All modern electronics depend on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Your PCB needs to perform effectively and last a long time, whether you’re constructing a simple gadget or a medical device that could save your life. But what makes a PCB work well? In this blog, we’ll discuss the most critical aspects of a high-reliability PCB. We’ll also discuss what to look out for when printing PCBs and creating prototypes, as well as how to ensure your PCB printed circuit board assembly lasts. We’ll use short sentences and basic vocabulary so that everyone can understand.
Why PCB Reliability Is Important
A well-designed PCB ensures your product operates safely and smoothly. The entire gadget can stop functioning if a PCB fails. This could be problematic in certain situations, such as with automobiles or medical equipment. That’s why it’s so crucial to design very reliable PCBs. You don’t want to put your goods or your name on the line.
1. Good base materials
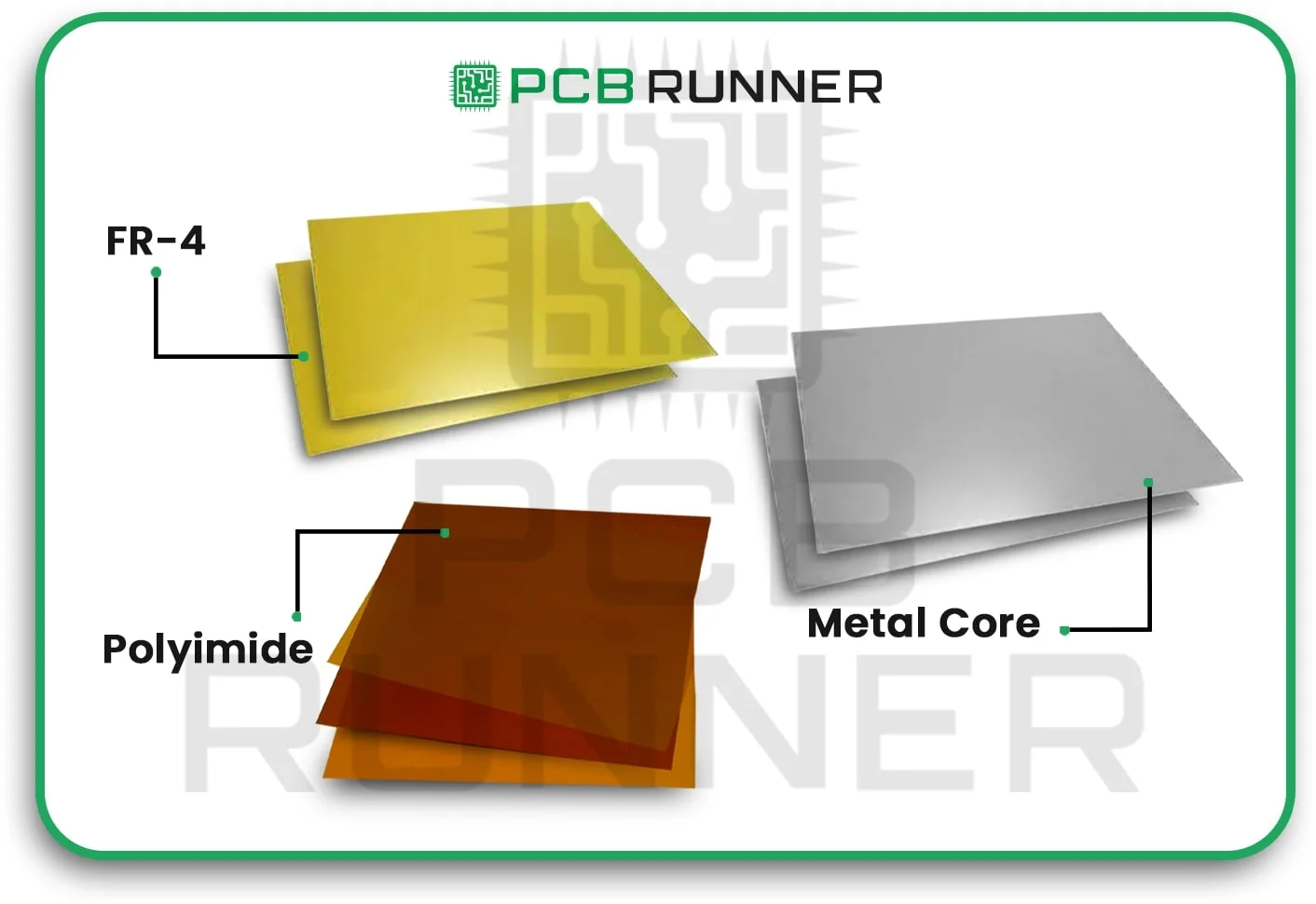
Choosing the correct materials is the first step in constructing a sturdy PCB. Fibreglass, ceramic, or polyimide are common materials for the base, or substrate. The board can handle heat, stress, and chemicals better with good materials. The board can break or stop working if the base isn’t strong.
Always use high-quality, tested materials for your PCB. This helps prevent issues like delamination or open circuits.
2. Copper cladding that is thick and even
Copper is utilised on the board to send signals and power. The copper layer must be thick enough and meet international standards, such as IPC-4101 Class B/L, for a PCB to be reliable. This helps maintain the insulation (dielectric) layer at the correct thickness, resolving performance issues.
Make sure the copper covering on your PCB meets or exceeds industry standards.

3. The right thickness of the hole wall
To link different layers, holes in the PCB are employed. Copper, which is usually at least 25 microns thick, covers the interior walls of these holes. This keeps the board from getting larger and maintains strong connections, even when they are under stress.
The main point is that thick hole walls make the board stronger and prevent cracks or breaks from occurring when it’s being assembled or in use.
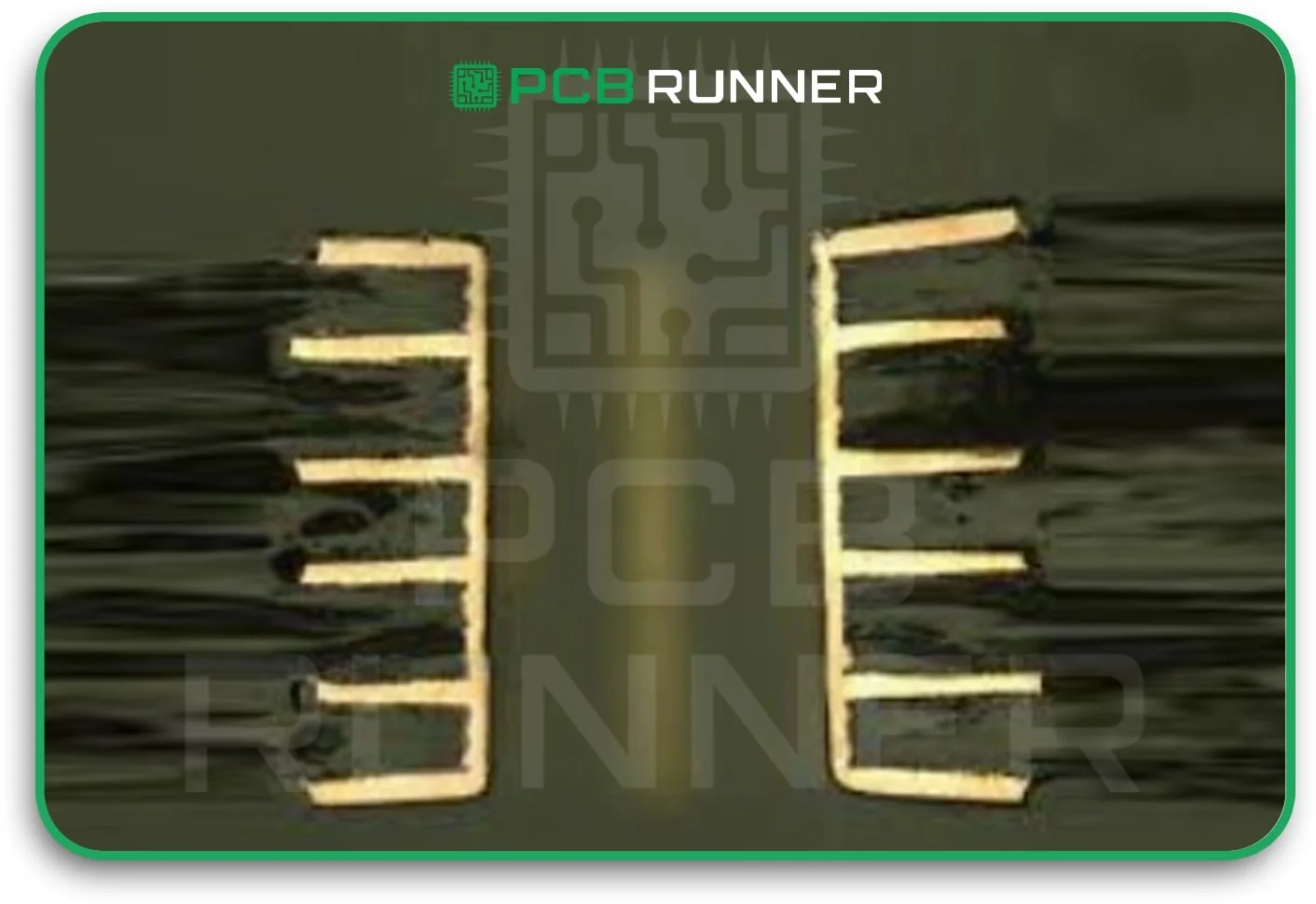
4. No solder repairs and cleanliness
A PCB that is clean is a dependable one. Dust, debris, or residual solder can cause faulty connections or shorts. High-reliability boards are cleaned with great care and rarely require repair with solder or replacement of damaged lines. Solder fixes can cover weak places that could break later.
Ensure the boards are clean and have no damage. This makes it less likely that something will go wrong.

5. Optimised PCB Design
Planning your layout carefully is essential for high-reliability PCB design. Avoid using sharp edges, ensure traces are short, and use wide traces for power lines. If necessary, add more copper or heat sinks to your design to enhance its performance. The board will continue to function even if one part fails, as it has redundant connections and sophisticated trace routing.
A good design keeps your signals strong and your board cool.
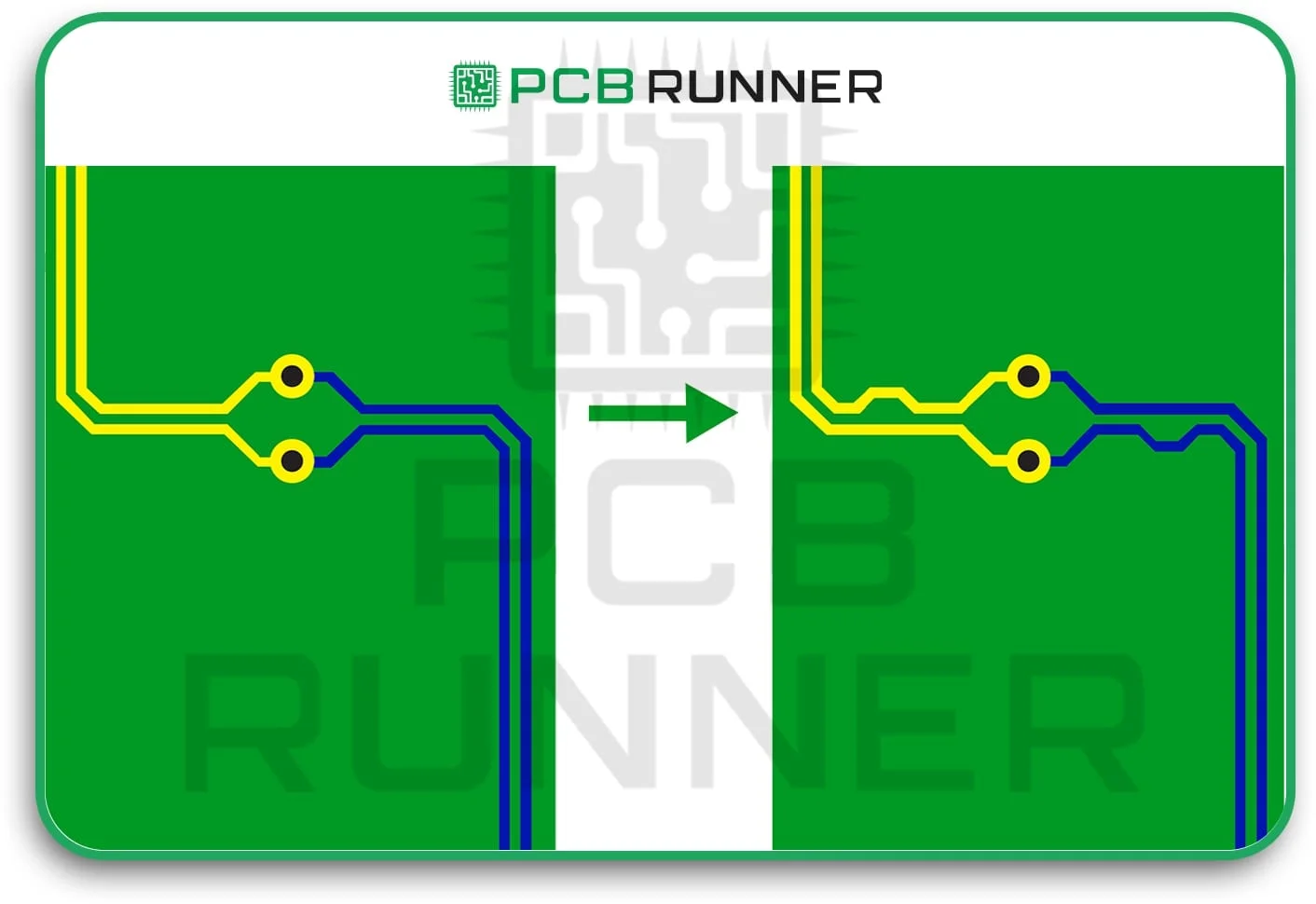
6. Correct Layer Structure
Many PCBs feature more than one layer. How you arrange these layers is essential. Multilayer boards can handle more connections and produce less noise, but they are more challenging to assemble. Blind or buried vias (holes that don’t extend all the way through) can make the board more reliable and occupy less space.
Select the appropriate number of layers and the most suitable types of vias for your specific needs.
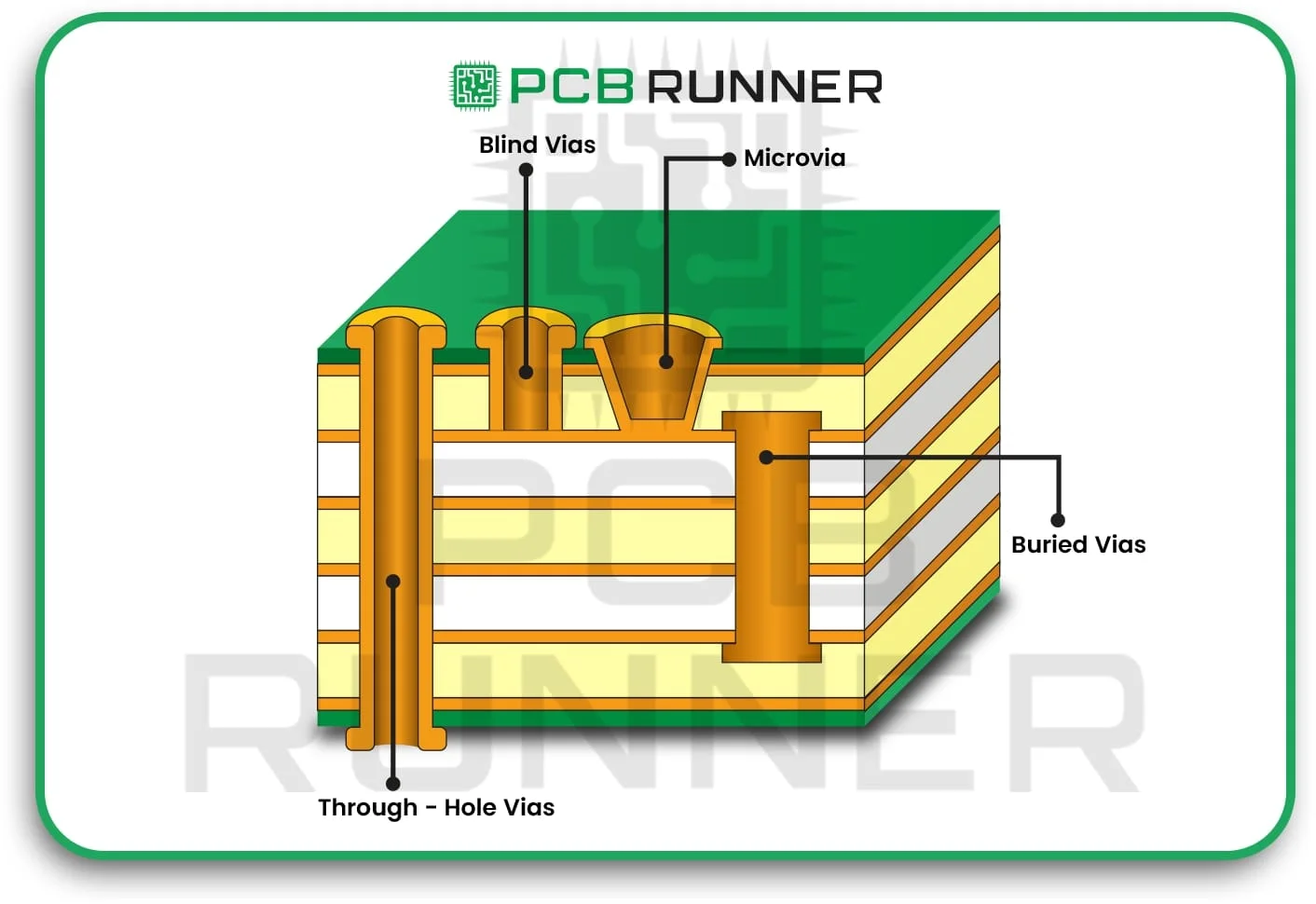
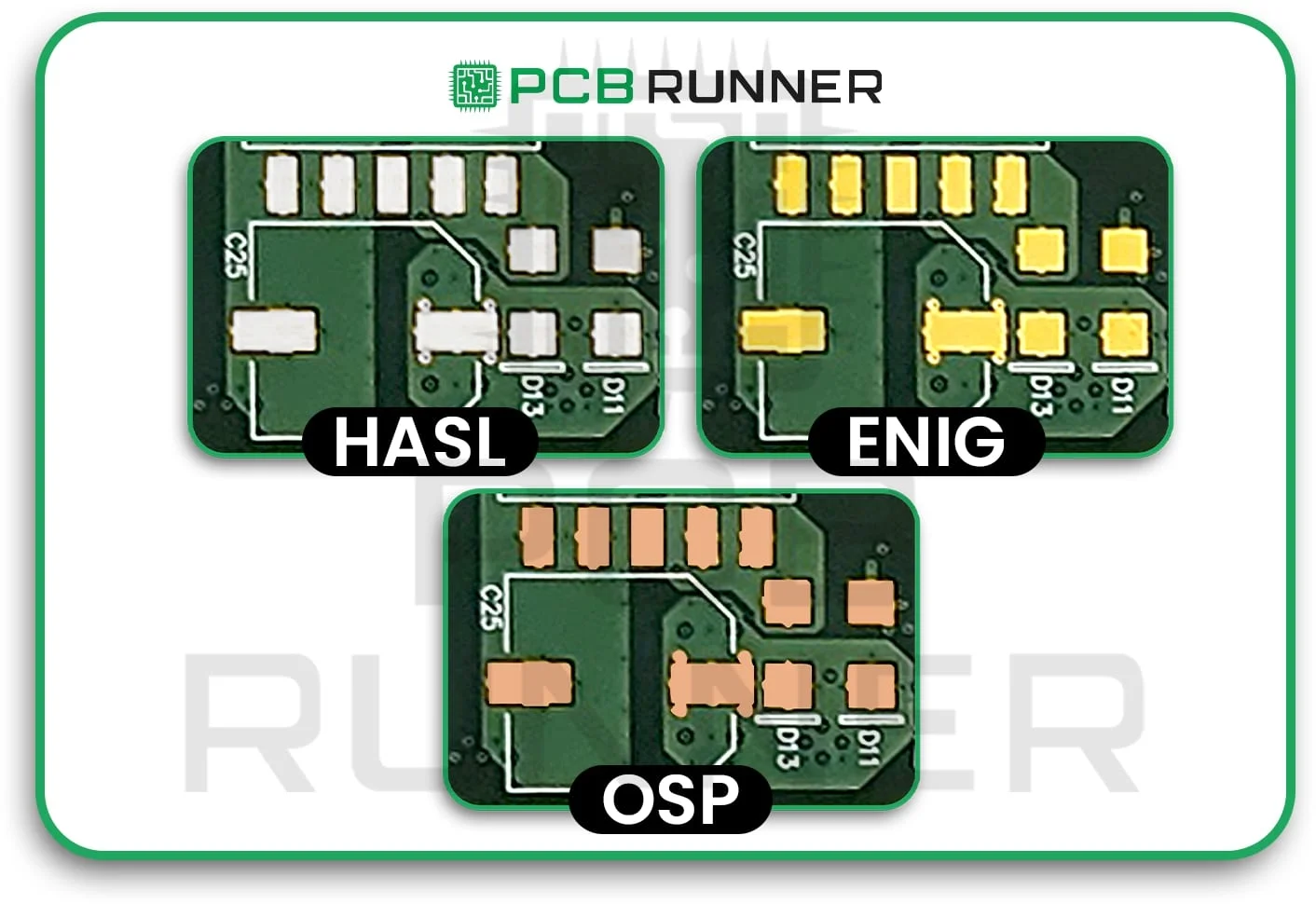
7. Good finish on the surface
The polish on the surface protects the copper and makes it easier to solder. HASL, ENIG, and OSP are some of the most common finishes. There are both good and bad aspects to each. The right coating makes it easier to solder and protects the board from rust.
Select a surface finish that complements the way you assemble the pieces and how the board will be used.
8. Strong Manufacturing and Testing
A good factory makes a reliable PCB. Find PCB printing and PCB prototype services that examine the quality of their work at every stage. Advanced factories utilise laser drilling, optical inspection, and electrical testing to identify faults before they escalate. They also check boards for humidity, heat, and vibration.
Select makers that thoroughly inspect and test every board.
9. Choosing and placing parts carefully
If the parts are defective or assembled incorrectly, even the greatest board will fail. Get your parts from providers you can trust. Put the parts in a place where they can cool and be soldered easily. Don’t crowd, and ensure everything is in its proper place.
Good parts and sensible placement make it easier and more reliable to put things together.
10. Protecting the environment
Some boards must operate in environments that are hot, cold, damp, or prone to vibration. These boards must be made of specific materials or have special coatings. If needed, add protection against electromagnetic noise and static electricity.
Make plans for the real world where your board will be used.
11. Consistent Production
It should be straightforward to create reliable PCBs repeatedly. Utilise existing ideas and collaborate with established manufacturers. This makes it easier to resolve problems when they arise and maintains high quality.
The main argument is that standard designs and methods lead to fewer surprises and better boards.
12. Simple to Test
It’s straightforward to test reliable boards. Place test points and clearly label your board so you can examine it both before and after assembly. This helps you detect and fix problems before they get to your consumer.
Include testing in your design from the beginning.

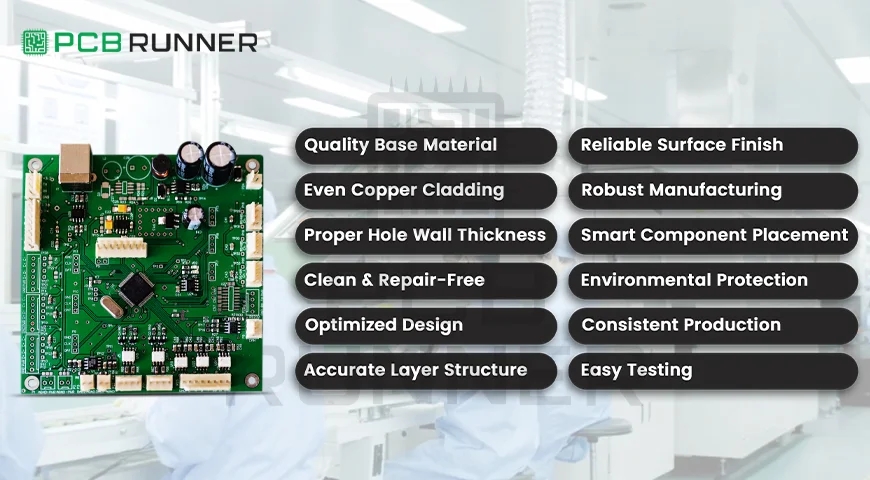
Critical Features for High Reliability PCB
| Feature | Why It Matters |
| High-quality materials | Handles heat, stress, and chemicals |
| Thick copper cladding | Strong signals and power, fewer failures |
| Proper hole wall thickness | Strong connections between layers |
| Clean, repair-free boards | No hidden weak spots or dirt |
| Optimized design | Less noise, better heat control |
| Correct layer structure | More connections, less noise |
| Good surface finish | Easier soldering, less corrosion |
| Strong manufacturing/testing | Catches problems early, ensures quality |
| Careful component selection | Reliable parts, easier assembly |
| Environmental protection | Survives tough conditions |
| Consistent producibility | Reliable boards, batch after batch |
| Easy testability | Find and fix problems quickly |
Why PCB Runner Cares About Dependability
We at PCB Runner realise that every device needs its PCB to work. That’s why we pay attention to every step, from printing the PCB and creating the prototype to assembling it and testing it. We only use the highest-quality materials, adhere to strict guidelines, and meticulously inspect the quality of every board. PCB Runner is a partner that prioritises high-reliability PCB design and all the key aspects of high-reliability PCBs. Every time, your boards will function better, endure longer, and help your products thrive.