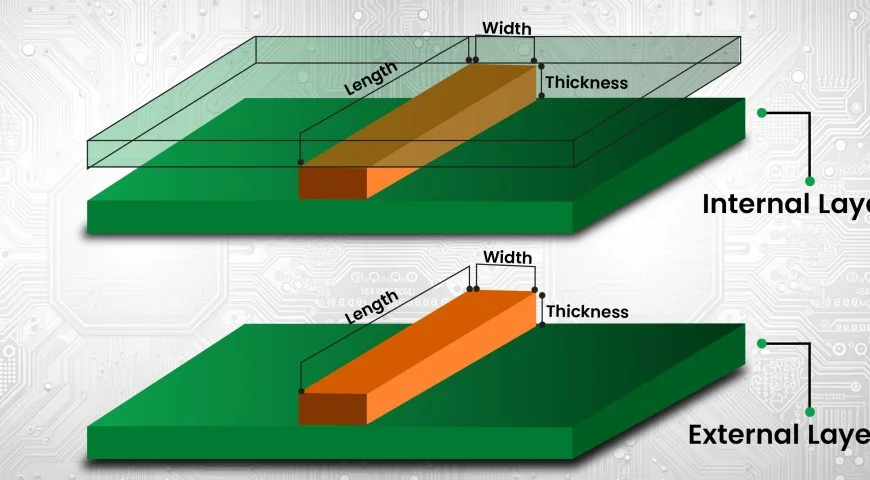
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of nearly all modern electronic devices. One of the key components of a PCB is its traces, which are the electrical paths that connect the various components of the board. These traces are responsible for carrying current and signals between components, so it’s crucial to ensure they are sized correctly for the board to function properly.
One of the most essential factors in PCB trace design is the trace width. The trace width refers to the physical width of the copper traces on a PCB. This width must be carefully calculated to ensure that the traces can carry the required current without overheating or becoming too weak to function correctly.
In this blog, we will walk you through the steps of calculating the correct PCB trace width, as well as how to use trace width calculators to make the job easier.
Why Trace Width Matters?
Before we dive into the details of how to calculate trace width, it’s essential to understand why it matters in the first place. PCB traces are made from copper, which is a good conductor of electricity. However, the width of the trace plays a crucial role in determining how much current the trace can safely carry.
If the trace is too narrow, it may overheat due to high current flow, leading to a failure of the PCB. On the other hand, if the trace is too broad, it may take up too much space on the PCB, leaving less room for other components or traces. Therefore, calculating the correct trace width is essential for both safety and efficiency.
Factors That Affect PCB Trace Width
When calculating PCB trace width, there are several factors you need to take into consideration:
- Current Carrying Capacity: This refers to how much current the trace needs to carry. Higher currents require wider traces to prevent overheating.
- Copper Thickness: The thickness of the copper used for the PCB will impact the trace width. Thicker copper can handle more current so that the trace width can be narrower.
- Temperature Rise: The temperature rise refers to how much the trace temperature increases due to the current. You want to keep the temperature rise within safe limits, so you need to adjust the trace width accordingly.
- PCB Manufacturer Specifications: Different PCB circuit board manufacturers may have different guidelines or limitations on trace width and spacing. Always check with your PCB board manufacturer for their specifications before finalizing your design.
How to Calculate PCB Trace Width
Now that we know why trace width is essential, let’s go over how to calculate the width of the traces for your PCB accurately. The formula for calculating trace width is based on the amount of current the trace needs to carry, the copper thickness, and the allowable temperature rise. Here’s a simple formula:
W=Ik×(Tr)0.5W = \frac{I}{k \times (T_r)^{0.5}}W=k×(Tr)0.5I
Where:
- W = Trace width (in mils or mm)
- I = Current (in amperes)
- k = A constant that depends on the copper thickness (typically between 0.5 and 1.2)
- T_r = Temperature rise (in Celsius)
While this formula gives you an idea of how to calculate trace width manually, it can be complex and time-consuming. Thankfully, there are tools available to make this process easier.
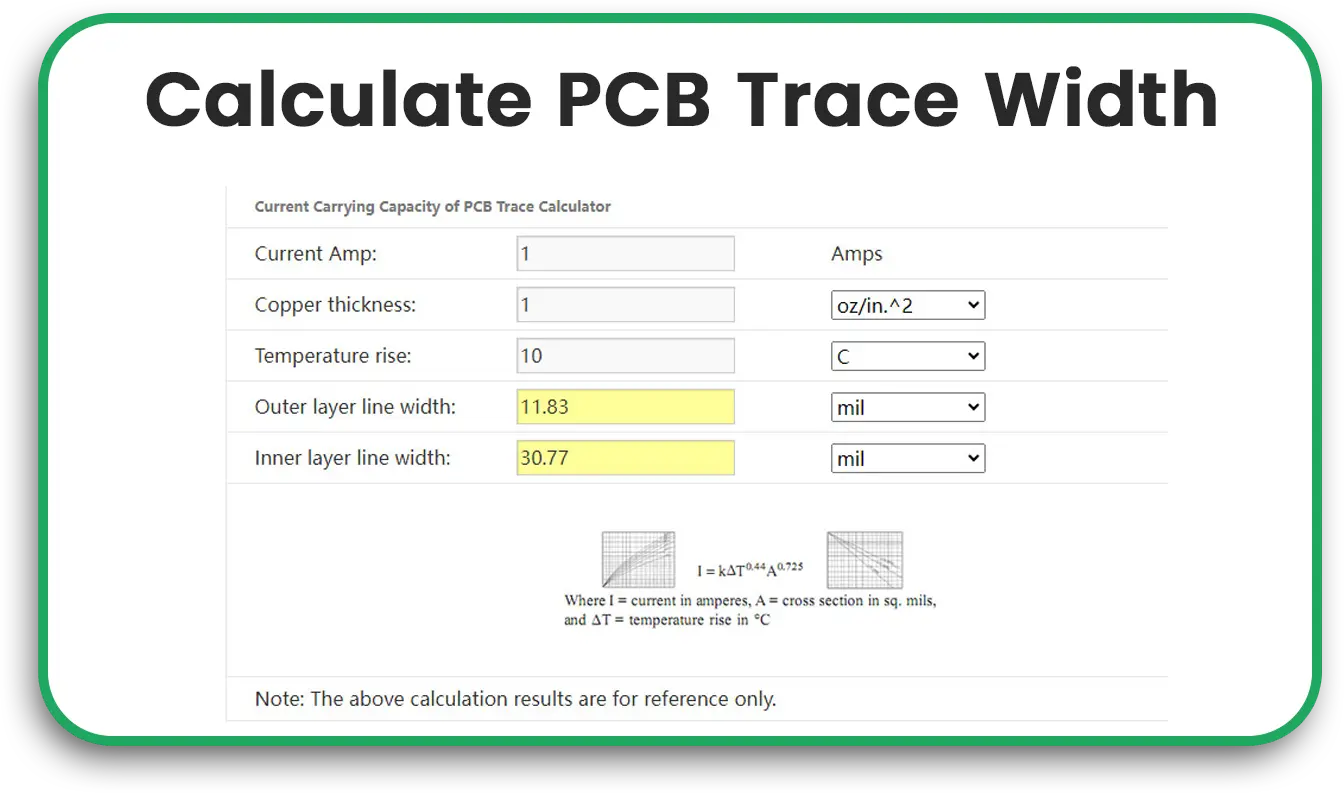
Using a PCB Trace Width Calculator
Rather than calculating trace width manually, many PCB board assembly companies and PCB circuit board manufacturers provide online trace width calculators to simplify the process. These calculators allow you to input key information, such as:
- Current (in amperes)
- Copper thickness (in oz/ft²)
- Temperature rise
- Units (mils or mm)
Once you input these values, the calculator will output the optimal trace width for your PCB design. Many online calculators are free to use and can help you save time and reduce the likelihood of errors.
There are several popular PCB trace width calculators available, such as:
- IPC-2221 Trace Width Calculator: This calculator follows the standards set by the IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits) and provides a reliable way to determine trace width.
- Online Trace Width Calculator by Advanced Circuits: This free tool allows you to quickly determine the trace width based on the current and other parameters.
- EasyEDA Trace Width Calculator: This tool is integrated with the EasyEDA design software, making it convenient for designers working with the EasyEDA platform.
By using these tools, you can quickly and accurately calculate the track width required for your PCB design without the need for complex formulas or manual calculations.
The Role of PCB Design Software
When designing a PCB, many PCB circuit board manufacturers and engineers rely on specialized printed circuit board design software to create the layout. These software tools often come with built-in features that can automatically calculate trace width, saving even more time and reducing the risk of human error.
Some PCB design tools that include trace width calculation features are:
- Altium Designer: One of the most widely used design tools, Altium Designer has an integrated trace width calculator that can help designers select the right trace width based on their design requirements.
- KiCad: A free and open-source PCB design tool, KiCad offers features to help you determine trace width based on current and copper thickness.
- Autodesk Eagle: Known for its user-friendly interface, Eagle allows designers to input trace width settings. It will provide feedback during the design process to ensure that the trace width is appropriate.
These tools often integrate directly with PCB fabrication processes, allowing manufacturers to transition from design to production without errors easily.
What Happens If You Get the Trace Width Wrong?
Incorrect trace width can lead to various problems in your PCB. If the trace width is too narrow, the trace may overheat, leading to potential failure. If the trace width is too wide, you may waste valuable PCB space, increasing the size and cost of your design.
In some cases, overly narrow traces can cause a PCB failure during operation. On the other hand, wide traces may contribute to larger board sizes or unnecessary cost increases. That’s why accurate trace width calculation is essential for maintaining reliability and performance.
Conclusion
Calculating the correct PCB trace width is crucial for ensuring the success of your PCB design. By understanding the factors that affect trace width, such as current carrying capacity, copper thickness, and temperature rise, you can make informed decisions about your design. Using trace width calculators and PCB design software will help you save time and reduce errors in your design. Whether you’re a PCB board manufacturer, engineer, or DIY designer, taking the time to calculate trace width accurately will ensure that your PCB works reliably and efficiently.
Make sure to check with your PCB board manufacturer for any specific design guidelines, and always test your designs thoroughly before moving to production. With the right tools and knowledge, you can create high-quality, reliable PCBs that meet your specifications.