In the world of PCBs, we frequently encounter two distinct types: rigid PCBs and flexible circuits. While both serve the purpose of interconnecting electronic components and facilitating device functionality, each type has unique characteristics and applications. If you are unsure which type best matches your requirements, this article aims to provide you with the necessary knowledge to make an informed decision.
What Is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)?
A PCB is a flat board with electronic components mounted on it and connected with wires through which electricity flows. It is responsible for controlling all primary functions of the device and, hence, the components are required to communicate effectively. The efficient and effective functioning of electronic components is directly contingent on the quality of the PCB.
The classification of PCBs is quite expansive; however, we can narrow it down into two categories: Rigid PCBs and flexible circuits.
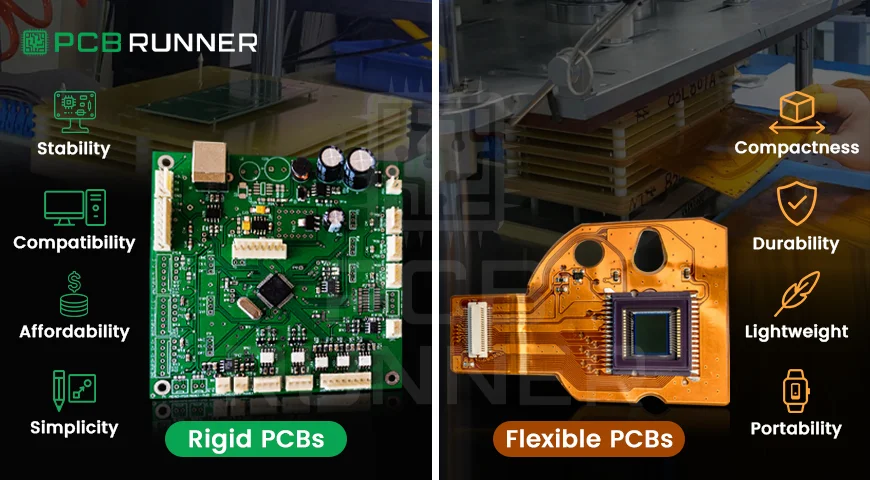
Rigid PCBs:
The Infidelities And Errant Behaviours Offered By The Sturdy And Monolithic PCBs
Rigid PCBs have the properties of solid materials such as fibreglass. They cannot be bent or twisted without breaking the internal connections and the board itself.
Benefits of rigid PCBs:
- Serves as a solid and stable support structure for components and peripherals.
- Suitable for medium to large-sized devices and equipment that are relatively more robust.
- Cost-effective for bulk production.
- Simplified design processes for non-flexing or non-folding boards.
Rigid PCBs are commonly installed in modern televisions and desktop computers as well as other stationary electronic devices.

Flexible Circuits: The Sturdy And Monolithic PCBs
Known as flex circuits, flexible PCBs are the most different. They can be twisted and bent due to the special type of plastic they are made from. Imagine a tiny, flat ribbon that can fold without breaking.
Why flexible circuits matter:
- Essential for tight, confined spaces.
- Less burden and weight than rigid boards.
- Great ability to absorb shocks and vibrations.
- Optimal for wearable technology and carried gadgets such as smartwatches and smartphones.
- If your device needs to move or if space is constrained, flex circuits are most likely the best solution.
Here is what some designers do when they want more than one option: they use rigid-flex PCBs. These boards feature rigid sections for mounting the components and flexible areas for interconnection.
This mixture is beneficial for:
- Situations when a device is supposed to be rigid in some areas but flexible in others.
- Weight and space optimisation.
- Situations where super reliability is needed, such as in aircraft, medical devices, and high-end smartphones.

What Should Guide Your Choice?
Let us now focus on how to make a decision. You want to ensure the PCB you select is tailored to your device’s requirements to avoid unnecessary expenditures or frustration.
Choose a rigid PCB when:
- The device is not required to move or bend.
- The user is designing a larger piece of equipment.
- Cost will probably be the most crucial factor if you are looking to manufacture in bulk.
- You prefer simple manufacturing.
- Choose a flexible circuit if:
- You are making a small wearable gadget.
- You are trying to minimise weight.
- Your device is prone to movement or impacts.
- You intend to position electronics in tight or irregular spaces.
Choose a rigid-flex PCB if:
- You intend to have significant structural support while maintaining some give.
- Your project requires high durability.
- You want a compact design without sacrificing reliability.
What About EMC in PCBs?
Electromagnetic compatibility may be a big question for you. Here is why it is essential: any gadget will have issues if it interacts with other systems due to unwanted electrical noise or if it is the one getting interfered with.
Make sure that with the PCB prototype order or the custom printed circuit board order that the EMC design is done correctly. It will not interfere with radios, phones or any other device in the vicinity. After construction, it is best to have the board undergo electromagnetic compatibility testing. This ensures that the board is built according to specs and functions correctly.
EMC concerns are applicable to both flexible and rigid boards. There are processes for testing how your PCB handles signals and interference. You might come across it as EMC PCB testing or use electromagnetic compatibility testing equipment.
Testing Circuit Boards: Don’t Skip It
Before a design is released, a board is tested for a range of factors, and it is not limited to EMC alone. Your PCB must also pass electrical and mechanical tests. These tests evaluate the integrity of the circuitry, ensure it can endure physical handling, and determine whether it is resistant to heat and vibration.
Comprehensive testing during these stages mitigates frustration when the device is customer-facing.
Tips to Remember for Your PCB Order
- When describing the needs of your device, ensure that you are precise when ordering a printed circuit board for customisation.
- Inquire about tests for electromagnetic compatibility and how they align with your predetermined specifications.
- Predict changes to the design. For changes that expect movement later, consider flexible or rigid-flex PCBs.
- Cost is essential, but prioritising quality and reliability is crucial.
- For beginners, a PCB prototype is the best starting point.
Wrap Up: What Would Be Your Best Choice of PCB?
As discussed, consider the needs of your gadget and not just the most popular or the least expensive option when you are selecting the type of PCB. For larger, sturdier devices, rigid PCBs are advisable. For smaller, more delicate devices, flexibles are preferable. For users who need both, rigid-flex permittivity is an ideal option.
Bear in mind that the design of custom printed circuit boards should be done strategically with EMC in mind. Testing designs helps avoid unexpected issues. For those looking to test or prototype their designs, PCB Runner is a good option.
Would you like to understand more about PCBs and their functioning? For accessible and reliable information, visit PCB Runner.
Knowledge of PCB options gives you leverage over your project. From the very beginning, whether you are starting with a basic PCB prototype or are prepared for large-scale production, having the correct type of board will be very beneficial. Reach out to PCB Runner for bespoke advice catered to your design. Every project needs a strong foundation, and the only way to achieve this is by having the correct PCB from the very beginning.
FAQs
Q1: What distinguishes a rigid PCB from a flexible circuit?
The bending feature is the key difference between Rigid PCBs and Flexible Circuits. Rigid PCBs cannot bend, while flexible circuits are designed to bend, fold, and twist.
Q2: Are flexible circuits always more expensive?
As is often the case for flexible circuits, they tend to be more expensive due to the specific construction processes and specialised materials they employ.
Q3: Can rigid PCBs be used in small gadgets?
They can, although there are limitations to areas that require bending, as they may not be able to fit into those regions.
Q4: Why is EMC testing necessary?
To prevent your PCB from electrically radiating noise or receiving radiation from outside sources, it is pertinent that EMC testing be performed.
Q5: Which Industries utilise rigid flex PCBs?
They are used in Aerospace, Military, Medical devices, and high-end consumer electronics.