Have you ever wondered how electronic devices are able to bend, twist, or stretch without damage? Electronics are a critical part of our daily lives, including high-tech medical devices and smart fitness trackers. Stretchable PCB technology tackles this issue. Stretchable PCB technology marks a potential shift from traditional rigid printed circuit boards. This technology proves revolutionary as it permits circuits to stretch up to 200% of it’s length like a rubber band.
The goal of this article is to provide a more detailed overview of stretchable PCBs and how it’s using today’s technology to innovate the electronics of tomorrow.
What a Printed Board Stretchable Circuits
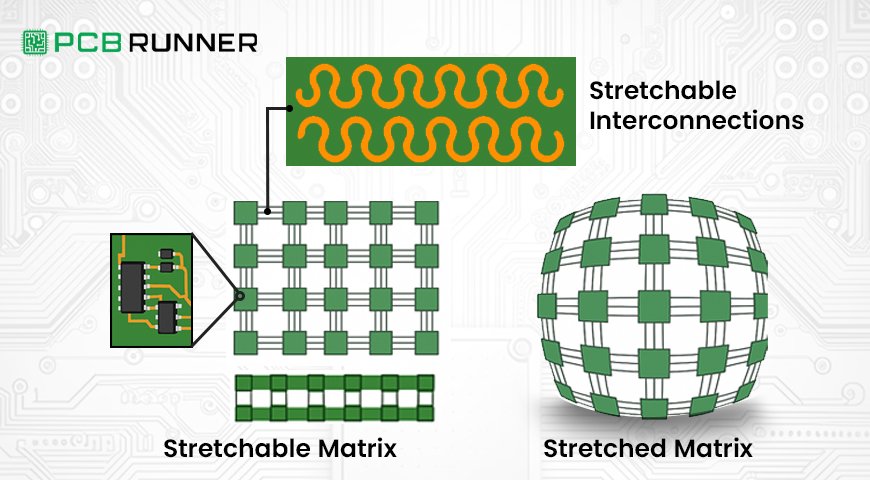
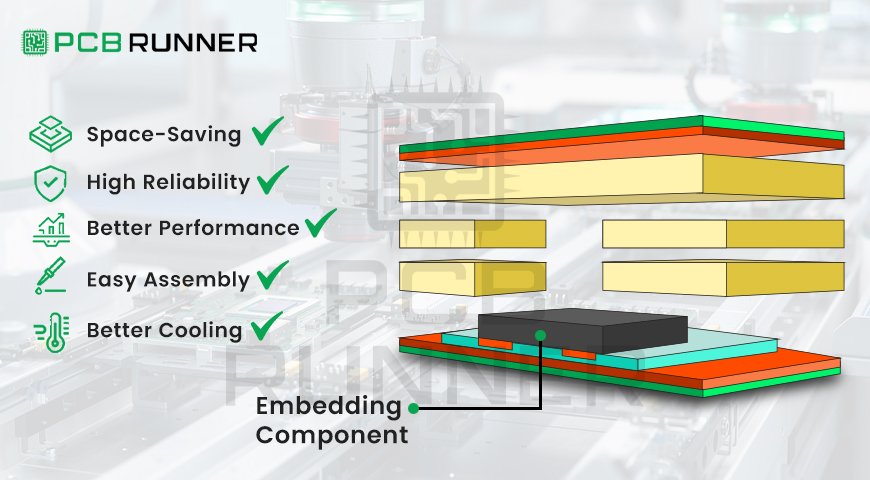
With today’s advanced technology, stretchable printed circuit boards (PCBs) are revolutionising circuitry by using new materials and designs that allow them to bend and twist. Unlike PCBs, which are rigid, stretchable PCBs have the ability to stretch, twist, and bend over 200% of it’s length without malfunctioning.
These PCBs are created using elastic materials along with specific designs, for example, serpentines (wavy lines), which ensure the stretching is distributed evenly across the circuit and no single point is overly stressed and damaged. This characteristic makes them especially helpful in applications where devices have to move or change shape frequently.
How does the technology for stretchable PCBs work?
The materials and the designs both have to work in tandem for stretchable PCB technology to function, especially:
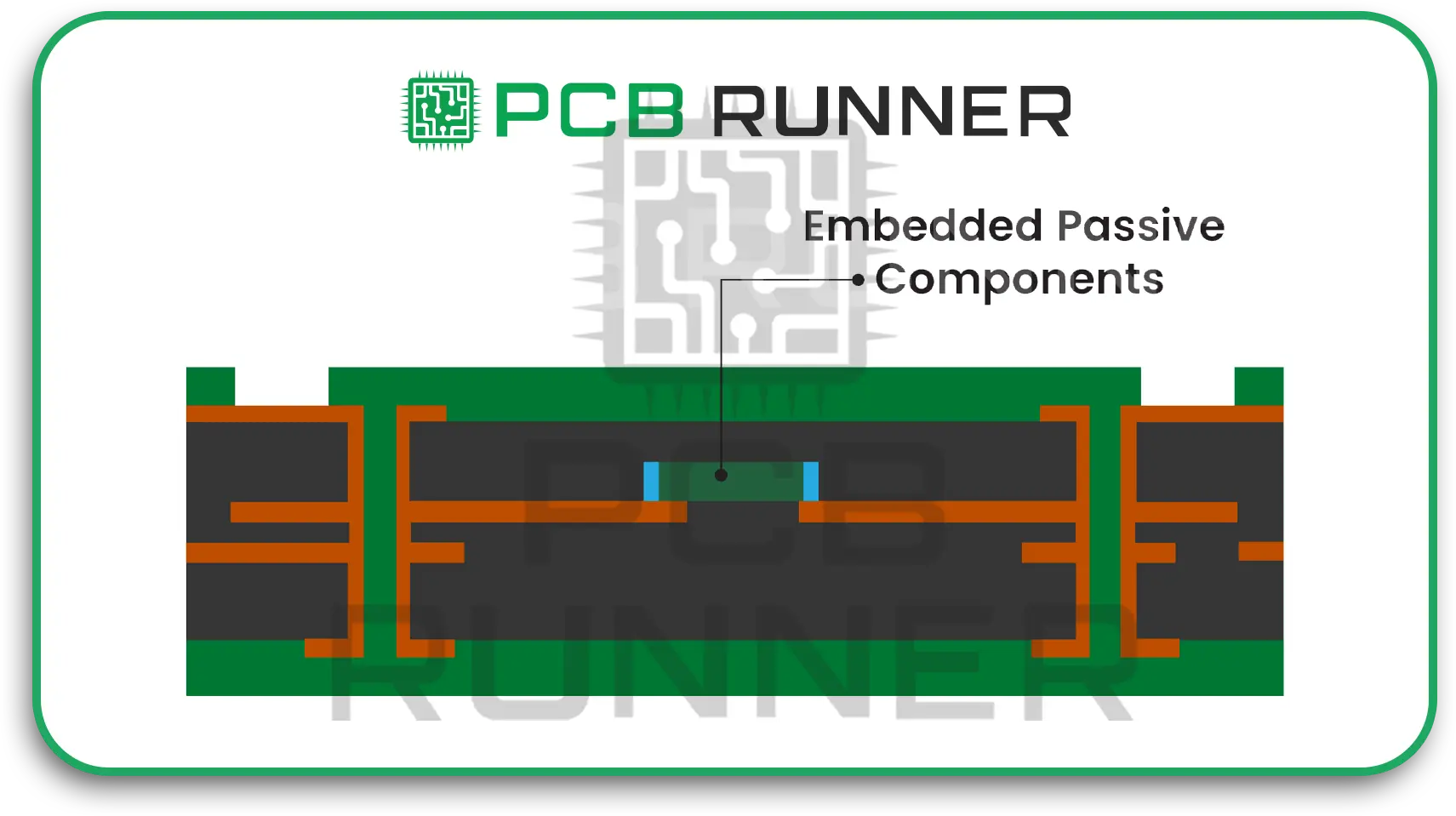
- Elastic Substrates: Rubbery materials such as silicones or specific polymers, which are soft and flexible, are known to stretch and not tear.
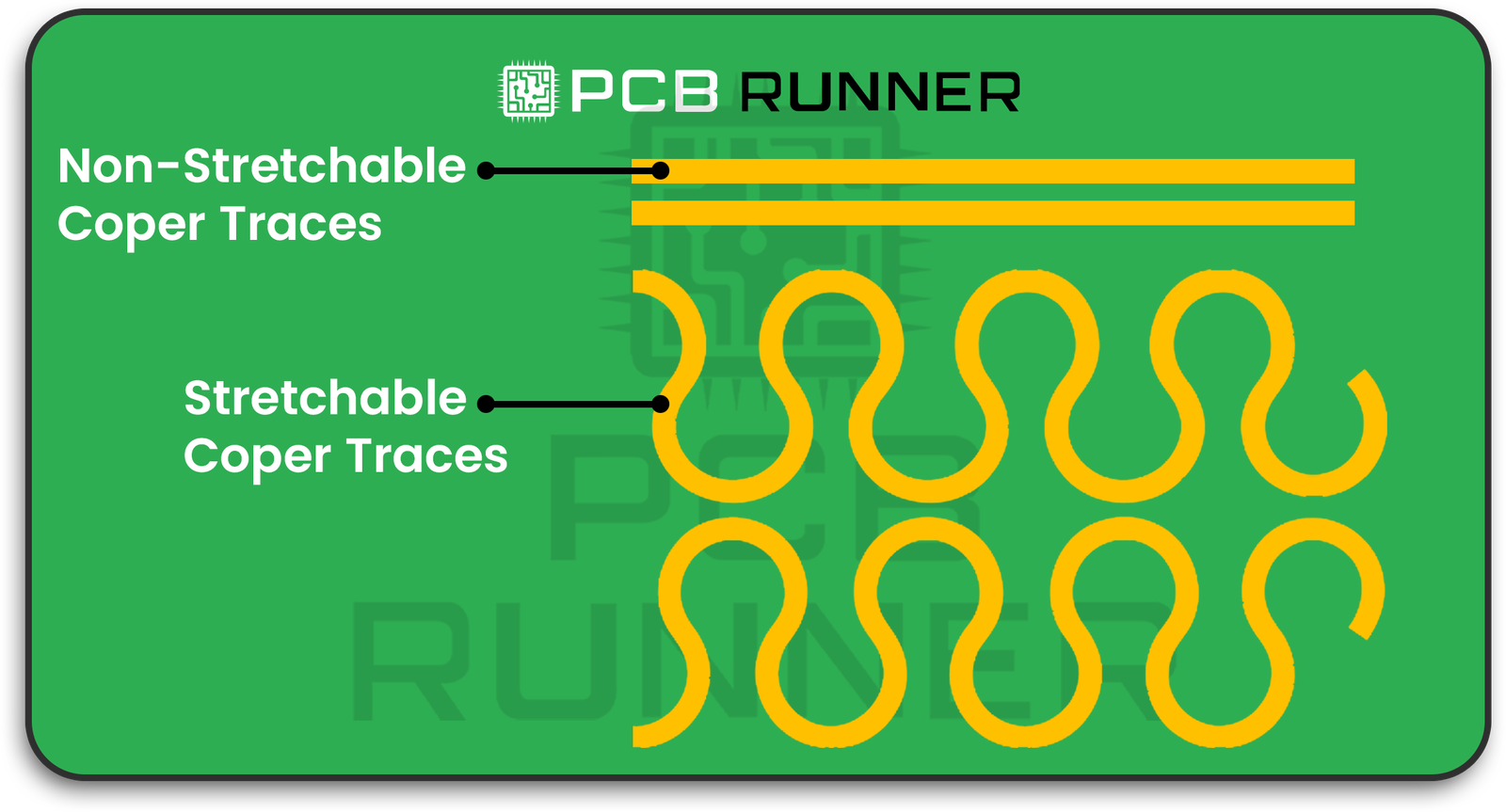
- Serpentine Copper Traces: The copper lines that transport current are not composed of straight lines; instead, they wiggle in snake-like shapes. Snake-like copper lines are able to stretch and loosen without breaking.
- Durable polyethene biosystem: This lays emphasis on the rings of the utilised materials, which are safe for the usage of wearing on skin or even fine for surgical implants.
Durability: Thus, PCBs are very reliable in the regard that they may be stretched several thousand times without any loss of function.
Flex PCB Fabrication and Rigid-Flex Boards
The older stretchable PCBs utilised Flex PCB fabrication or rigid-flex boards. The elderly boards with rigid-flex boards are made from rigid and flexible parts, meant to allow some movement, though overall limited:
- Flex PCBs are bendable, though they restrict stretching.
- Combining solid sections that hold maximum stability with flexible sections results in rigid-flex boards that are not stretchable.
Flex PCBs already enable wearables and high-movement electronics. Stretchable flex PCBs take this further by permitting real stretchability, all while ensuring reliability, which deepens possibilities within wearables and other high-movement electronics.
Where Can Stretchable PCB Technologies Be Applied?
Stretchable PCBs, Crosswear Ergonomics, and Advanced Materials Creatively:
- Wearable Electronics: Smart clothing and health monitors must expand and contract seamlessly. Stretchable PCBs seamlessly support dynamic movements.
- Medical Devices: Stretchable PCBs are integral to devices like skin patches, monitoring heart rate, and neural interfaces that wrap around nerves to ensure proper function while allowing user comfort.
- Robotics: Soft robots require stretchable PCBs to provide suitable circuits for motion-responsive sensor skins and joints.
- Consumer Electronics: Stretchable circuits in new foldable phones and curved screens enable these devices to function even when bent or folded.
- Automotive: Stretchable PCBs are essential for sensors in car seats and dashboards that flex with the interior contours.
All these disciplines gain from the capability to design electronics, not only offering flexibility, but also the ability to stretch and adapt to real-world dynamic shapes.
What Makes Stretchable PCB Technology Essential?
Known electronics can be bulky and rigid, which is a problem for some modern devices. Designers of devices and equipment no longer face rigid boundaries concerning the form of a circuit board with the advent of stretchable printed circuit technology. This signifies:
- Enhanced Comfort: Wearable gadgets and devices will be more comfortable as they will naturally move along with the body.
- Improved Durability: Devices will be able to endure repeated bending and stretching without sustaining damage.
- Advanced Electronics: Devices can be embedded into garments, soft medical implants, or the skins of robots.
- Enhanced Effectiveness: Even with stretching or twisting, the accuracy of the sensors and components is retained.
What Are the Issues?
Despite the fantastic capabilities of stretchable PCBs, they do pose a few unique challenges:
- Specialised materials and careful designs to ensure the circuit’s integrity while stretching make fabrication complex.
- Regular PCBs tend to be more affordable as compared to these materials and designs.
- Extreme repetitive stretch or harsh environment testing of the devices is critical.
- As stretchable PCB technology matures and more manufacturers focus on investment, the unique challenges are bound to lessen.
How to Pick the Optimal PCB Technology
For designers working on stretchable circuits, these points should be noted:
- Know how your device moves: Will it be bending, twisting, or stretching? Only stretchable PCB technology works for devices that absolutely need to stretch.
- Analyse the biocompatible option: encapsulation and elastic substrates differ in a wide range for various uses. Consider the medical devices that need such materials.
- Work with PCB producers who have vast experience in flexible and stretchable PCB production.
- Blend in rigid-flex board designs in portions that require stretchable and flexible elasticity.
- Conduct durability and electrical performance tests on the prototypes.
Stretchable PCBs and the Future of Electronics
Stretchable PCB technology is making it possible to create extraordinary new devices as electronics shrink and become smarter. Think of medical patches that continuously monitor health stats invisibly, or sensor-laden smart fabrics that change colours in reaction to the wearer’s movements.
Those boundaries continue to be pushed for stretchable printed circuit boards as researchers find ways to make them stretch even more and for longer. These printed circuits are essential for the Internet of Things, or IoT, as the smart devices need to be well integrated into daily activities.
Conclusion
The stretchable PCB technology serves more than just a purpose; it’s a unique gift of modern engineering that facilitates the flexing of the newest electronic devices. Stretchable circuits improve the functionality of devices in the medical field, robotics, and many other gadgets, making devices smarter and more durable.
Most people are concerned with electronic design and technology innovation, and for them, embracing stretchable PCB technology will be a must for adoption.
At PCB Runner, we help by making these innovations known to designers, engineers, and technology lovers, and in the process, they understand the innovations and stay prepared for the upcoming challenges and innovations.