Producing a PCB is similar to constructing a well-built house. Every individual step is essential. One such step is glue application. Glue is used to assist with the friction fit of components during assembly. Like with many processes, using too much or too little can cause problems. This document outlines glue dosing methods for PCBs, addressing the importance of glue, its applications, and how to achieve consistent accuracy.
What is Glue Dosing in PCB Production?
Glue dosing refers to the application of small quantities of adhesive to a PCB board in the course of assembly. The adhesive secures components during the curing and soldering stages. This is useful for small components that are situated at the bottom of the board to prevent them from falling off due to gravity during the soldering stage.
Glue dosing is applicable at various stages of PCB production. This is observed in both PCB prototype work and volume production runs.
What is the purpose of glue in PCB assembly?
- Maintaining the positional accuracy of the components: Glue prevents components from shifting prior to soldering.
- Increases assurance: Effective glue application enhances stability and fortifies your PCB printed circuit board assembly.
- Assistance with custom shapes: Some custom PCB assembly projects involve parts with unusual shapes that require additional support.

Glue Category Used in PCBs
Not all glues can be compared. Your requirements determine the type you choose.
- Epoxy glue: Widely used and potent. Requires heat to cure.
- Silicone glue: Suitable for parts that move or vibrate, offering pliability.
- Acrylic Glue: Good for fast jobs and cures quickly.
- Hot melt glue: Ideal for parts that require heating to melt and cooling to harden.
- UV curable glue: Cures when exposed to certain light.
Fulfilling different purposes, different types of glue exist. Always verify the part’s datasheet or consult your PCB producer for the proper recommendations.

How to Prepare Glue Dosing
- Before anything else, confirm that your PCB boards are free of grit. Glue, especially, won’t adhere to surfaces contaminated with dust, oil, or dirt.
- Clean with 90% isopropyl alcohol (IPA) solutions.
- Do not use your bare hands to touch the treated surfaces post cleaning.
- Allow the surfaces to dry completely before applying the product.
Applying glue will benefit significantly from a well-prepared surface, resulting in a longer-lasting bond.
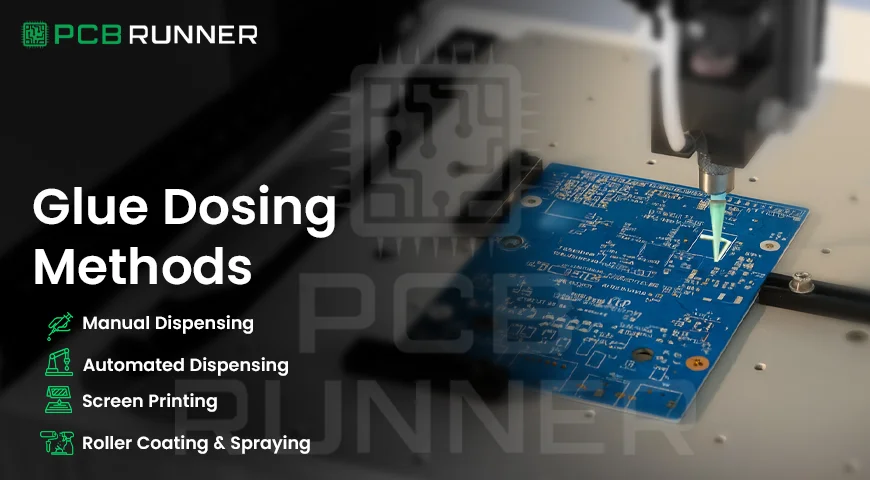
Glue Dosing Methods
Different techniques can be used to apply glue to a PCB. Your choice of methods will depend on the size of your project and the type of glue you are using.
Manual Dispensing
- Use a syringe or a small bottle.
- Best suited for prototypes or small batches.
- You dictate where the glue goes and in what quantity.
Automated Dispensing
- These are machines that place glue dots at specific locations.
- Best suited for massive production runs.
- Faster than manual work, and more accurate too.
Screen Printing
- Glue is stuck to the board through a stencil.
- Best suited for applying glue to multiple areas at once.
- This is common in some big factories.
Roller Coating and Spraying
- Glue is either rolled onto the board or sprayed onto it.
- Best for a large custom board.
- Most companies prefer automated dispensing because it is fast and accurate.
How Much Glue Should You Use?
This is crucial. Too little glue will allow parts to drop off, while too much will create short circuits in other regions.
- Use just enough glue to keep the item in position.
- For most parts, a small dot of glue works best.
- For larger components, two or more dots may be necessary.
- Refer to the datasheet for the recommended size and position of the glue.
If you are confused, contact your board manufacturer for advice regarding their default adhesive dot size.
Where to Apply Glue
- For small chip components, use glue targets that are smaller than the centre of the part.
- For large chips, dot glue at both ends and on the sides.
- Avoid placing glue near the part’s leads or pads, as it may block the soldering process.
- Avoid placing glue on or around test points or connectors.
Effective placement is advantageous for printing the PCB and for the overall assembly.
Curing the Glue
Glue, once applied, needs to be cured or hardened, which is defined as curing.
- With epoxy glue, the required curing method is heating the glue in an oven.
- With hot melt glue, it naturally sets as it cools.
- UV glue requires specific ultraviolet light to cure.
- Acrylic may require room temperature, heat, or a combination of both to cure.
- Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s guidelines on waiting duration and temperature when curing. Uncured components are likely to shift when soldered unless proper measures are taken to prevent them from moving.
QC for Glue Dosing
- Visually look for glue dots that should be marked as placed and positioned correctly.
- Check for overflow. Ensure the adhesive is within proper margins and does not extend towards the pads or leads.
- Confirm that the glue effectively holds the component in place; this is referred to as a bond strength test and should be completed for substantial-sized projects.
- Some factories have incorporated cameras and automated inspections for monitoring glue dot placement.
If an issue arises, ensure that it is resolved before proceeding to the next step.
Issues from Poor Glue Application
- Components detached: There was neither sufficient glue nor had it cured.
- Soldering problems: Pads or leads that are glued could be covered by solder.
- Short circuits: There may have been too much glue added, which is now spreading and causing shorts.
The most challenging part of the change is that the excess glue can hinder the regular replacement of the parts, making it complicated.
Always strive for the proper amount of glue and its application. Also, ensure that you cure it adequately.
Improvement Techniques for Glue Application
- Start with less demanding projects before moving to more advanced ones.
- Maintain consistency by using the same type of glue for each batch.
- Store adhesive in a cool, dry place to prevent spoilage.
- Regularly clean your dispensing tools to prevent blockages caused by dirt and debris.
- Talk to your PCB designer for specific glue dosing instructions.
Glue Application in Custom PCB Assembly
While placing an order for custom PCB assembly, discuss the glue with your supplier. Let them know if your components are heavy, irregular, or need extra support to hold them in place. They can recommend the best glue and the optimal dosing procedure for your specific case.
Safety related to PCB Glue
- Use a well-ventilated area.
- Put on gloves, a face shield, and safety goggles.
- Do not inhale glue vapours.
All steps provided by the glue manufacturer must be followed.
The Importance of Professional Assistance with Dosage PCB Glue
Getting the glue dosing wrong can derail the creating of quality PCB boards. The more correctly glue is applied, the right amount, in the correct location, and at the right time, the better the boards will be in quality. With clean boards, careful placement of glue, and proper curing, you can eliminate issues such as parts coming loose or experiencing soldering problems. Never skip checking your work, following safety protocols, and seeking guidance when necessary.
Having a dependable partner, such as PCB Runner, is helpful when you need advice or professional manufacturing services. PCB Runner is notable for its knowledge and dedication in the area of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturing and assembly. They guide you from prototype to production, paying attention to details such as glue dosing, assembly, and quality checks. Their team understands that every step is essential and works to ensure your boards are accepted without any rework.
Choosing a knowledgeable partner, such as PCB Runner, ensures that your PCBs will be built with utmost care, adhering to best practices for glue dosing and all other aspects of functionality. This improves the chances of your projects succeeding and ensures your boards function effectively in the world.