Have you ever wondered how your smartwatch bends around your wrist or how foldable phones actually work? The answer lies in the world of flexible circuit technology, a field that’s changing how we think about electronics. As devices get smaller, lighter, and more adaptable, the demand for flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) is skyrocketing. If you’re curious about the future of this technology, or you work with a rigid-flex PCB manufacturer, flex PCB production, or custom PCB assembly, this blog is for you.
What Are Flexible Circuit Boards?
A flexible circuit board, sometimes called a flex PCB, is a thin, bendable electronic circuit. Unlike traditional rigid boards, these can twist, fold, or fit into tight spaces. This makes them perfect for wearables, medical devices, automotive sensors, and even aerospace applications. But the innovation doesn’t stop there, flex and rigid PCB designs are now being combined to create even more powerful solutions.
The Rise of Rigid-Flex and Flex PCBs
Traditional PCBs are stiff and can crack if bent. Flexible PCBs, on the other hand, use special materials like polyimide that can handle repeated bending. Rigid-flex PCBs take things a step further by combining rigid sections (for mounting components) with flexible sections (for connections and movement). This hybrid approach lets engineers design products that are both sturdy and adaptable.
Why is this important?
- Devices can be smaller and lighter.
- Fewer connectors and cables are needed, reducing weight and failure points.
- Complex shapes and 3D assemblies are possible, opening new design doors.
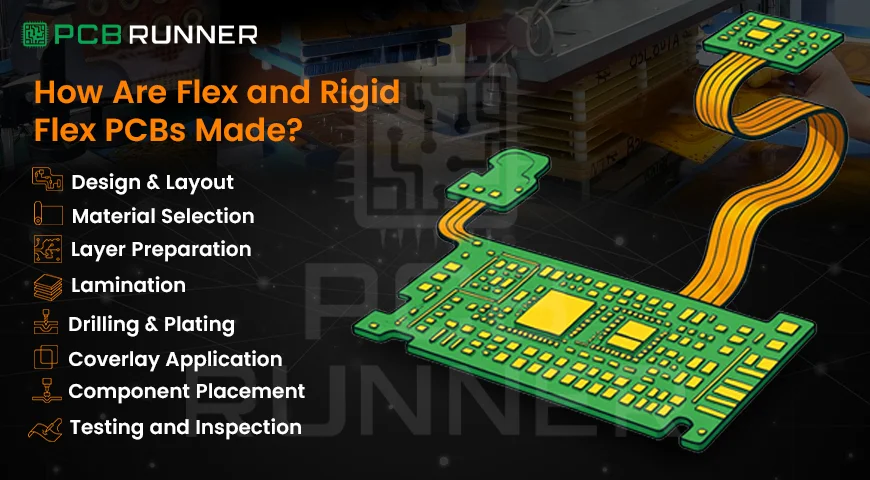
How Are Flex and Rigid Flex PCBs Made?
The process of flex PCB production and rigid-flex PCB manufacture is more complex than making standard boards. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works:
1. Design and Layout
Everything starts with a detailed rigid-flex PCB design. Engineers must plan the number of layers, where the board needs to bend, and how components will be placed. Careful attention is paid to the bend radius and stress points, if these are ignored, the board can crack or fail.
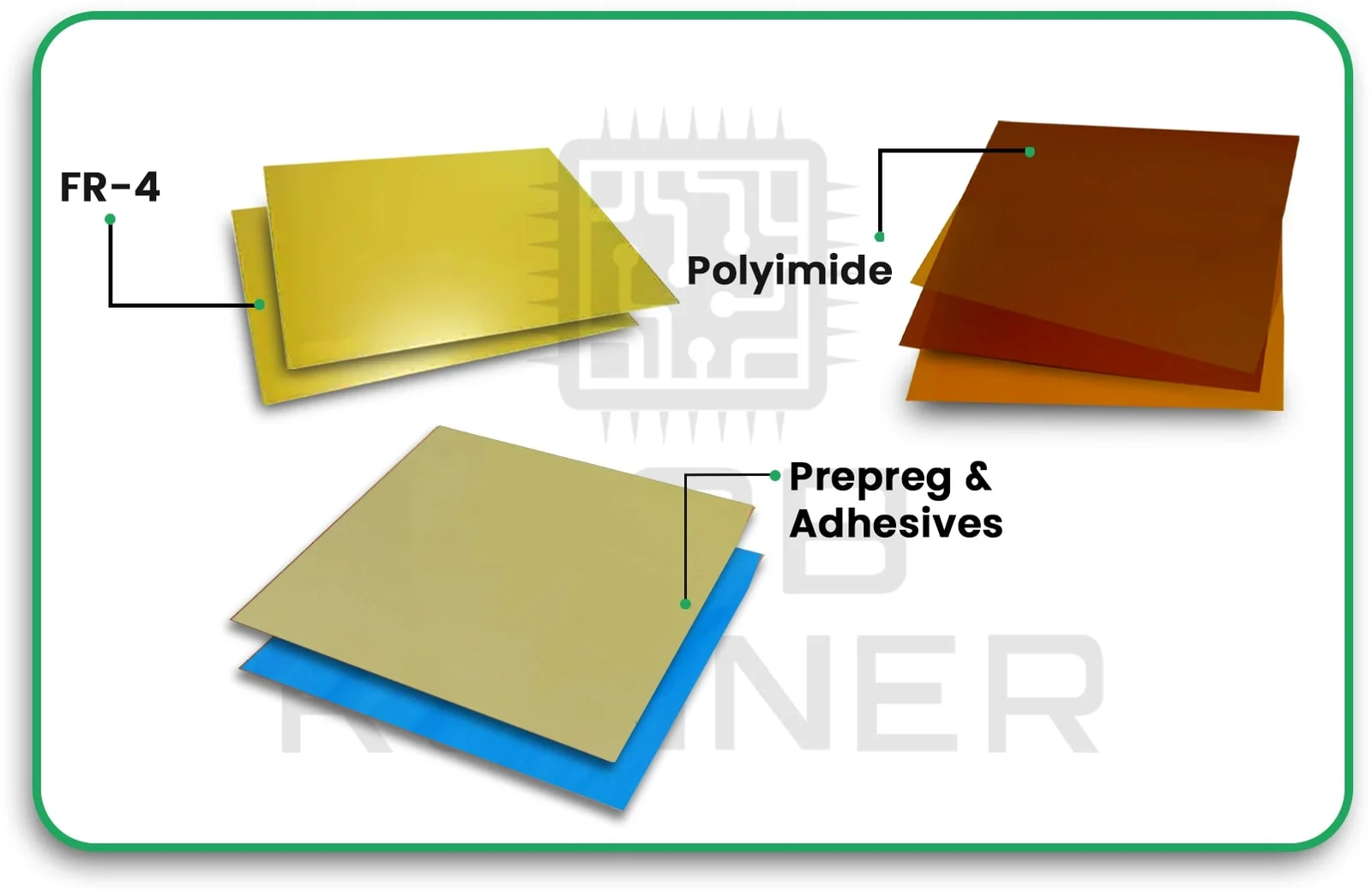
2. Material Selection
- Rigid sections: Usually made from FR-4 or high-temp FR-4.
- Flexible sections: Use polyimide or polyester films for flexibility and thermal stability.
- Adhesives: Acrylic or epoxy-based adhesives bond the layers together.
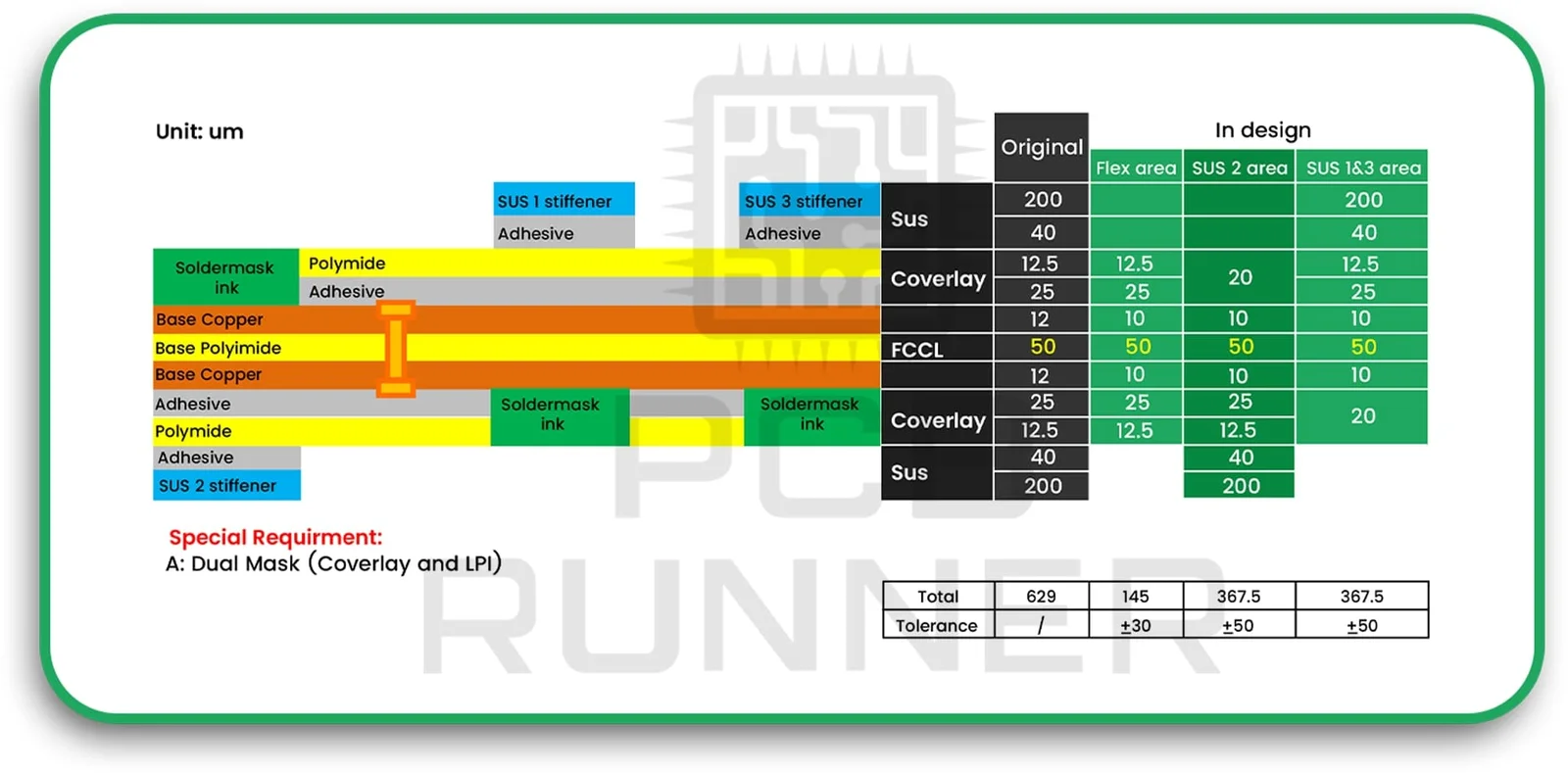
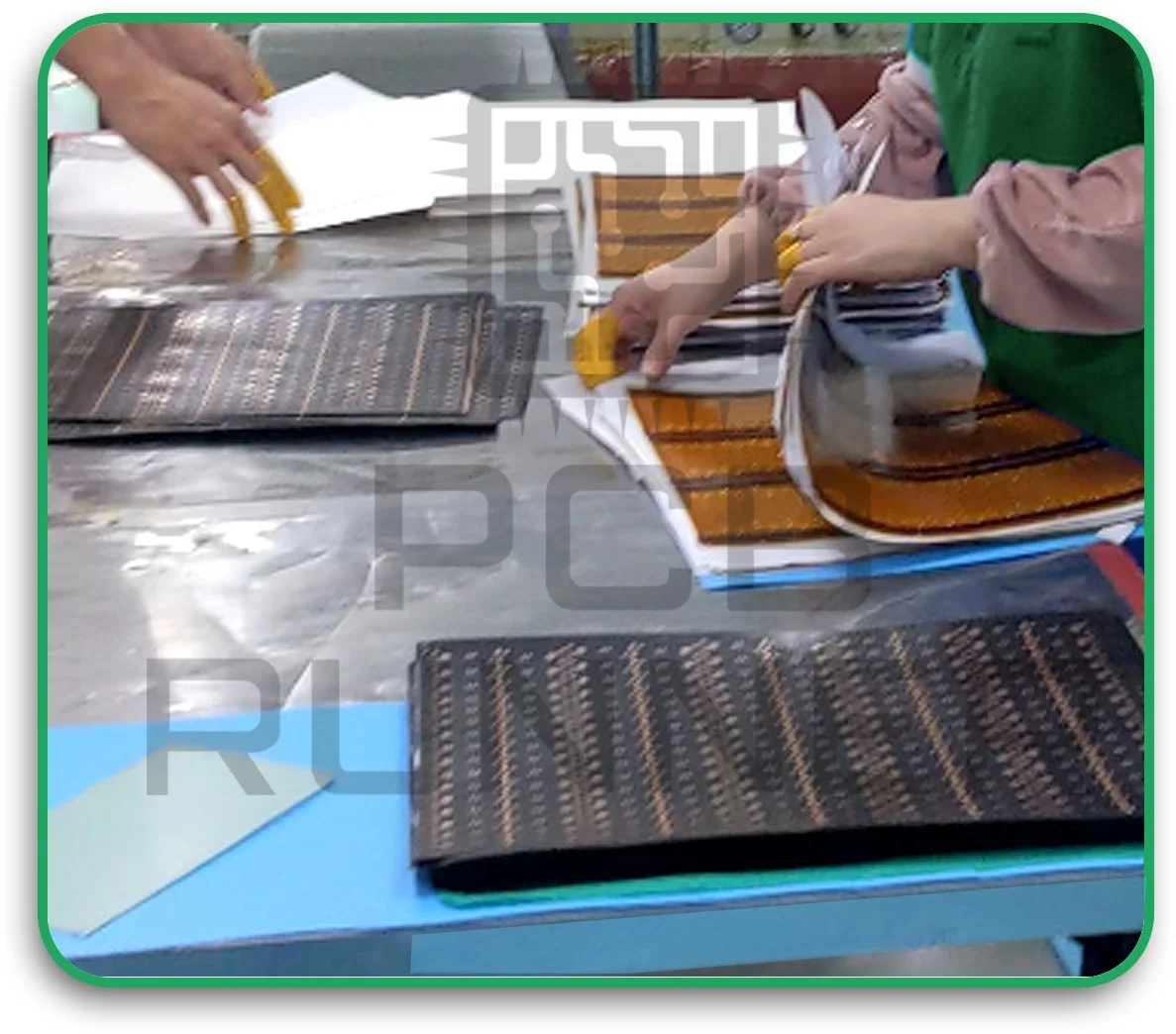
3. Layer Preparation and Circuit Generation
Each layer is created separately. Flexible layers are thinner and require extra care. Copper is laminated onto the flexible substrate, and the circuit pattern is etched using chemical processes.

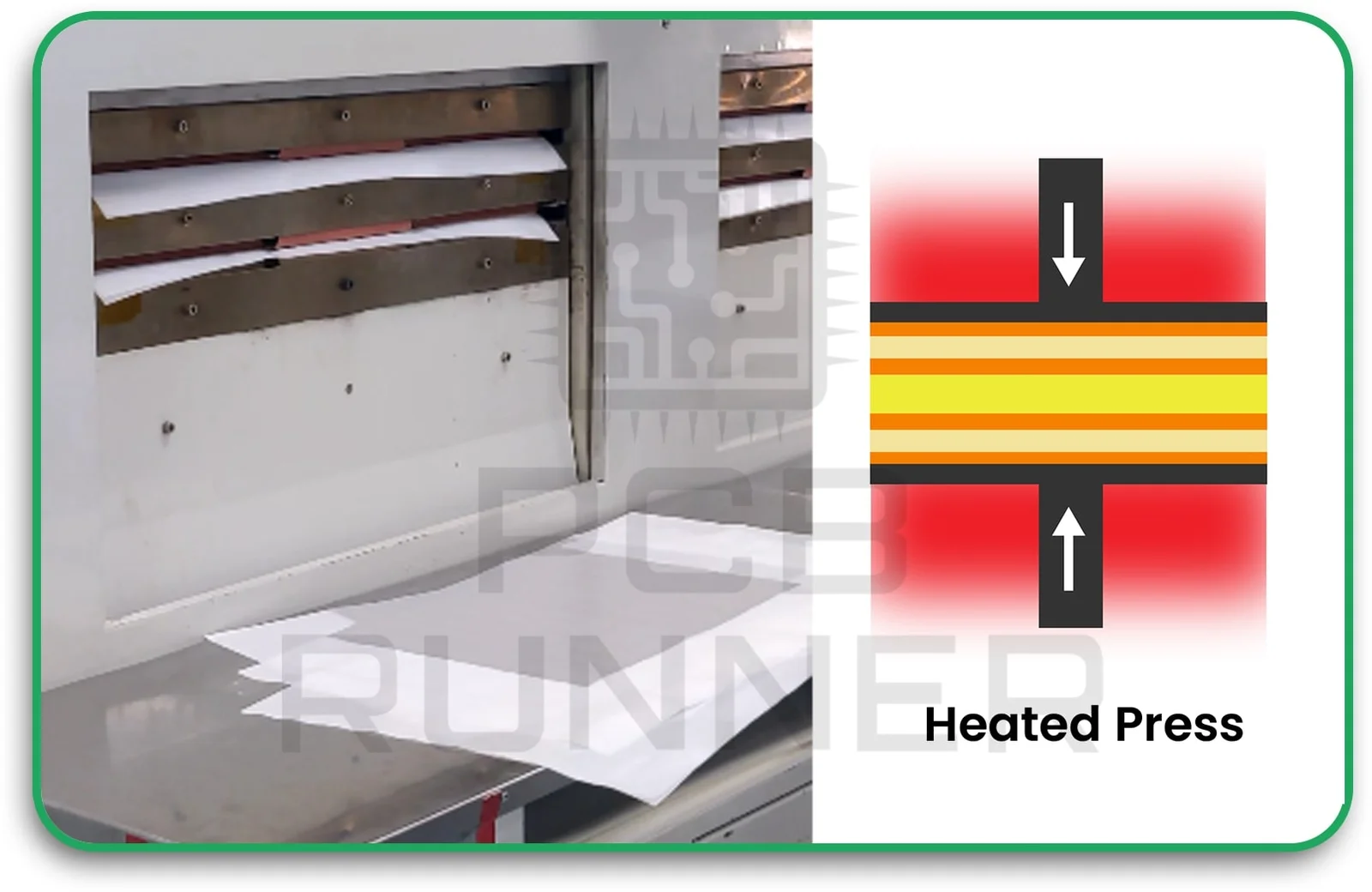
4. Lamination
The rigid and flexible sections are precisely aligned and laminated together using heat and pressure. This step is tricky, if layers shift, the board won’t work properly.

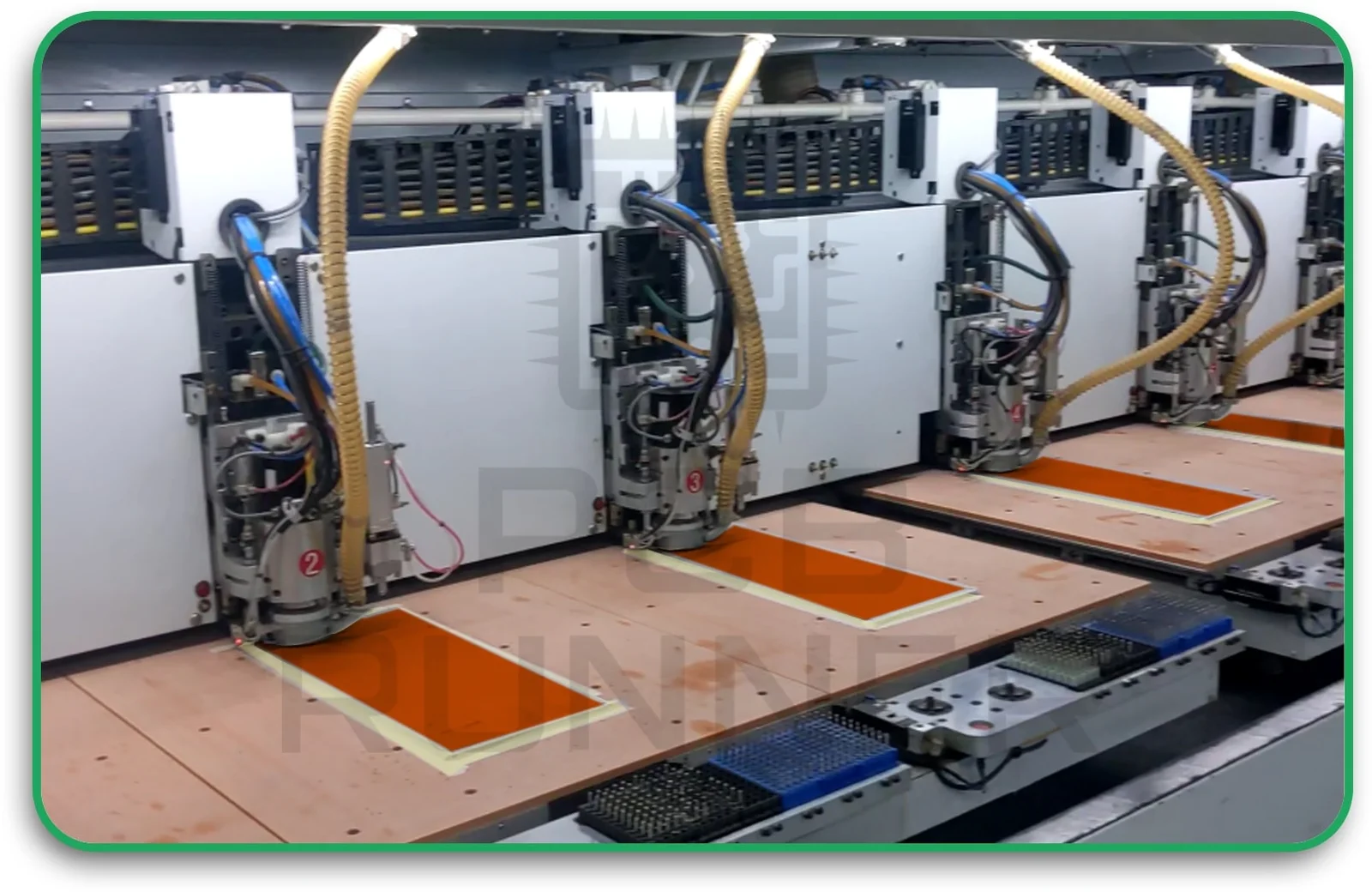
5. Drilling and Plating
Holes are drilled to connect layers. In flex areas, it’s important not to drill where the board will bend, as this can cause cracks. The holes are then plated with copper to create electrical connections.

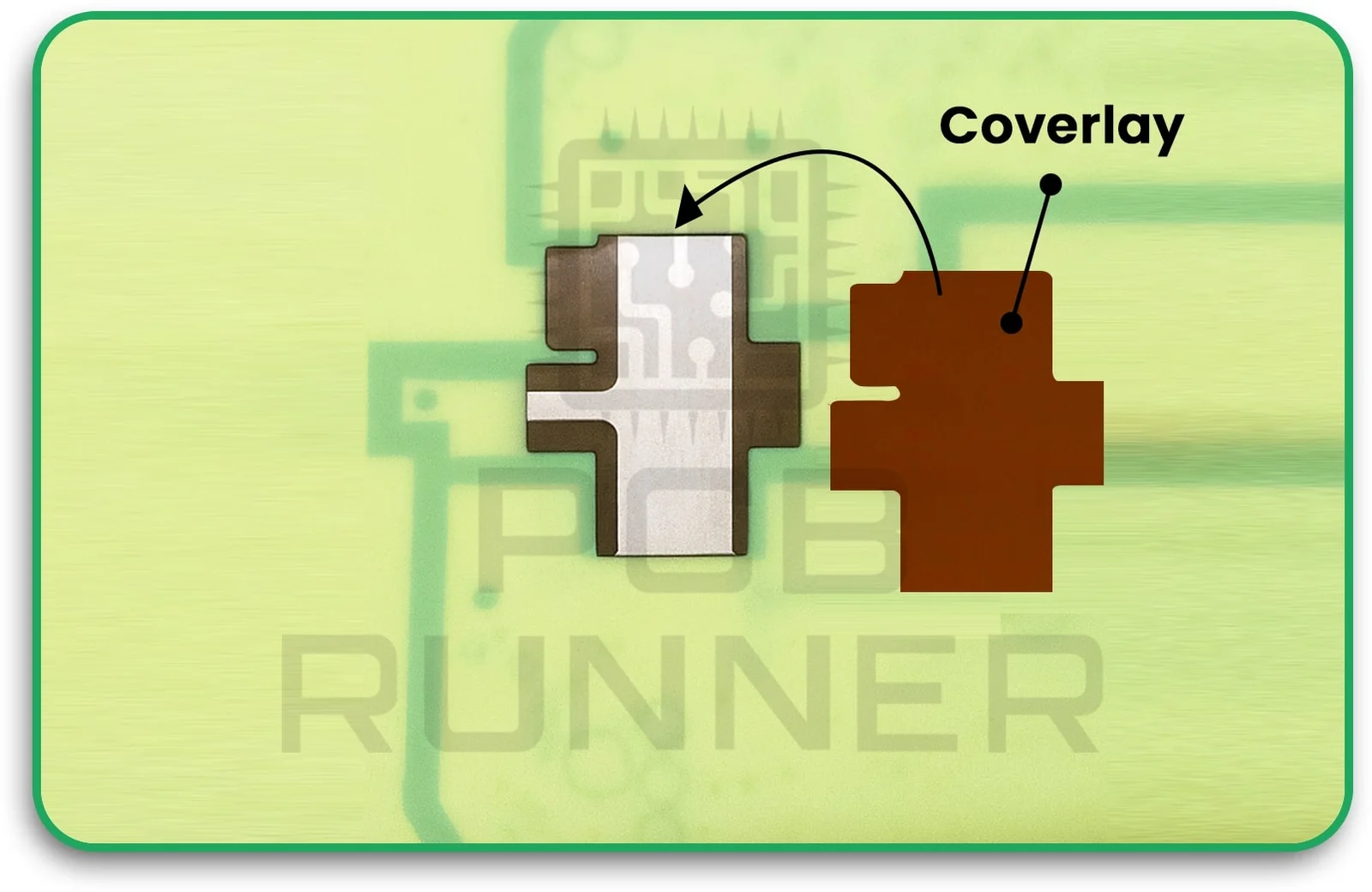
6. Coverlay Application
An overlay (usually polyimide film) is applied to protect the flexible sections. This keeps out moisture and dust and helps the board survive repeated bending.
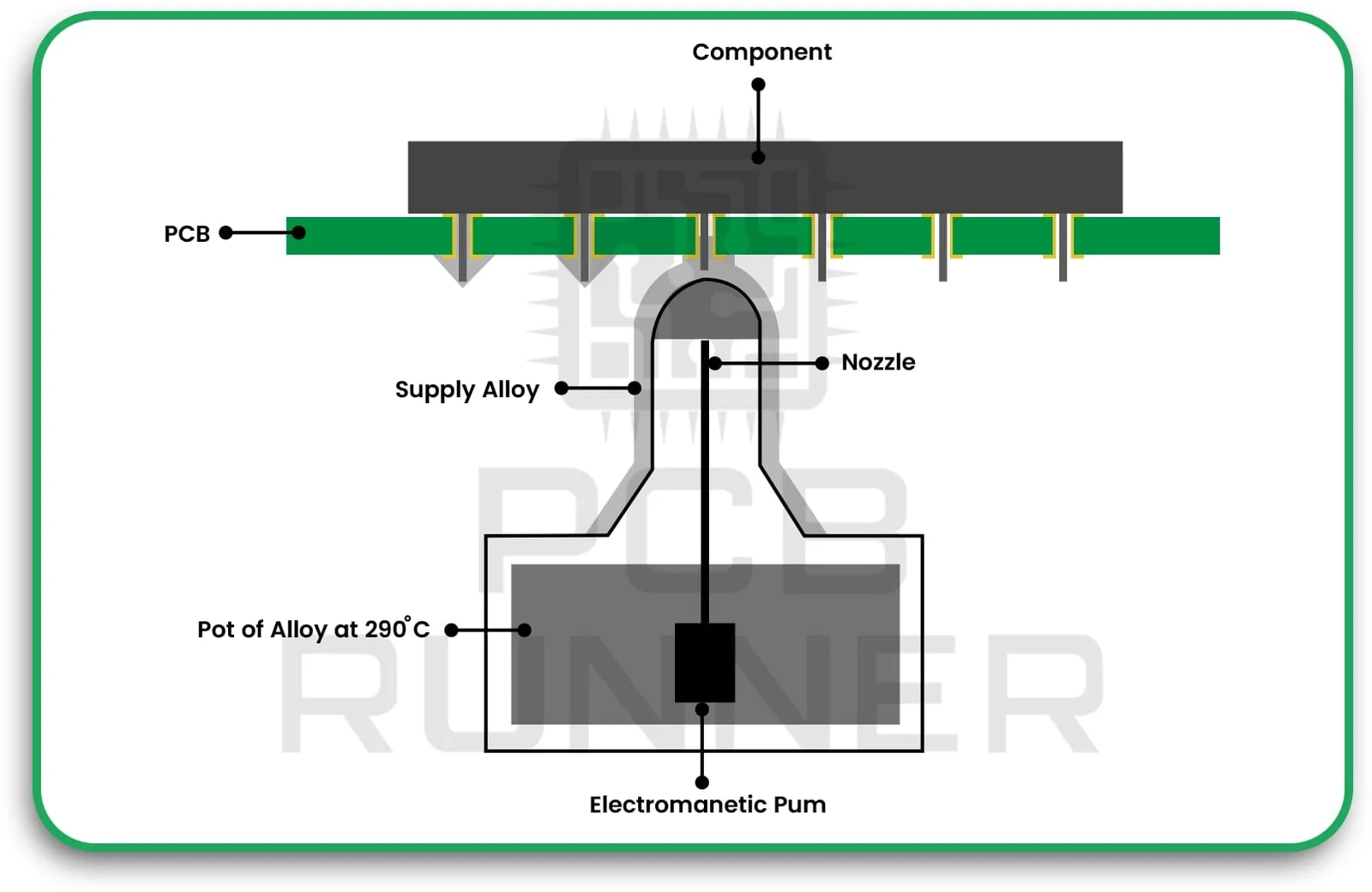
7. Component Placement and Soldering
Components are placed on the rigid sections using automated machines. Soldering is done carefully to avoid damaging the flexible areas. Rigid-flex PCB assembly may use reflow, wave, or selective soldering, depending on the parts.
8. Testing and Inspection
The final board is cleaned and inspected. Tests include electrical checks, bend tests, and sometimes environmental stress tests to ensure the board will last.

Where Are Flexible Circuit Boards Used?
The future of flexible circuit technology is bright because it’s useful in so many ways:
- Wearable Tech: Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitors wrap around your body thanks to flex PCBs.
- Medical Devices: Flexible boards fit inside catheters and implants, making them less invasive.
- Automotive: Sensors and displays in cars use flex and rigid PCB designs for reliability in tight spaces.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, bendable boards help reduce weight and fit into unusual shapes.
- Consumer Electronics: Foldable phones, tablets, and even headphones rely on flex PCB production.
Why Are Rigid Flex PCBs the Future?
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the best of both worlds. You get the strength of a rigid board for mounting parts plus the flexibility to fit into tight or moving spaces. This makes them ideal for devices that need to be small, reliable, and tough.
Benefits of rigid-flex PCB design:
- Fewer connectors, which means fewer points of failure.
- Better signal integrity because there are no long cables.
- More design freedom for engineers and product designers.
As technology advances, expect to see more products using rigid flex PCB assembly for better performance and durability.
Challenges in Flex PCB Production
While flexible circuit boards are amazing, they aren’t easy to make. Here are some common challenges:
- Complex Design: Every bend and fold must be planned to avoid stress and cracking.
- Material Handling: Flexible materials can tear or wrinkle if not handled carefully.
- Assembly: Soldering components onto a board that bends takes special skills and equipment.
- Testing: Boards must be tested for both electrical performance and mechanical durability.
Working with an experienced rigid-flex PCB manufacturer is key to overcoming these challenges and getting reliable results.
Innovations to Watch
The future of flexible circuit technology is full of exciting possibilities:
1. Thinner, More Durable Materials
New materials are making flexible circuit boards even thinner and more robust, allowing for tighter bends and longer life.
2. 3D and Multi-Layer Designs
Engineers are stacking multiple flexible and rigid layers to create complex 3D shapes. This is perfect for aerospace, automotive, and next-gen consumer electronics.
3. Advanced Custom PCB Assembly
Custom PCB assembly techniques are letting manufacturers place tiny chips and sensors directly onto flexible substrates, opening the door for smarter, smaller devices.
4. Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
As demand grows, more companies are looking for ways to make flex and rigid PCB production greener, using less energy and fewer chemicals.
How to Get the Most from Flexible Circuit Boards
If you’re planning a new product or want to upgrade your current design, here are some tips:
- Work with a specialist. Choose a rigid-flex PCB manufacturer with a strong track record.
- Plan your design carefully. Think about where the board needs to bend and where components will go.
- Test prototypes thoroughly. Make sure your design can handle real-world use.
- Stay updated on new materials and techniques. The field is changing fast!
Action Steps for Your Next Project
- Start with a clear design. Map out where you need flexibility and where you need strength.
- Choose the right materials. Polyimide for flex, FR-4 for rigid, ask your manufacturer for advice.
- Partner with experts in flex PCB production. They’ll help you avoid common pitfalls.
- Consider custom PCB assembly. This lets you add unique features and get the exact performance you want.
- Test, test, test. Don’t skip mechanical and electrical testing before full production.
Final Thoughts
Flexible circuit technology is changing the way we build and use electronics. From smart gadgets to cars and planes, flexible and rigid PCB designs are making products lighter, smaller, and more reliable. As materials and manufacturing methods improve, the possibilities are endless.
If you want your next product to stand out, explore what flexible and rigid-flex PCBs can do. Work with a skilled rigid-flex PCB manufacturer, use the latest flex PCB production techniques, and don’t be afraid to push the limits of design. The future is flexible, are you ready to bend with it?