Have you stopped to think about how your TV, phone as well and your espresso maker actually work? It’s not just about the buttons you push or the display you view. It’s the hidden components in the. One of the most crucial components in almost all electronic devices is what’s known as the printed circuit board manufacturers, or PCB for short.
An electronic circuit acts similar to the nervous system of electronics. It connects various components, resistors, sensors, etc., so that they are able to communicate with each other and enable your devices to work. Without PCBs, the current world we live in today would not exist at all.
But here’s the deal: PCB technology is changing. Like how phones became smarter and cars became more eco-friendly, PCB design and manufacturing are undergoing massive changes. If you’re looking for the latest developments in electronics, it’s essential to know what’s next.
Let’s examine the latest trends, concepts and technological breakthroughs that will shape our future design of PCBs that range from the newest materials to greener production.
Why PCBs are Evolving So Quickly
Technology moves fast. Consider how fast smartphones evolved from chunky bricks to sleek and stylish devices that can fit into your pockets. A similar speed change is occurring in the design of PCBs and their assembly.
There are several significant reasons for this dramatic shift:
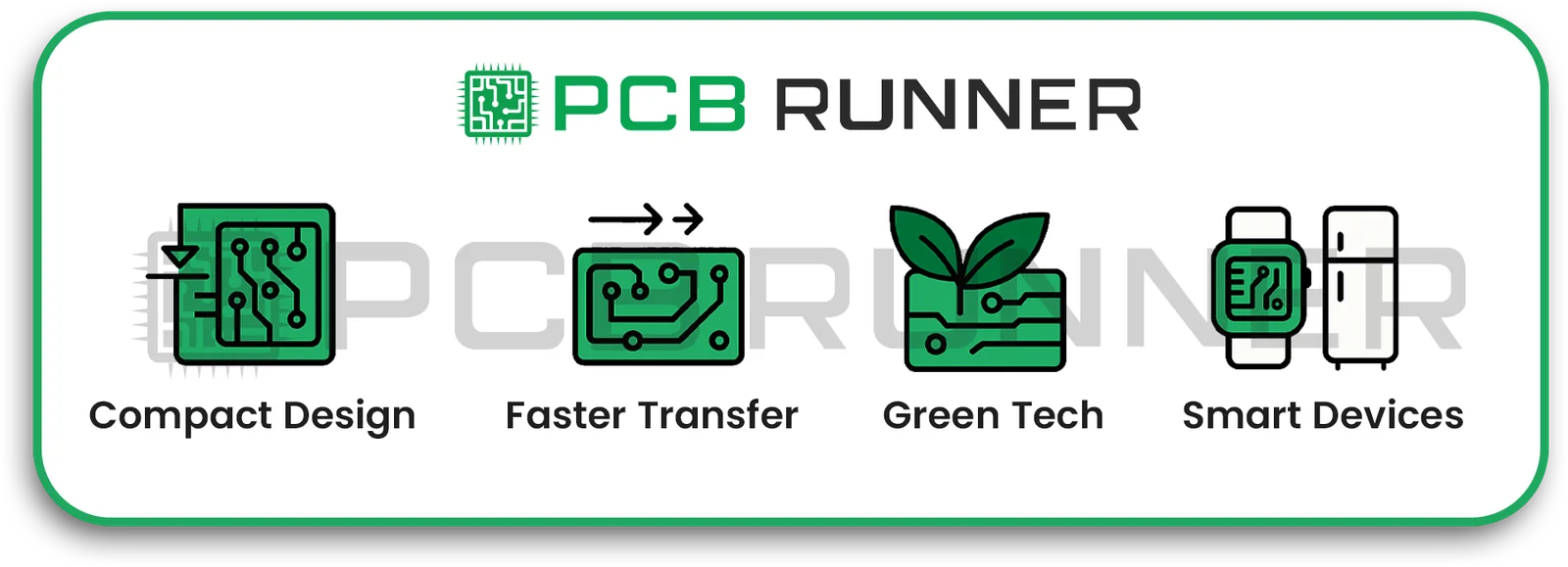
- Devices are smaller but more robust. That means we require a simple PCB circuit design that can fit many components in less space.
- Speedier data transfer. Modern electronics require PCBs that can handle high-speed signals without causing interference.
- Goals for greener technology. Manufacturers are seeking environmentally friendly materials, as well as energy-efficient PCB manufacturing techniques.
- The rise of bright things. From smart fridges to wearable health trackers, every device requires a customised PCB design that is lighter, smaller, and more efficient.
This is pushing producers of printed circuit boards from the UK as well as around the globe to implement new methods.
From Simple to Smart: The Changing Face of PCB Design
In the past, PCBs were relatively simple. They came with a flat board and copper paths that linked several components. But what about today?
- We have PCBs with flex and rigid-flex that are flexible and bendable for wearable technology.
- HDI (High-Density Interconnection) boards cram more circuits onto smaller boards.
- Key PCB assembly services can handle everything from printing PCBs to attaching chips in one step, thereby cutting down time.
It’s similar to comparing an old chalkboard for a class to a new smartboard. The goal is the same, but the capabilities are on an entirely new level.
Emerging Trends in PCB Fabrication and Assembly
Here are a few trends you’ll need to keep in mind if you’re an electronics enthusiast:

- A) Miniaturisation and a Higher Density
Electronics are becoming smaller without dropping performance. It means PCB designers have to work with small lines and fine vias while making sure that the board is reliable.
B) Flexible and wearable PCBs
Imagine a fitness band. It must flex when you move. This is why flexible PCB printing and designs with rigid-flex shine.
C) Eco-friendly customised materials
The drive towards sustainability is also impacting prototype PCB production. Modern materials are less harmful, and some are biodegradable.
D) AI-Assisted Design of PCBs
Artificial intelligence is now helping engineers design more effective PCB layouts that are less prone to mistakes and quicker turnaround times.
E) 3D Printing on PCBs
It’s not science fiction, researchers are currently researching 3D printing on PCBs, which means designs can be transformed from concept to board in much less time.
Common Questions About the Future of PCBs
Q: Will PCBs keep getting smaller forever?
It’s unlikely to last forever, however, in the next 10 years, at the very minimum, miniaturisation will be on the rise. There’s room to squeeze more performance in a smaller space.
Q: Are custom PCB designs expensive?
Not necessarily. With the advancement of technology and automation, as well as complete PCB manufacturing, custom designs are becoming less expensive, particularly for small quantities.
Q: Is PCB printing the same as regular printing?
Not quite. As opposed to ink, PCB printing makes use of conductive materials such as copper to make electrical paths.
How Designers Keep Up
PCB fabrication and design requires the ability to think and creativity. Designers usually begin with a simple PCB circuit design and later improve it to better meet the needs of the product. They should:
- Select the appropriate materials.
- Make plans for signals with high speeds.
- Check that the board is able to take on heat.
- Make sure everything is checked prior to the prototype of the PCB.
This is the reason manufacturers of printed circuit boards in the UK frequently review designs of their customers prior to making them, as it helps avoid costly mistakes down the line.
From Idea to Product: The PCB Production Journey
Here’s a step-by-step guide on the process of making modern PCBs:
- Design phase: Engineers create an outline using CAD software.
- PCB printing: The design is printed on copper-clad boards.
- Etching copper that is not needed is removed, leaving the necessary paths.
- Drilling: Small holes are drilled to accommodate components, lead and vias.
- Plated surfaces and holes are coated to provide greater conductivity.
- Solder Mask: A layer of protection is added to protect against short circuits.
- Assembly: When it comes to the design of PCBs, in assembly components are soldered into place.
- Testing: The board is inspected to verify that it is working exactly as it was planned.
Every step is crucial. Even the most minor mistakes could cause a device to stop working.
The Role of Prototypes in Innovation
Before a product goes into production, it requires an initial PCB prototyping. This is similar to creating the prototype prior to making hundreds of devices.
Prototypes aid manufacturers:
- Test performance.
- Make sure that the item is in its casing.
- Catch errors early.
- Avoid costly errors. million tonnes
This is the reason firms invest in custom PCB designs as early as possible because it’s the base of the whole project.
Sustainability and the Future
Electronics waste is becoming a significant issue. Many old gadgets end up in landfills, and a lot of them contain hazardous materials.
The positive side? PCB manufacturers are collaborating on solutions:
- Utilising solder without lead.
- The creation of boards is made from biodegradable or recyclable materials.
- It is designed for ease of disassembly so that components can be used again.
Based on the records estimates, the amount of electronic waste in the world could reach the 74 million tonne mark in 2030. A sustainable PCB design could contribute significantly to cutting down on that number.
Skills Needed for Tomorrow’s PCB Designers
As PCBs get more sophisticated, designers require new abilities:
- Expertise in HDI and PCB fabrication using flex.
- Knowledge of how to manage thermal in small devices.
- The ability to design software using AI-assisted tools.
- Be aware of the eco-friendly products and methods.
The future PCB design jobs require a combination of electronic knowledge, imagination and problem-solving.
Final Thoughts
PCBs aren’t huge, however, they’re the foundation of the electronic world. Starting from simple circuits designed for the design of PCBs to sophisticated customised PCB manufacturing, the evolution of PCBs makes devices smaller, more efficient and more cost-effective.
In the coming years, we’ll witness increasingly adaptable design, AI-driven layouts, and environmentally sustainable manufacturing methods. The result is that electronic devices will not just be more intelligent but also more considerate of their surroundings.
Although the improvements have been exciting, basic principles remain the same. Every great device begins with a top PCB.
Companies such as PCB Runner will continue to innovate, adapt and create boards that meet the requirements of the future’s technologies.