Effective testing is essential for ensuring the success of PCB assembly. Whether working with a prototype or a large production run, testing helps detect and resolve issues before they become costly problems. For PCB assemblers, comprehensive testing methods improve quality control, reduce failures, and ensure reliability.
Testing is a critical step in the PCB fabrication process. It helps confirm that all components function correctly, connections are secure, and the board meets performance expectations. This blog will explore the best testing strategies for PCB assembly, from initial inspections to advanced testing techniques.
The Importance of PCB Testing
PCBs are at the core of modern electronics. Any defect in a PCB can lead to malfunctions or system failures. Without proper testing, manufacturers risk delivering faulty products, leading to potential recalls and customer dissatisfaction.
Key reasons why PCB testing is crucial:
- Identifies defects early in the production process
- Ensures proper component placement and soldering
- Prevents short circuits and electrical failures
- Improves overall product reliability
- Reduces manufacturing costs by minimizing rework
Testing is not just about preventing defects; it is also about optimizing the production process and ensuring that each PCB meets industry standards.
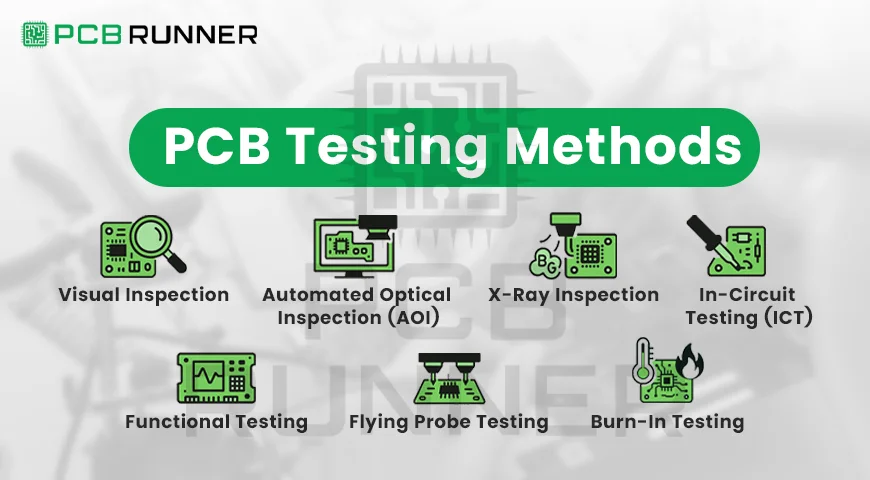
Key PCB Testing Methods
Visual Inspection
The first step in PCB testing is visual inspection. This method helps detect apparent defects such as misaligned components, soldering issues, or missing parts.
- Identifies physical damage or contamination
- Detects incorrect part placement
- Ensures connectors and pads are properly aligned
While visual inspection is proper, it cannot detect hidden faults, making additional testing necessary.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) uses cameras and image processing to detect defects. This method is more efficient than manual inspection and helps identify issues like:
- Soldering defects such as bridges or cold joints
- Misaligned or missing components
- Variations in solder paste application
AOI is widely used in circuit board assembly because it provides quick and accurate results.
X-ray Inspection
X-ray inspection is crucial for high-density interconnect PCBs and multilayer designs. It helps detect defects that are not visible through AOI, such as:
- Voids in solder joints
- Hidden cracks in traces
- Misalignment in multilayer PCB assemblies
X-ray testing is beneficial for boards with Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, where connections are hidden beneath the package.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
In-circuit testing (ICT) checks individual components and connections on the PCB. This method verifies:
- Resistance, capacitance, and inductance values
- Voltage levels and signal integrity
- Short circuits or open circuits
ICT is effective for detecting early-stage assembly defects before functional testing.
Functional Testing
Functional testing ensures the PCB operates as intended. It simulates real-world conditions to check:
- Power regulation and signal flow
- Communication between components
- Response to inputs and outputs
Functional testing is essential for validating prototype PCB assembly before full production.
Flying Probe Testing
Flying probe testing is ideal for low-volume production and prototype PCB assembly. Unlike ICT, this method does not require custom test fixtures, making it more cost-effective.
- Tests continuity and component functionality
- Detects open and short circuits
- Suitable for multilayer PCBs with complex layouts
Burn-In Testing
Burn-in testing evaluates how a PCB performs under stress. It involves operating the PCB at high temperatures and voltages to detect potential failures.
- Identifies early component failures
- Ensures reliability in extreme environments
- Used for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications
Best Practices for PCB Testing
To improve PCB quality, manufacturers should follow these best practices:
- Use multiple testing methods: Combining AOI, ICT, and functional testing ensures a thorough inspection.
- Test early in the process: Catching defects early reduces rework and costs.
- Implement real-time monitoring: Automated systems can track defects as they occur, improving efficiency.
- Follow industry standards: Adhering to IPC and ISO guidelines ensures compliance with global quality benchmarks.
- Train personnel: Skilled technicians can identify issues that automated tests may miss.
How Testing Enhances PCB Fabrication and Assembly
By incorporating rigorous testing strategies, PCB assemblers can:
- Improve product reliability and longevity
- Reduce defects and manufacturing delays
- Lower production costs by minimizing rework
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations
- Deliver high-quality PCBs that meet customer expectations
Testing is not just about identifying issues; it is a crucial step in refining the manufacturing process and ensuring high-quality PCB assembly.
Conclusion
Effective testing is key to ensuring the success of PCB fabrication and assembly. By implementing a combination of visual inspection, AOI, X-ray testing, ICT, functional testing, and burn-in testing, manufacturers can detect and correct defects before they become serious problems. Partnering with a reliable PCB assembler that follows rigorous testing standards can help you achieve superior product quality. Whether you are working on a prototype or a large production run, investing in proper testing strategies will lead to better performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Looking for High-Quality PCB Assembly?
At PCB Runners, we specialize in PCB fabrication, circuit board assembly, and testing solutions to ensure reliable and high-performance PCBs. Contact us today to learn how our testing strategies can enhance your production process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most effective testing method for PCB assembly?
A combination of AOI, ICT, and functional testing provides the most comprehensive quality control.
2. Why is functional testing necessary?
It verifies that the PCB operates correctly under real-world conditions.
3. How does AOI improve PCB quality?
AOI quickly detects soldering defects, misaligned components, and other issues, reducing manual errors.
4. What testing methods are best for prototype PCB assembly?
Flying probe testing, AOI, and functional testing are commonly used for prototypes.
5. How can I ensure my PCB meets quality standards?
Work with an experienced PCB assembler that follows industry best practices and rigorous testing protocols.