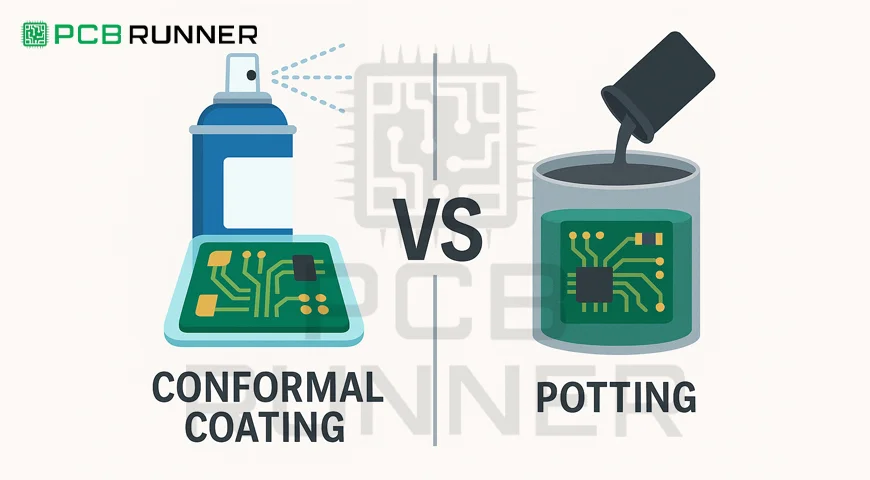
The introduction of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) has allowed all modern electronic devices to function seamlessly. They remain one of the most important components of every electronic device. PCBs do have a downside, as they are highly susceptible to external factors like humidity, dust, chemicals, and temperature.
These factors have the potential to cause serious damage to delicate electronic parts. To salvage the effectiveness of Printed Circuit Boards, a myriad of methods, such as potting material or conformal coating, are used.
Such techniques aid in averting corrosion, physical damage, and short circuits, which in turn enhances the lifespan of electronic devices. But how do these two methods compare with each other? Which one would suit your needs best?
In this article, we will explore the differences between circuit board conformal coating and PCB potting materials, including their value and weaknesses.
What Is Conformal Coating
Conformal coating PCB refers to a flexible coat that protects the PCB board from physical factors such as moisture, heat, and solvents. These coatings are perfect for Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) because they are applied in liquid form and solidify once they have dried up. This helps them ‘conform’ to the various components on the PCB.
Types of Conformal Coating Materials
Every type of circuit board conformal coating entails its own set of advantages and disadvantages. With that said, below are a few examples:
- Acrylics (AR): They are simple to apply and remove. Furthermore, they provide moisture resistance.
- Silicones (SR): Perfect for environments with high temperatures. Silicones offer superior resistance to high temperatures.
- Polyurethanes (UR): Great flexibility with strong chemical resistance.
- Epoxies (ER): Hard and rigid coating, difficult to remove.
Benefits of Conformal Coating
- Shielding against moisture, dust or any other contaminant
- Giving electrical insulation
- Increases reliability of the device in severe conditions
- Very light and does not add weight to the PCB
- Less complex for inspections and repairs compared to potting.
Limitations of Conformal Coating
- No ability to encapsulate completely
- Some protection from extreme mechanical stress, but not enough
- Certain coatings need environmental or UV curing conditions for application for the coating to work.
What is Potting?
It is a process by which a coating is applied to the entire PCB or other specific components, providing a protective shell around the electronics for higher durability and resistance to severe conditions.
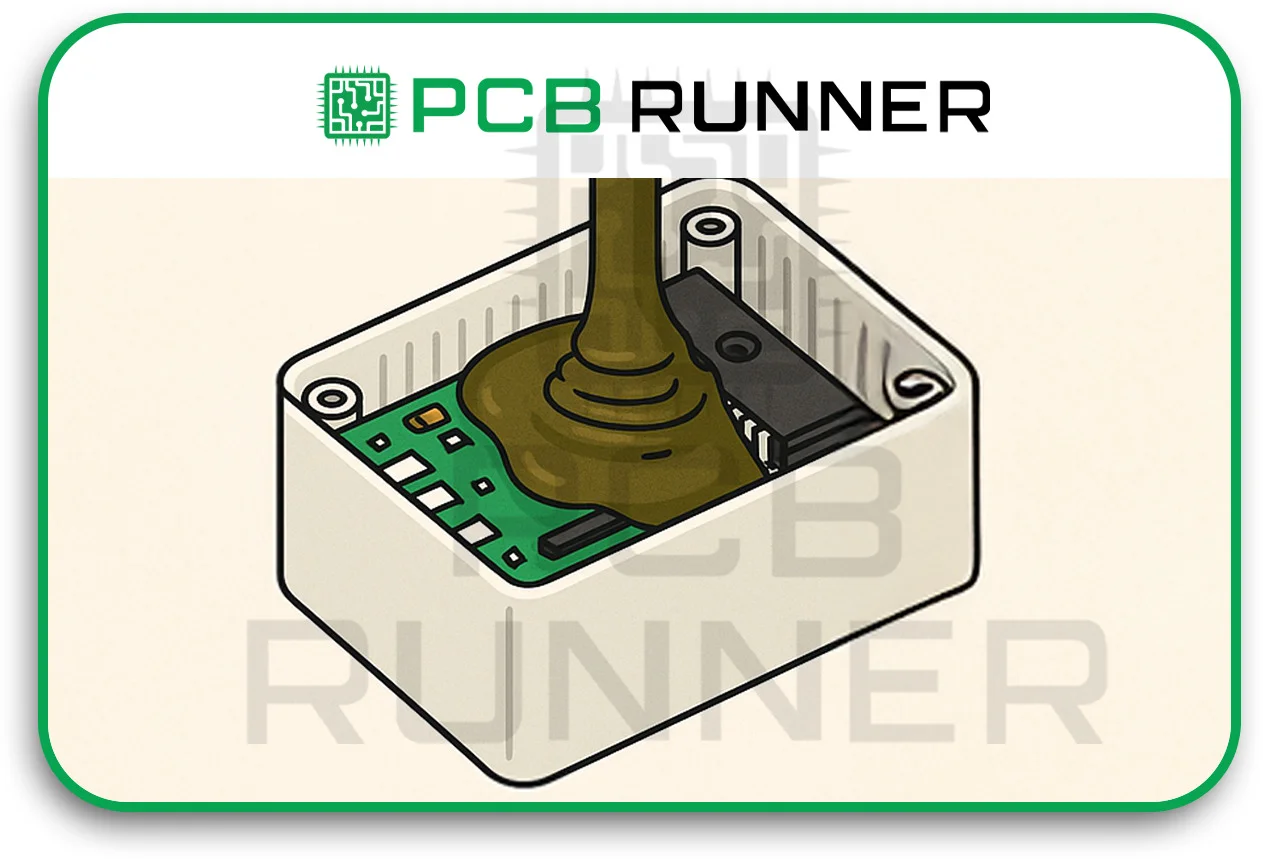
Types of Potting Materials
Different types of PCB potting materials available, like conformal coatings, have different characteristics with distinct results:
- Epoxies: Excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
- Silicones: Able to endure considerably greater flexing and extreme temperature changes.
- Polyurethanes: Good combination of flexibility and hardness, in addition to being resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Advantages of Potting
- Provides deep guarding against moisture, vibration and mechanical forces.
- Supports durability in extreme environments.
- Provides excellent electrical insulation.
- Resists damage from harsh chemicals and solvents.
Disadvantages of Potting
- Adds substantial weight and size to the PCB.
- Repair and inspection are very challenging post-application.
- Costly and can be tedious in nature when applying.
Potting Vs Conformal Coating – Key Differences
| Feature | Conformal Coating | Potting |
| Protection Level | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Repairability | Easy | Difficult |
| Weight Addition | Minimal | Heavy |
| Application Process | Simple | Complex |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Expert Insights
Studies have focused on the effects of conformal coatings and potting materials on the effectiveness of a PCB during thermal cycling. They concluded that mechanical characteristics like elastic modulus and thermal expansion of these protective constituents can affect electronic components’ reliability. Encapsulates endure temperature shifts, they dilate and shrink and mechanically enforce stress on solder interconnects, which can jeopardize the bond reliability in the long run. Conformal protective coatings cast while providing light protection might induce some solder fatigue over time. In contrast, potting materials give full-featured protection but might create restrictions because of the tough nature of the material. Making the appropriate choice of the material used will greatly impact the protection versus overall reliability of the different components.
Selecting the Best Method for Protection
Both conformal coating PCB and potting material for PCB need to be weighed carefully with the following in mind:
- Potting is the better option when dealing with liquids, vibrations, or chemicals. Conformal coating works best for moderate protection.
- Prior inspection is much easier with conformal coating.
- If weight and size are a major factor, conformal coating is more effective.
- While conforming coating is inexpensive and simple to apply, potting is much more time-intensive.
Conclusion
Even though both conformal coating PCB and PCB potting material are able to provide adequate protection for PCBs, they are not interchangeable. For lightweight moisture and contaminants, they rely on conforming coating and potting provides the ability to withstand extreme conditions. It’s easy to see how knowing the benefits and disadvantages of each method would greatly help in deciding what is most appropriate for each specific situation.
Want to ensure your PCB protection is done correctly? Don’t hesitate to contact PCB Runners so we can explain how we can protect your electronics with the best solutions.