notable research gaps in DfMA for Dfab and DfAM. Addressing these gaps could enhance operational performance, reduce material waste, and support more sustainable construction practices. As the industry continues to evolve, further research and innovation in DfMA will be essential for shaping the future of construction.
Conclusion
To enhance reliability, lower costs, and optimize pc board assembly and construction administration, applying DFMA techniques for PCBs is critical. The simplification of design, selection of solder mask, and reduction of steps in assembly all serve to increase production effectiveness.
With the multifunctional capabilities of PCBs, they are faster to design alongside assembly integration and the process as a whole. Thus, time-to-market is lessened, and product quality is improved.
At PCB Runners, we offer professional assembly services and circuit board manufacturing. Call us today so we can assist you in improving your PCB production processes and for greater savings without compromising quality standards!
FAQs
What is DFMA in PCB manufacturing?
Within the scope of PCB manufacturing, DFMA (Design for Manufacturing and Assembly) is the approach that optimizes the design process by making it easier to manufacture and assemble the product.
Why is DFMA important in circuit board assembly?
It simplifies the construction and assembling processes of the circuit board in a way that standard components can be suitably integrated within.
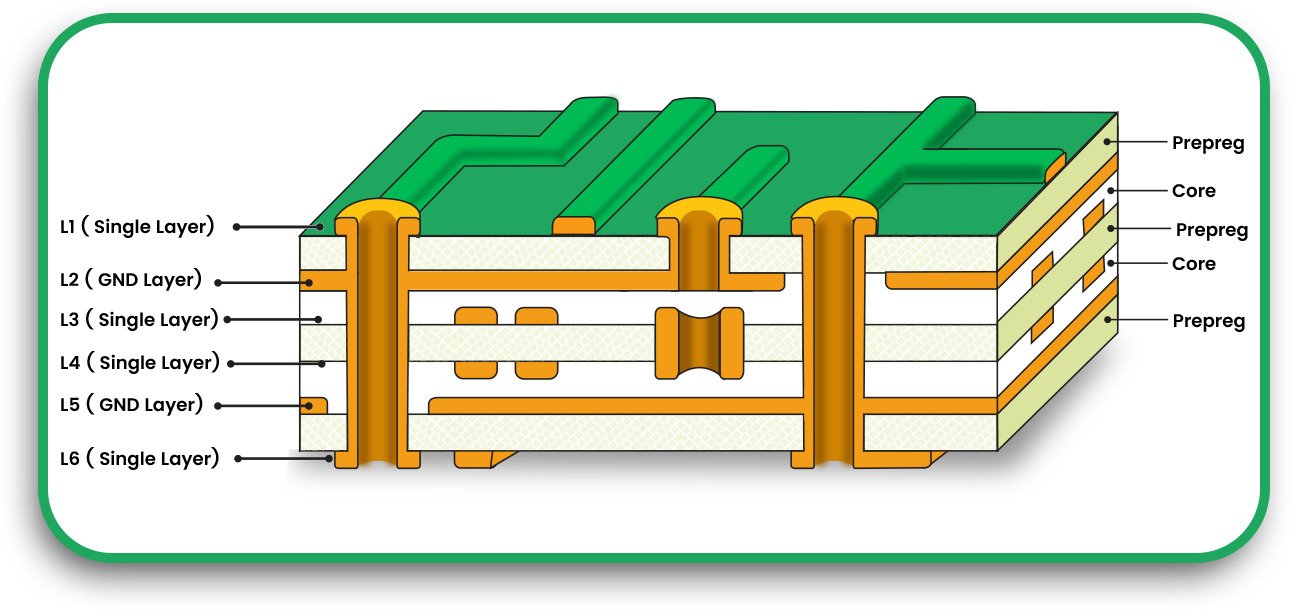
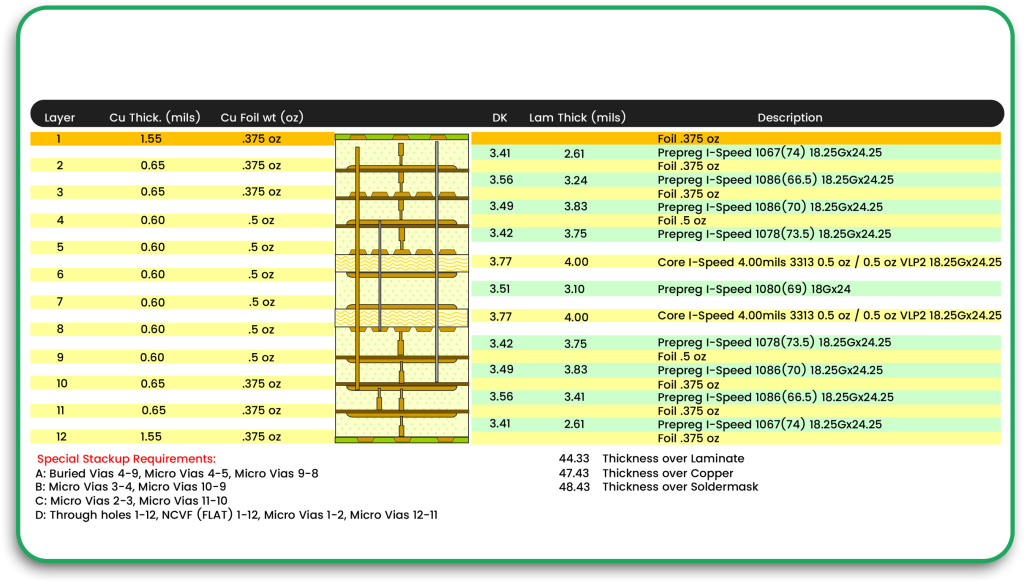
How does DFMA impact multilayer PCBs?
Cost reduction is the most obvious advantage of adopting multilayer technology. Most stack-up designs are optimized for performance, reliability, electrical integrity, and ease of manufacturability.
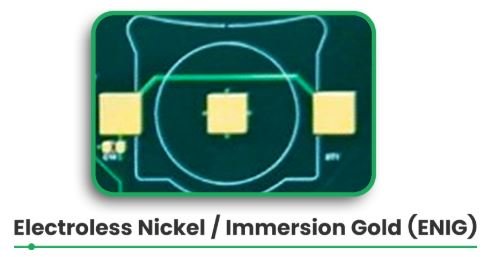
What role does solder mask material play in DFMA?
The best solder masks prevent the exposure of the copper circuitry to oxygen in the environment. These aids in avoiding PCB oxidation, prevents short circuits, and make the circuit board more robust.
How can PCB Runners help with DFMA-compliant PCB design?
With PCB Runners, you are assured that your boards will be assembled with care and accuracy. We employ strategies that are cost-effective while ensuring the highest quality in PCB assembly.