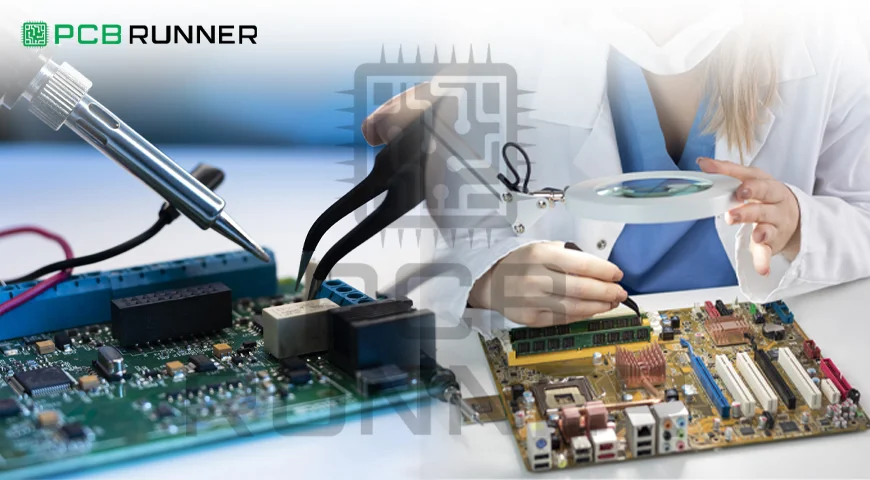
When you build or buy a printed circuit board (PCB), you want it to work the first time. Whether it is going into a phone, a car, or an industrial machine, your PCB must be reliable. This is why PCB functional testing and quality assurance matter so much. If something goes wrong after the board is assembled, fixing it later can cost time and money. Even worse, a bad board in a critical system can lead to more significant problems. Let us look at why testing and quality checks are a must and how they work.
Why Reliability in PCBs Matters?
Your PCB is like the heart of your device. If it fails, the whole system can stop working. For you as a user, this means frustration. For businesses, it can mean returns, repairs, and unhappy customers. Poor reliability can even damage a brand’s name. That is why reliable boards are a top priority for PCB manufacturers.

What Is PCB Functional Testing
PCB functional testing is the process of checking whether your board does what it is supposed to do. After the board is built and all the parts are in place, it is tested using tools that simulate how it will work in real life. It is like a final exam for your board.
Here are some things tested:
- Power supply lines
- Signal lines
- Response to inputs
- Output levels
If anything does not work as expected, it is flagged and reviewed.
What Does Quality Assurance Mean in PCBs?
Quality assurance (QA) is a set of steps taken during PCB design and assembly to ensure the end product works as expected. It starts even before the board is built. QA helps catch problems early so you don’t waste money building boards that don’t work.
Some QA tasks include:
- Checking the design using printed circuit board design software
- Making sure parts are placed correctly
- Testing how well solder joints are made
- Final inspection of each board before it leaves the factory
This is where trusted PCB manufacturers make a big difference.
Different Types of PCB Testing
There are many ways to test a PCB. Each one looks at something different. You can think of them as layers of checks, each catching something the other might miss. Here are the most common PCB inspection methods:
1. Visual Inspection
This is the first step. A technician looks at the board with the naked eye or a magnifier. They check if parts are aligned and if there are any apparent problems, such as missing parts or extra solder.
2. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
This uses cameras to scan the board and compare what it sees to the design files. If there is a mismatch, the board is marked for review. AOI is fast and can spot tiny problems humans might miss.
3. X-Ray Inspection
If your board has parts hidden under chips, like with flex and rigid PCB designs, X-rays help see through layers. They can also check for hidden solder issues or broken connections.
4. In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
This test checks each part on the board. It can test resistors, capacitors, and chips to see if they are working and if each part is in the right place.
5. PCB Functional Testing
This final test checks whether your board behaves as it should. It is usually done with a test fixture made for your board. The fixture connects to the board and runs real-world tests on it.
Quality Assurance Starts with Design
The first step in quality assurance PCB work starts with good design. If your design has mistakes, no amount of testing can save it. That is why printed circuit board design software plays such a significant role. These tools can catch many issues early, such as short circuits, wrong part placements, or spacing problems.
Once the design is checked and approved, the fabrication and assembly process begins. Multistep QA processes are in place throughout:
- Clean rooms to keep dust out
- Machines that place parts with high accuracy
- Heating systems for perfect solder joints
- Ongoing spot checks during the circuit board assembly process
Flex and Rigid PCB Testing
Flex PCBs can bend, while rigid ones cannot. Some boards combine both. Testing these requires special care. If not made right, flex boards may fail after bending. Testing includes stress tests to see how many times the board can bend before it breaks. This is key for products like wearables and foldable electronics.
Why PCB Reliability Testing Is Crucial
Even if a board passes early tests, it may still fail later. That is why PCB reliability testing checks how your board holds up over time. These tests include:
- Heat tests (does it work in hot conditions?)
- Cold tests (can it handle freezing temperatures?)
- Vibration tests (will it stay together in a moving car?)
- Humidity tests (does moisture cause shorts or corrosion?)
These tests help prove that the board will work for years, not just for a few hours.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
Not all PCB manufacturers are the same. You want a company that takes quality seriously. Look for those that:
- Use up-to-date printed circuit board design software
- Have strong QA teams
- Offer both flex and rigid PCB production
- Have good reviews and strong client feedback
Ask if they do full PCB functional testing and how they handle failures during testing. Good suppliers will explain their inspection and testing process in detail.
What You Can Do as a Customer
You do not need to test your boards yourself, but there are things you can do to help the process go smoothly:
- Share clean design files
- Include test points in your layout
- Choose a PCB board manufacturer like PCB Runner with proven QA experience
Your choices can help catch problems early and avoid extra costs later.
Final Thoughts
Reliable boards do not happen by accident. They are the result of careful design, quality materials, good assembly, and vigorous testing. When you work with printed circuit board manufacturers who understand the importance of quality assurance PCB methods, you get better results. From the tools used in printed circuit board design software to the final PCB functional testing and reliability checks, every step matters. Whether you are building a single board or thousands, never skip testing. Your users, your product, and your peace of mind depend on it.