Every great electronic product starts with a well-thought-out design, but it’s the assembly that brings it to life. The choice of the PCB assembly method you use can dramatically impact the performance, cost, and durability of your device. Whether you’re working with a prototype or a full-scale production run, understanding the printed circuit board assembly process is essential.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the types of PCB assembly methods, what factors influence the best choice for your design, and how to work effectively with a PCB assembly manufacturer to bring your project to market.
Why the PCB Assembly Method Matters
Did you know? Around 70% of product quality issues in electronics can be traced back to poor PCB assembly processes or design-for-assembly oversights.
The PCB-printed circuit board assembly stage connects the design blueprint with real-world functionality. It involves placing and soldering components onto a bare board, followed by rigorous inspection and testing. The success of this step directly affects signal integrity, reliability, and lifespan of the final product.
Understanding the PCB Assembly Process
Before choosing the right method, it’s essential to grasp the printed circuit board assembly process itself.
Core Steps in Manufacturing PCB Assembly:
1. Solder Paste Application
A stencil is used to apply solder paste to specific pads on the PCB where components will be placed.
2. Component Placement
Surface-mount or through-hole components are positioned accurately using high-speed machines.
3. Soldering
Components are soldered to the board using reflow (for SMT) or wave soldering (for through-hole).
4. Inspection & Quality Control
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray, and manual inspection ensure proper alignment and connections.
5. Functional Testing
Each assembled PCB is tested to confirm it meets the intended electrical and performance criteria.
This standard PCB assembly method serves as the foundation for multiple types of board configurations and complexity levels.
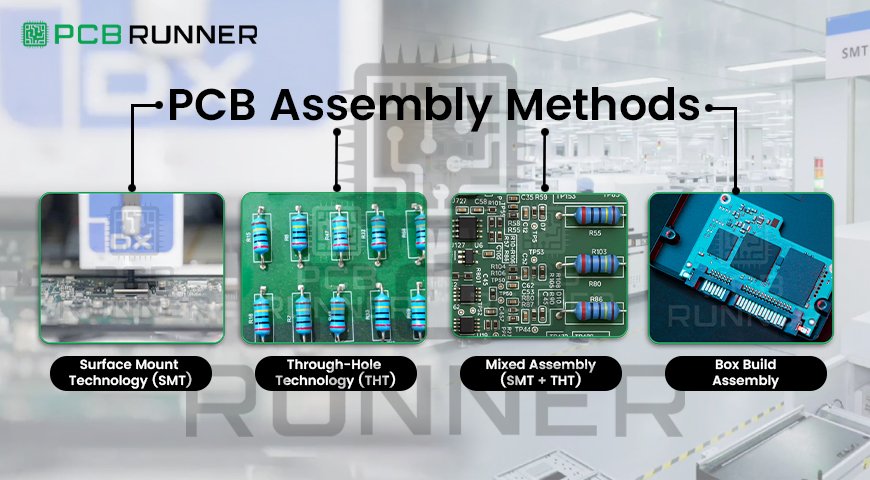
Common PCB Assembly Methods
The method you choose depends on your product’s requirements, component type, and budget. Below are the most commonly used PCB assembly methods in the industry:
1. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Ideal for: Compact, high-speed, automated assembly
Used in: Consumer electronics, wearables, communication devices
SMT is the most widely used PCB assembly method today. Components are mounted directly onto the board’s surface, allowing for a compact layout and efficient automated production.
Benefits:
- High-speed assembly
- Lightweight and space-efficient
- Suitable for double-sided boards
- Lower cost in high volumes
Limitations:
- Not suitable for significant or high-power components
- It may require specialized reflow ovens.
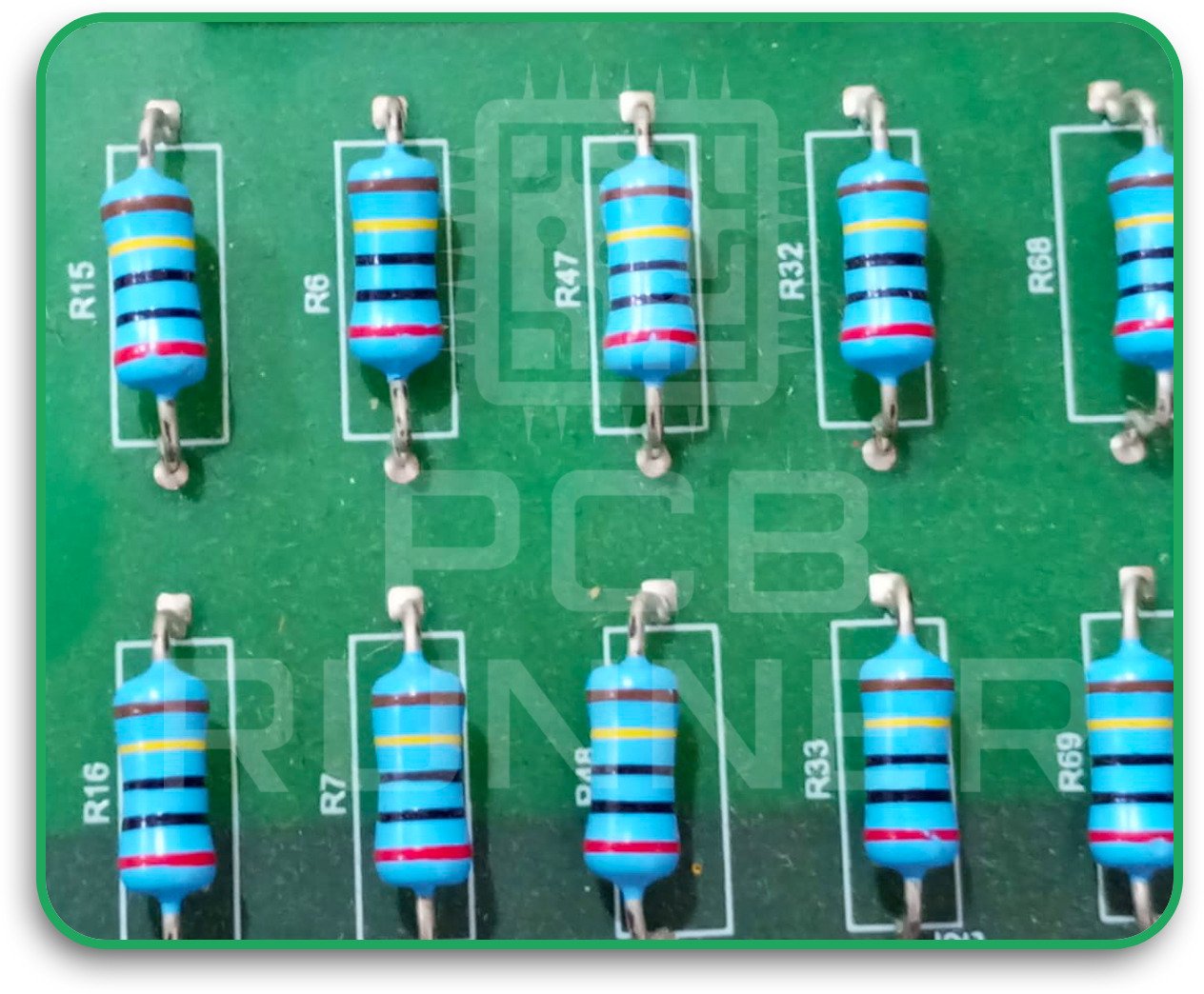
2. Through-Hole Technology (THT)
Ideal for: Strong mechanical bonding, high-current applications
Used in: Aerospace, automotive, power equipment
THT involves inserting component leads through holes in the PCB and soldering them on the opposite side. It’s slower and more labour-intensive but offers superior durability and thermal performance.
Benefits:
- Excellent mechanical strength
- Better for thermal dissipation
- Preferred for heavy or bulky components
Limitations:
- A larger board size is required
- Costlier than SMT for high-volume runs
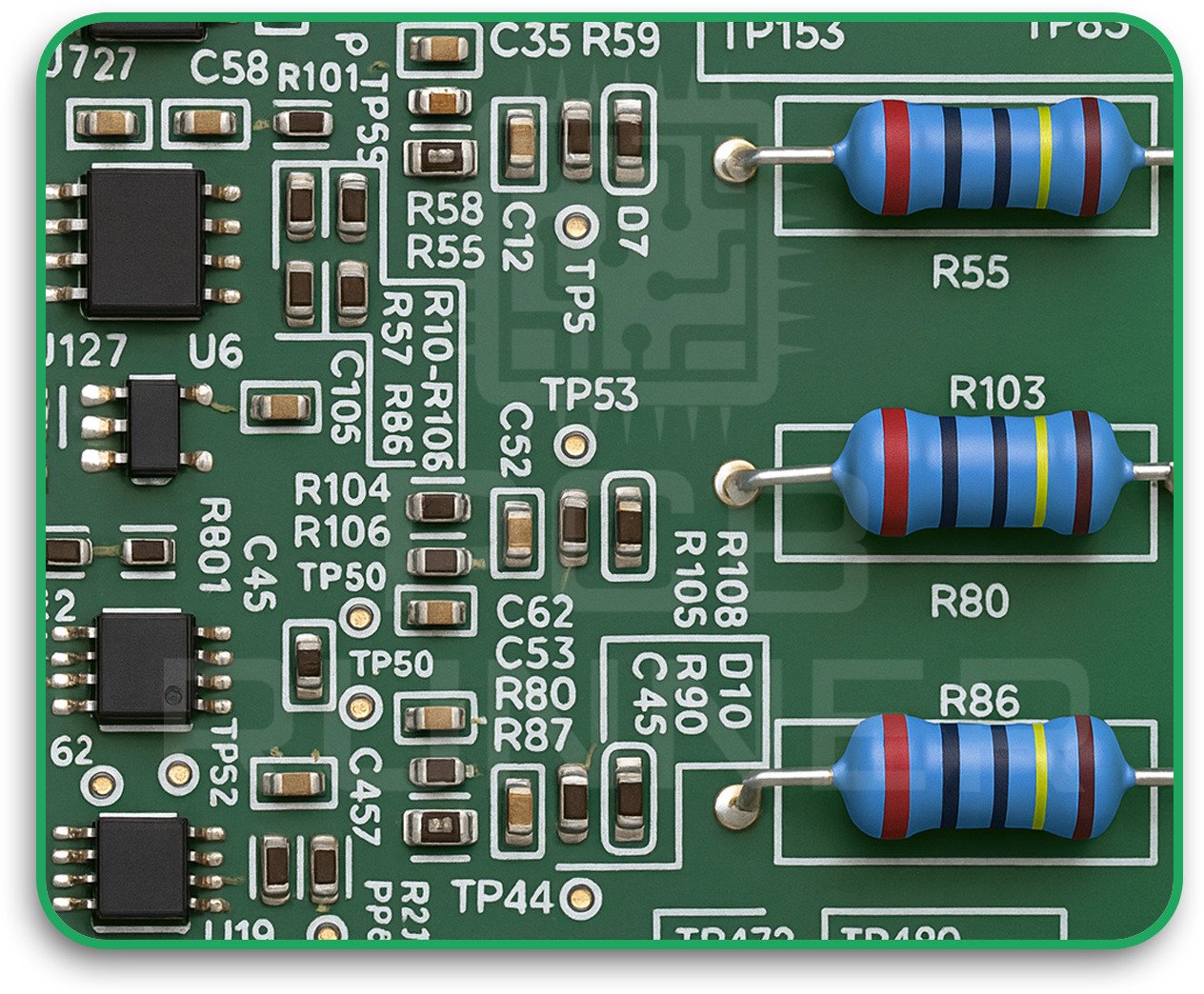
3. Mixed Assembly (SMT + THT)
Ideal for: Complex designs requiring both precision and power
Used in Industrial control systems, medical equipment
Mixed assembly uses both SMT and THT techniques on a single board. SMT components provide compactness, while THT supports heavier elements like transformers or connectors.
This custom PCB assembly method gives you flexibility in balancing performance and cost but requires precise coordination and design.
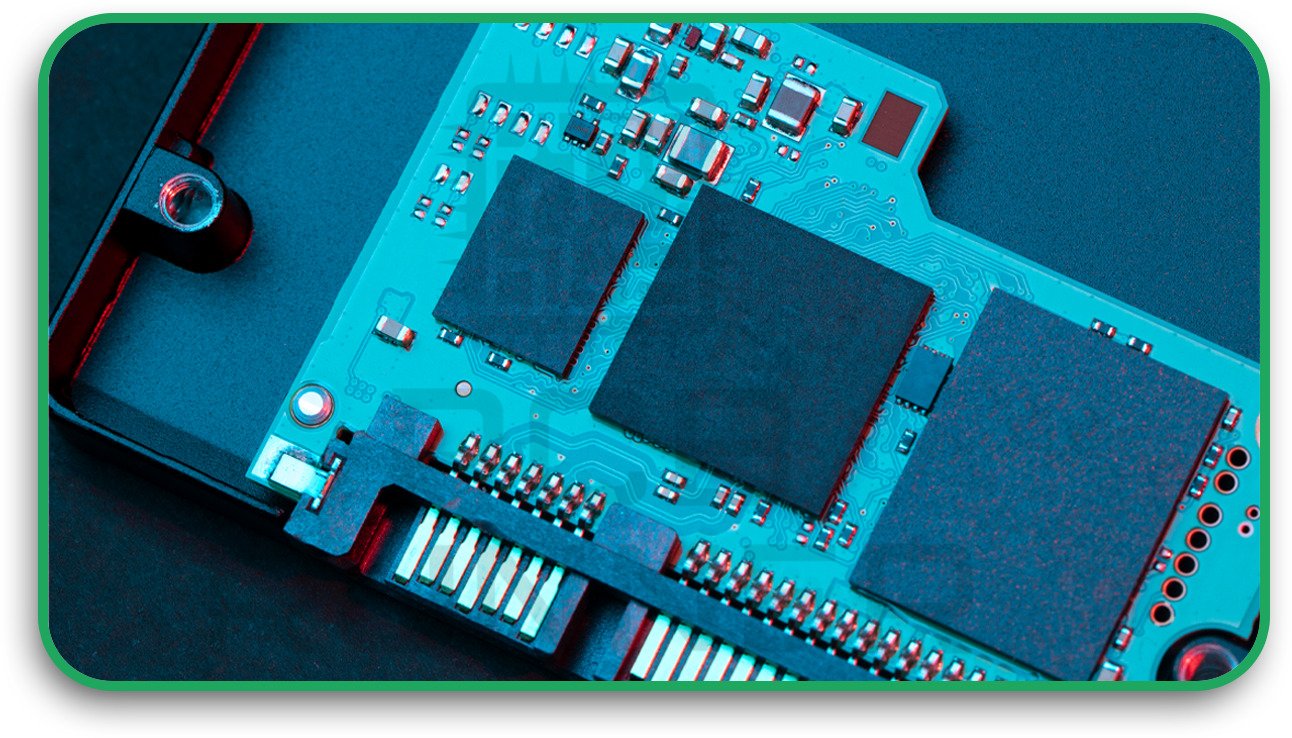
4. Box Build Assembly
Ideal for: End-to-end solutions involving enclosures, wiring, and complete product build-out
Used in: IoT devices, industrial products, smart systems
Beyond just the PCB printed circuit board assembly, box build includes cable harnessing, mounting PCBs into enclosures, and final system testing.
A good PCB assembly manufacturer offering box build services can help reduce your overall supply chain complexity and improve turnaround.
How to Choose the Right PCB Assembly Method for Your Design
Every product is unique, and the PCB assembly method must align with your technical and commercial goals. Here are key factors to consider:
1. Component Type and Density
- SMT is ideal for small, lightweight components in high-density layouts.
- THT is better suited for large, high-current, or high-temperature components.
2. Board Size and Layers
- Complex multilayer boards benefit from automated SMT.
- Simple two-layer boards might be suitable for manual or hybrid assembly.
3. Production Volume
- For prototyping or small batches, manual or semi-automated assembly might be sufficient.
- For mass production, fully automated SMT lines offer cost efficiency.
4. Budget Constraints
- Consider manufacturing PCB assembly options that reduce rework and scrap.
- Working with an experienced custom PCB assembly partner ensures more innovative cost planning from the design phase.
5. Environmental Requirements
- Harsh environments require robust soldering methods and protective coatings.
- Your printed circuit board assembly manufacturer can guide you on conformal coatings and encapsulation.
Custom PCB Assembly for Specialized Applications
If you’re developing a product with unique requirements, like flexible boards, RF components, or non-standard shapes, you’ll need custom PCB assembly.
Look for a printed circuit board assembly manufacturer with experience in:
- RF and high-frequency board assembly
- Rigid-flex PCB assembly
- Medical-grade and aerospace-certified PCBs
- Lead-free and RoHS-compliant builds
Tip: A custom partner can offer Design for Manufacturability (DFM) support, ensuring that your design not only works but is optimized for scalable and cost-effective production.
Working with a PCB Assembly Manufacturer: What to Expect
Choosing the proper PCB assembly manufacturer is just as important as selecting the method. Here’s how to ensure a smooth collaboration:
What to Look For:
- In-house capabilities for SMT, THT, testing, and box build
- ISO or IPC certifications
- Transparent quoting and lead time estimates
- Engineering support during design reviews
- Proven track record with similar products
What to Provide Them:
- Gerber files and Bill of Materials (BOM)
- Assembly drawings and pick-and-place files
- Test plans and quality specifications
- Details about special requirements (e.g., RoHS, high-temp, RF)
Working closely with a manufacturer from the start will ensure that your chosen PCB assembly method aligns with your goals and prevents surprises during production.
Cost Considerations in PCB Assembly
The total cost of manufacturing PCB assembly depends on several variables:
- Component sourcing (standard vs. custom parts)
- Labour and automation level
- Volume (economies of scale apply for larger runs)
- Testing and quality assurance
- Lead times (rush jobs may cost more)
A reputable pcb assembly manufacturer will help you optimize these factors for a balance between cost and quality.
Final Testing and Quality Control
No PCB-printed circuit board assembly is complete without thorough testing. This includes:
- In-circuit testing (ICT) – to verify component function and placement
- Functional Testing (FCT) – to test actual device performance
- X-ray or AOI Inspection – to catch soldering or alignment issues
Testing ensures that your PCB assembly method delivers a reliable and high-performing product. It’s the last but crucial checkpoint before market release.
Conclusion: Tailoring the Right PCB Assembly Method for Your Needs
Selecting the proper PCB assembly method isn’t a one-size-fits-all decision. It’s about understanding your design, production volume, and quality expectations, and matching those to the proper process and partner.
Whether you’re creating a wearable device, an industrial controller, or a medical instrument, choosing a trusted printed circuit board assembly manufacturer ensures that every component is precisely placed, soldered, and tested.
Need expert help with your design? Partner with a leading PCB assembly manufacturer offering custom PCB assembly, fast turnarounds, and end-to-end support, because the right assembly method can mean the difference between a prototype and a product that wins in the market.