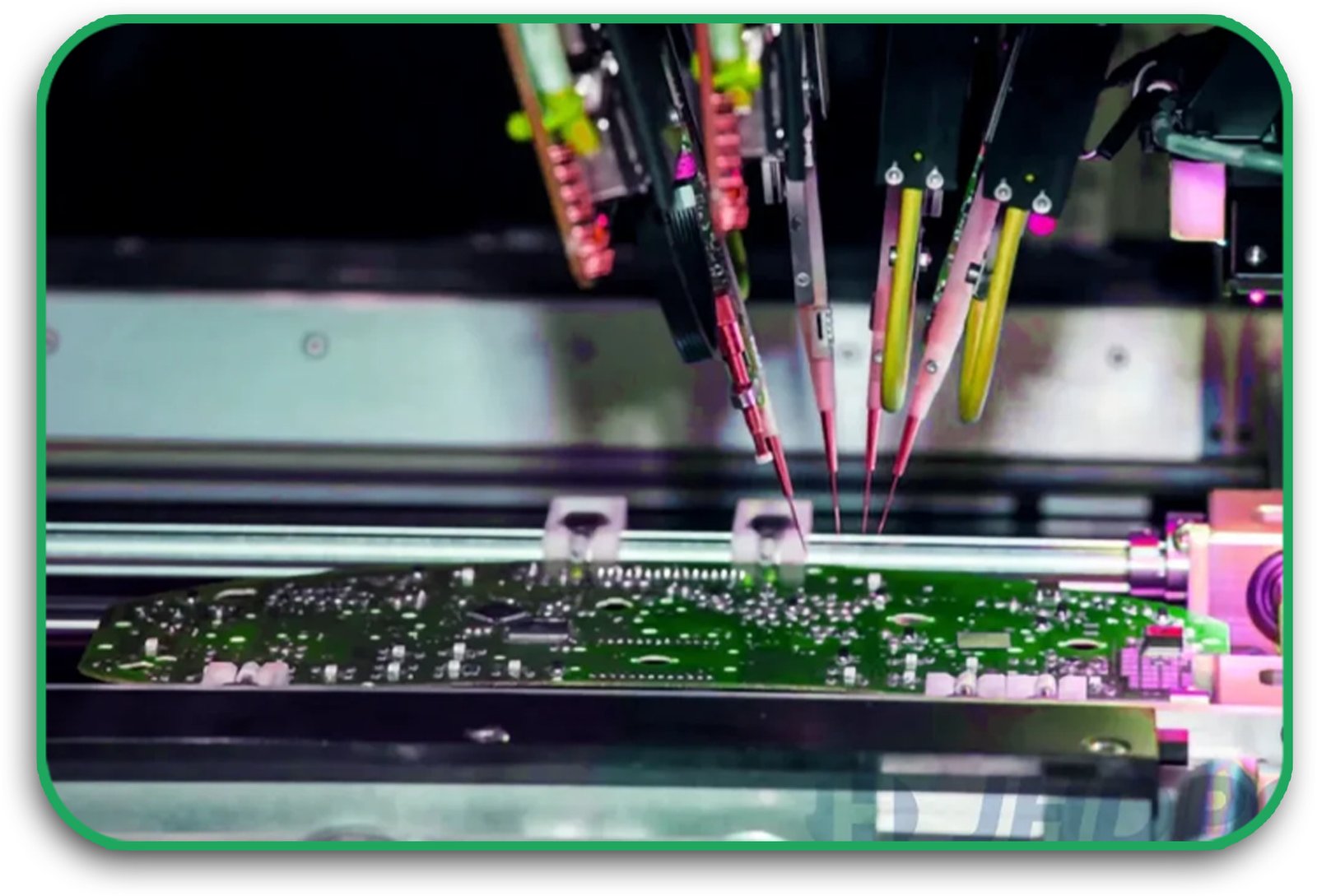
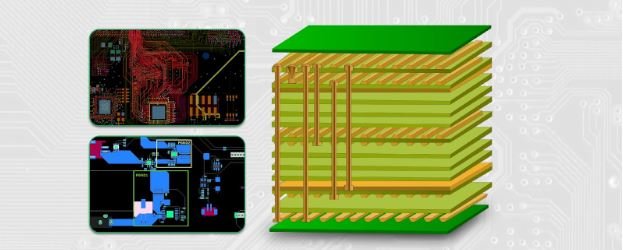
As modern electronics evolve, the demand for ultra-multilayer PCBs continues to grow. These complex circuit boards allow for higher functionality, improved performance, and greater miniaturization in devices ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace systems. Multilayer printed circuit boards are now essential in applications where high-speed data transmission, power management, and space efficiency are critical.
For engineers, designers, and manufacturers, understanding the latest multilayer PCB design innovations is key to staying ahead in the competitive electronics industry. In this guide, we’ll explore how ultra-multilayer PCBs are advancing circuit design, their manufacturing process, and why they are vital for the future of electronic devices.
What Are Ultra-Multilayer PCBs?
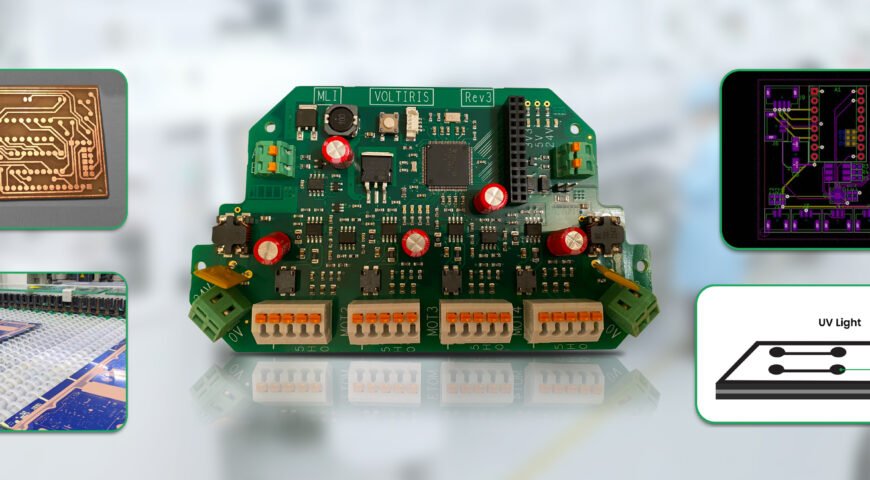
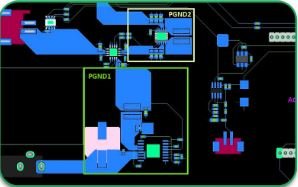
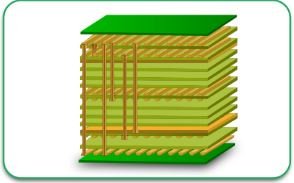
A multilayer PCB board consists of multiple copper layers stacked together with insulating materials in between. While traditional PCBs have two to eight layers, ultra-multilayer designs can go beyond 50 layers, allowing for more intricate circuitry and increased electrical performance.
These advanced PCBs are widely used in high-speed computing, medical equipment, telecommunications, military applications, and aerospace systems, where complex electronic functions need to fit into compact spaces without compromising signal integrity.
Benefits of Ultra-Multilayer PCBs
1. High Component Density
With multiple layers, custom-printed circuit boards can integrate more circuits and components within a smaller area, making them ideal for miniaturized electronic devices.
2. Enhanced Signal Integrity
Ultra-multilayer PCBs use dedicated signal and power planes, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, which is crucial for high-speed and high-frequency applications.
3. Improved Thermal Management
Advanced multilayer PCB fabrication techniques incorporate heat dissipation methods, such as thermal vias and copper planes, ensuring devices remain cooler and more reliable during operation.
4. Greater Design Flexibility
Engineers can customize multilayer PCB designs to meet the specific needs of automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications, offering versatile routing solutions for complex circuits.
5. Increased Reliability
Due to advanced material selection and manufacturing processes, multilayer PCB manufacturers ensure these boards offer higher durability and longer lifespans, making them ideal for mission-critical applications.
How Ultra-Multilayer PCBs Are Manufactured
1. Designing the PCB Layout
Using advanced PCB design software, engineers map out the circuit layers, component placements, and signal routing while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
2. Layer Stack-Up Planning
The PCB circuit board manufacturer carefully selects dielectric materials, copper thickness, and layer arrangements to optimize electrical performance and thermal management.
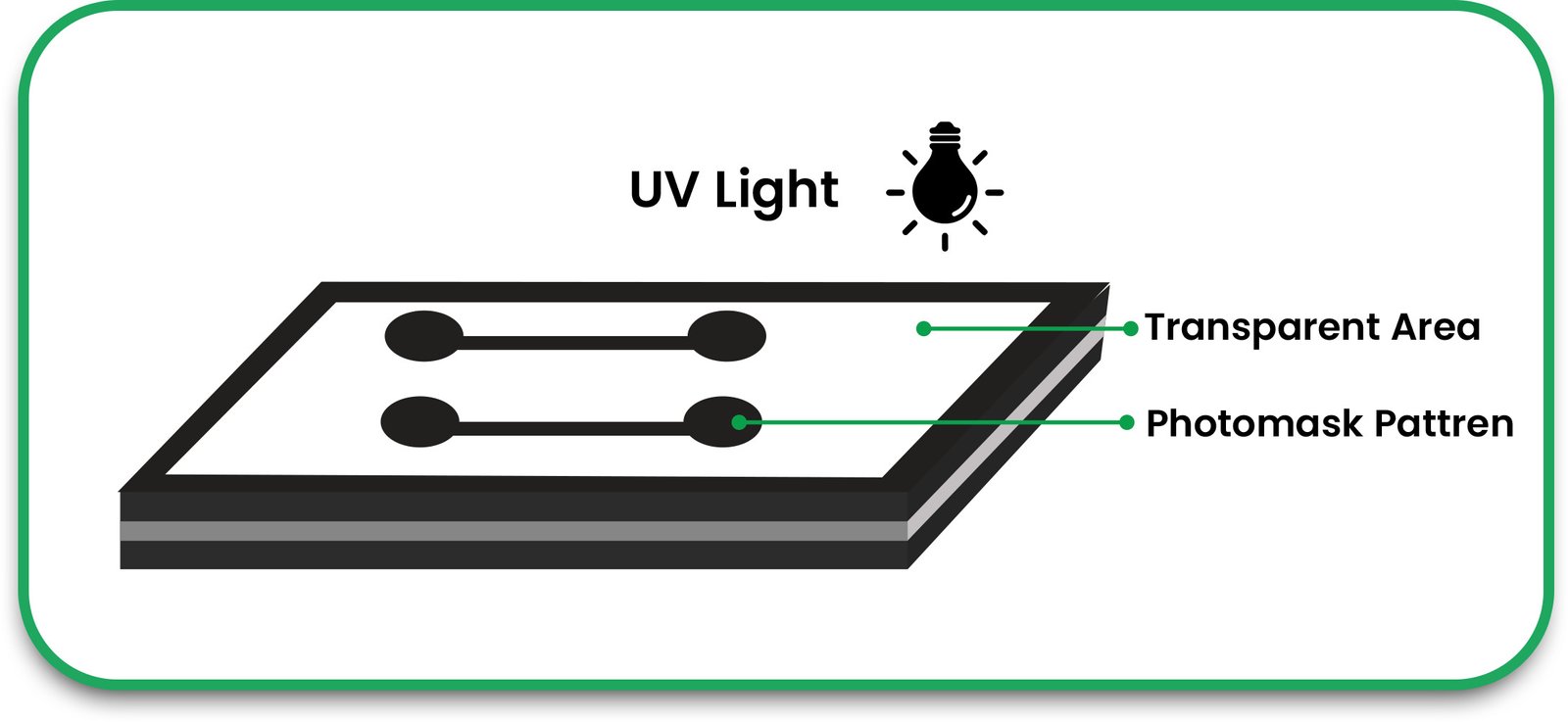
3. Inner Layer Imaging and Etching
Each copper layer is coated with photoresist material, exposed to UV light, and then etched to create the required circuit patterns.
4. Lamination and Layer Bonding
The layers are aligned and laminated together under high pressure and temperature, ensuring a strong bond between conductive and insulating materials.
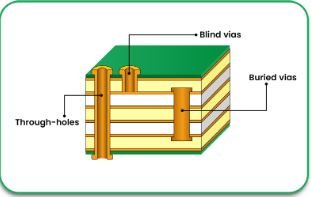
5. Drilling and Via Formation
Precision laser or mechanical drilling creates micro vias, blind vias, and buried vias, allowing for interconnection between multiple layers.
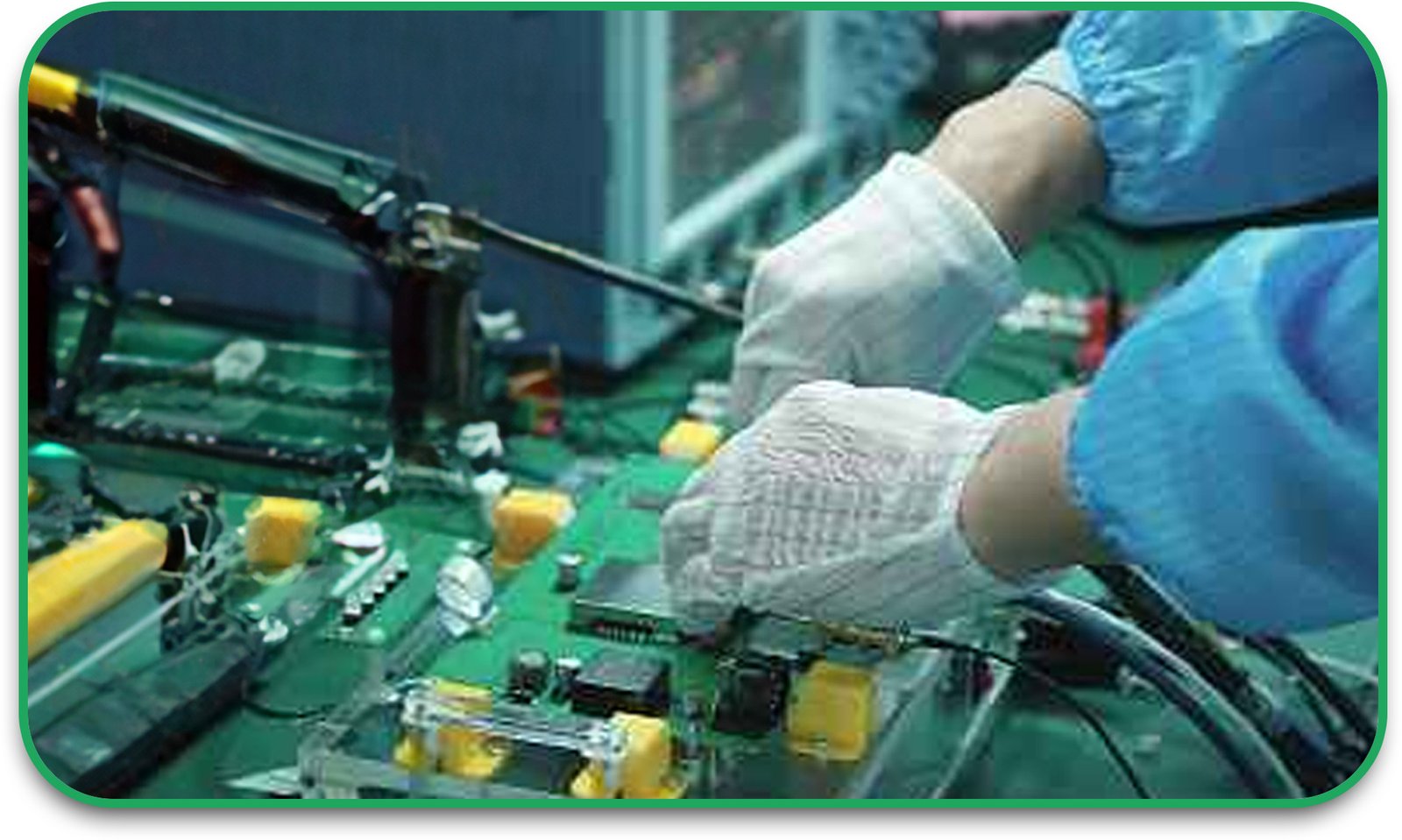
6. Copper Plating and Surface Finish Application
The plated-through holes (PTHs) are coated with copper, enhancing conductivity and mechanical strength. A protective surface finish is applied to prevent oxidation and ensure solderability.
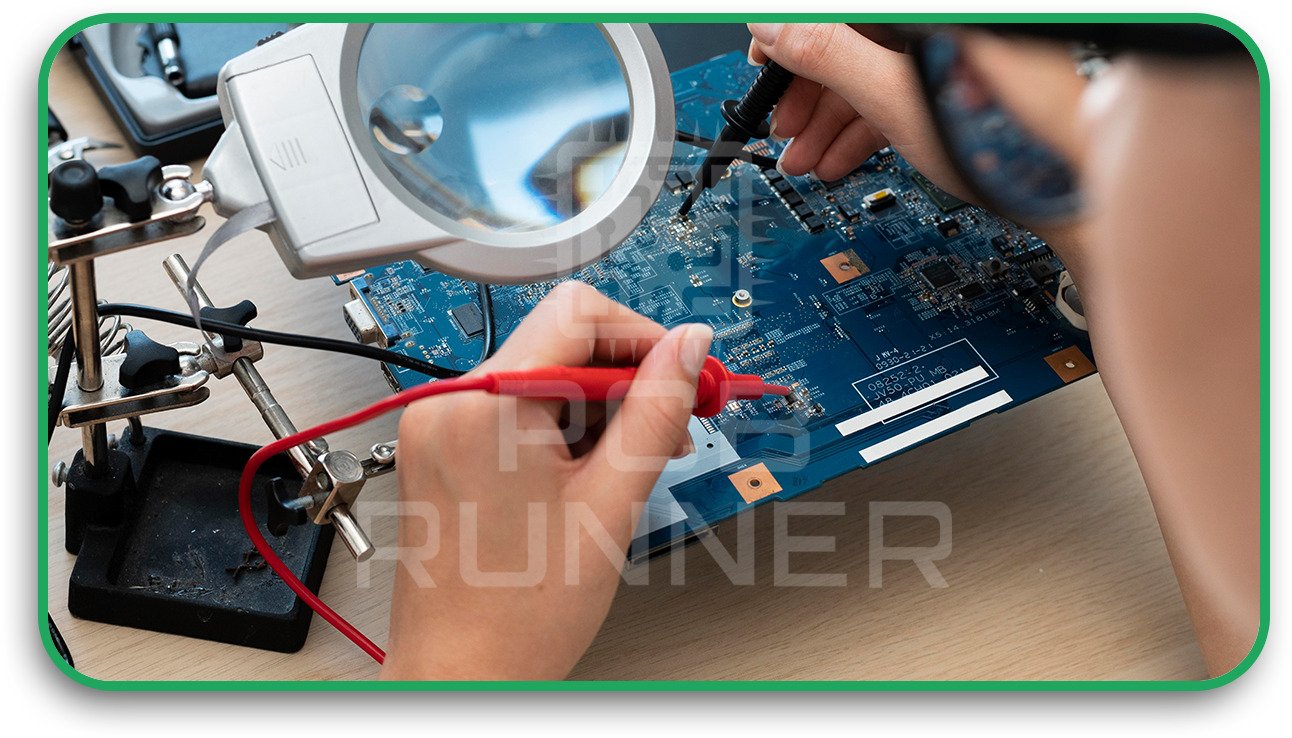
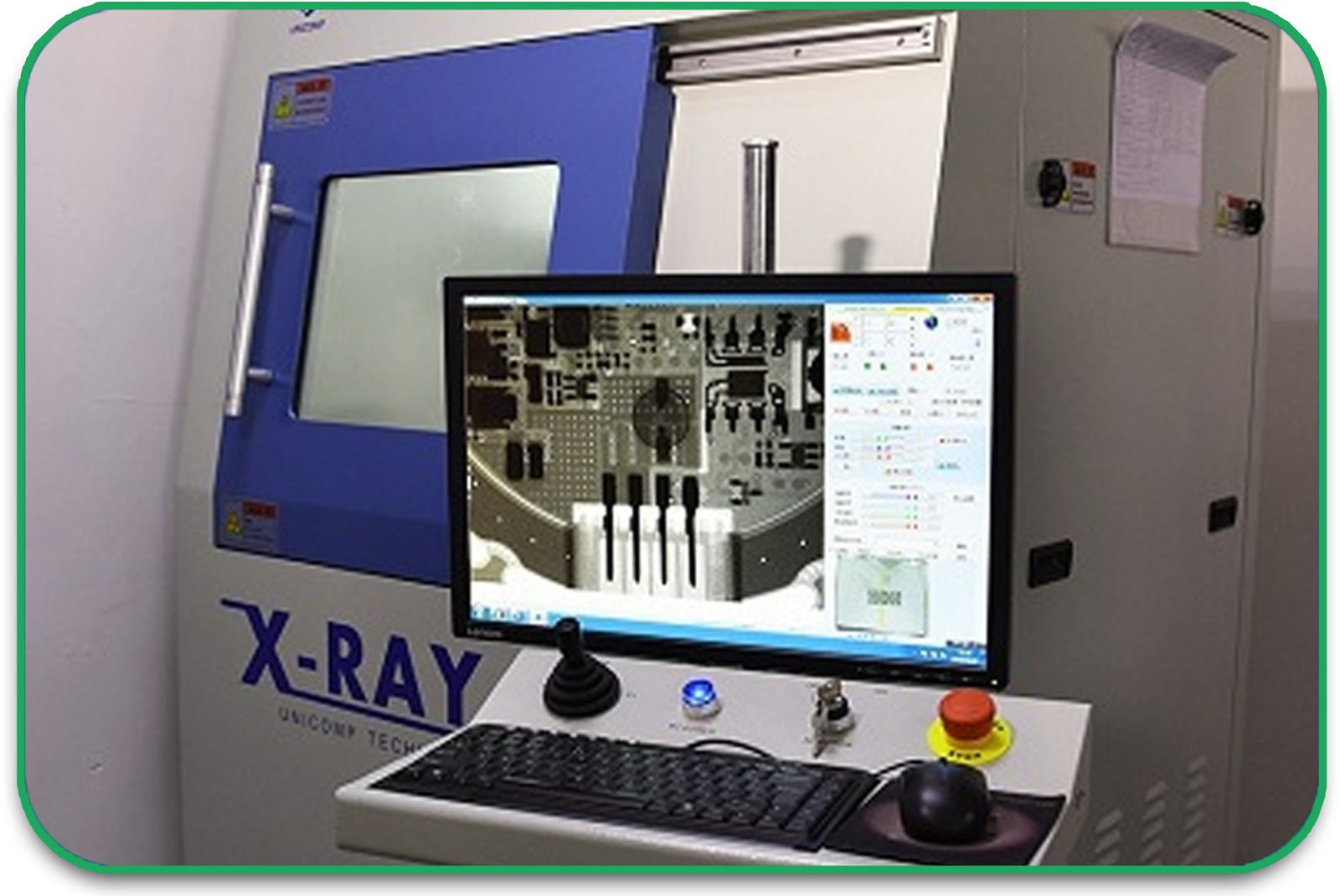
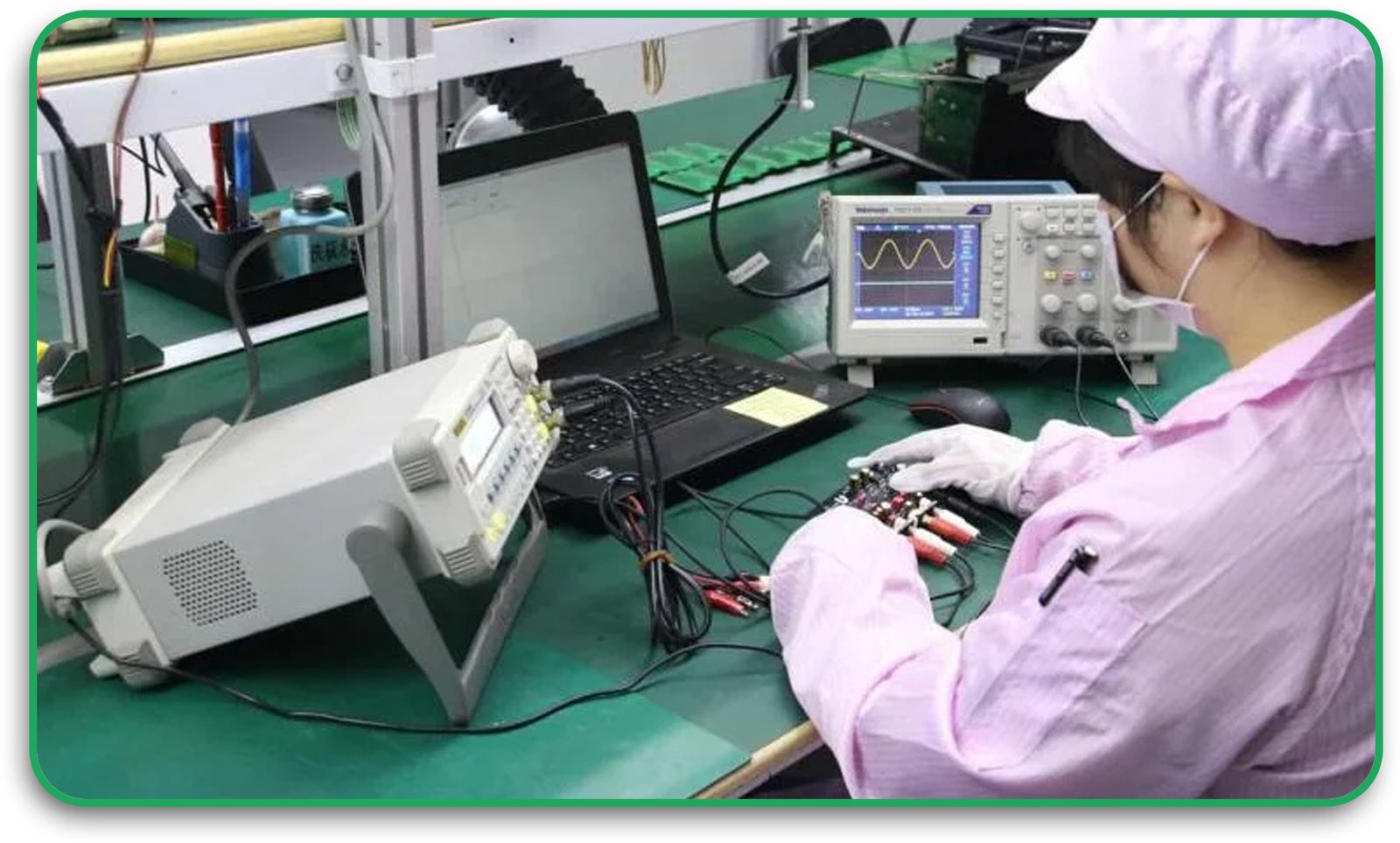
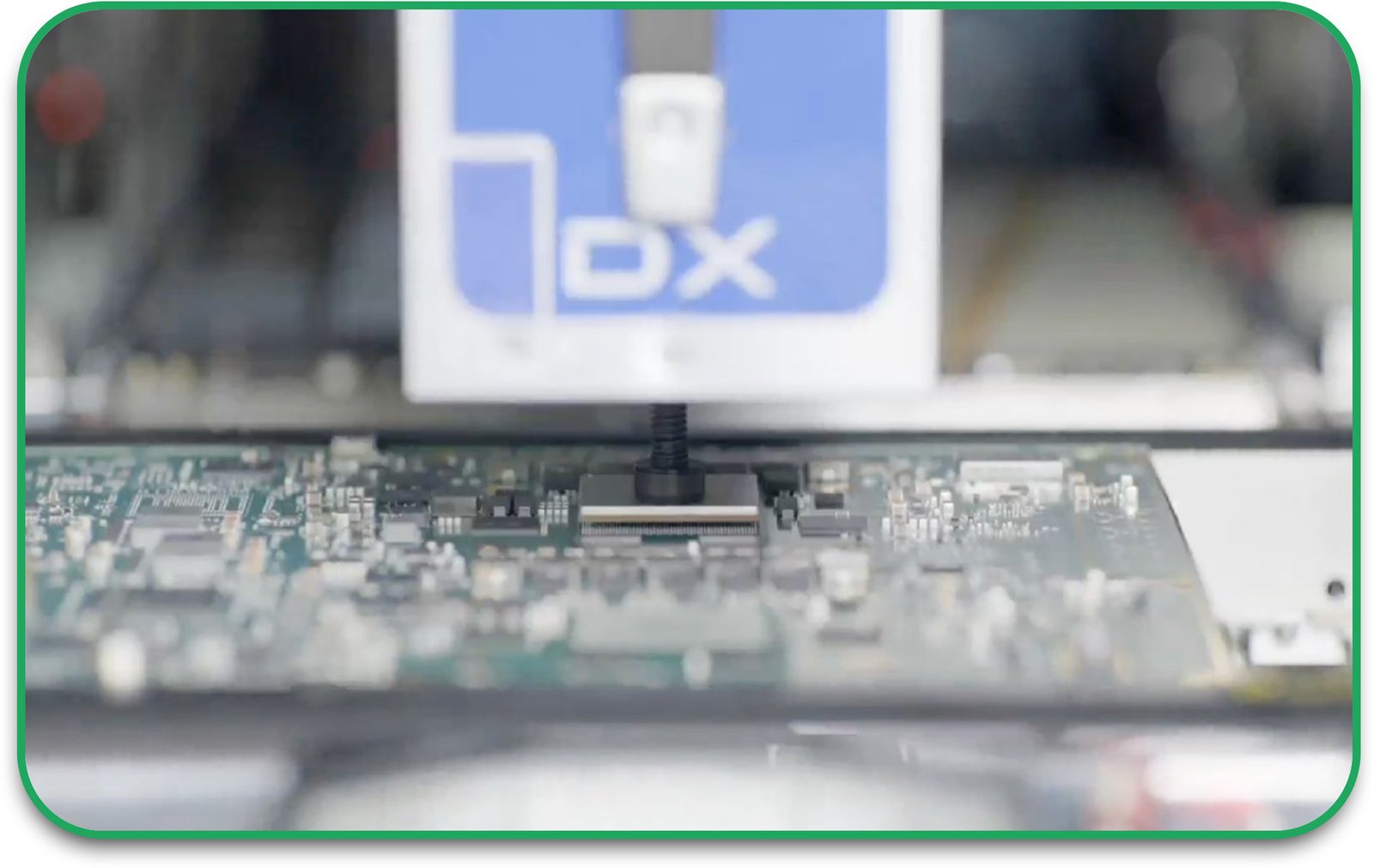
7. Testing and Quality Control
Each board undergoes electrical testing, automated optical inspection (AOI), and X-ray inspection to detect defects or inconsistencies before final assembly.
Key Design Considerations for Ultra-Multilayer PCBs
1. Signal Layer Arrangement
Placing high-speed signal layers between ground planes helps minimize EMI and signal loss, improving performance and reliability.
2. Thermal Via Placement
Using thermal vias helps in conducting heat away from power-intensive components, reducing the risk of overheating and component failure.
3. Via Structure Optimization
Different via types, including blind, buried, and stacked microvias, are used to optimize routing density and electrical performance.
4. Material Selection
Choosing low-loss materials, such as PTFE, FR-4, and high-Tg laminates, ensures greater durability and signal integrity in demanding applications.
5. Power Distribution and Grounding
Carefully designed power and ground planes improve voltage stability and reduce power noise, which is crucial for high-frequency circuits.
Applications of Ultra-Multilayer PCBs
1. Telecommunications and Networking
Ultra-multilayer PCBs are used in 5G infrastructure, fibre optic networks, and data centres, where high-speed signal transmission is essential.
2. Aerospace and Defense
Military-grade PCBs must endure extreme conditions, making custom-printed circuit boards with high-density interconnect (HDI) technology a critical choice.
3. Medical Devices
From MRI scanners to implantable medical devices, multilayer PCBs ensure high reliability and precision in healthcare applications.
4. Automotive and Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Modern vehicles require complex electronic control systems, including ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), which rely on robust multilayer PCB designs.
5. Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, tablets, and wearables demand ultra-thin multilayer PCBs to maximize performance while minimizing size and weight.
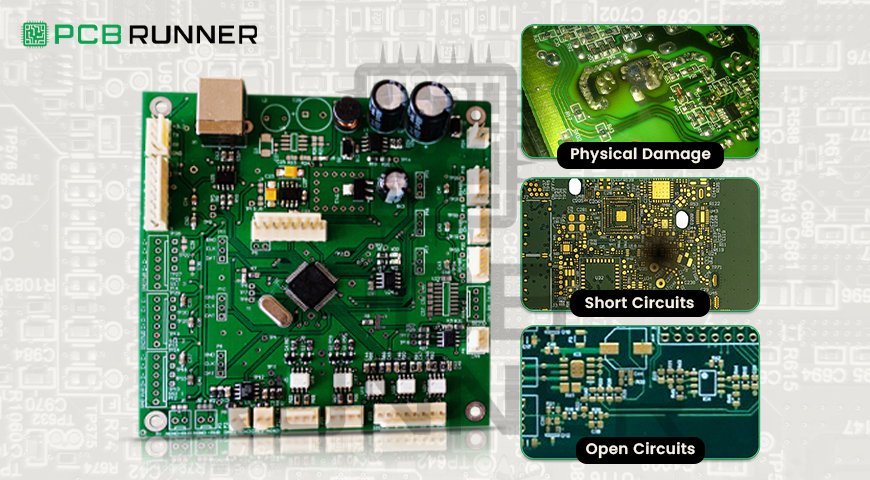
Challenges in Multilayer PCB Fabrication
1. Increased Manufacturing Complexity
Producing ultra-multilayer PCBs requires advanced fabrication equipment and skilled engineers, adding to manufacturing time and costs.
2. Material Cost and Availability
Specialized dielectric materials and high-performance laminates can be expensive, affecting overall production budgets.
3. Quality Control and Reliability Testing
Ensuring consistent quality across multiple layers requires rigorous inspection and testing to prevent electrical failures or design flaws.
4. Heat Dissipation and Power Management
High-density circuits generate excess heat, necessitating efficient thermal management strategies, including heat sinks, thermal vias, and copper pours.
Future Trends in Ultra-Multilayer PCBs
1. Increased Layer Count for AI and High-Performance Computing
As AI and machine learning applications expand, PCBs with 50+ layers will become standard in high-performance computing.
2. Integration of Flexible and Rigid-Flex Technologies
Combining multilayer PCBs with flex and rigid-flex designs will enable more versatile and durable circuit solutions.
3. Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Laser drilling, 3D printing, and automated assembly will further improve multilayer PCB fabrication processes.
4. Eco-Friendly and Lead-Free PCB Production
Sustainability is driving the industry towards greener manufacturing using RoHS-compliant materials and low-impact production methods.
Conclusion
Ultra-multilayer PCBs are shaping the future of electronics design, offering high-density integration, superior performance, and advanced durability. These custom-printed circuit boards are essential in telecommunications, aerospace, medical, and automotive applications, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable.With ongoing advancements in multilayer PCB manufacturing, companies can expect even greater efficiency, miniaturization, and functionality in next-generation electronics.
Looking for Expert Multilayer PCB Solutions?
At PCB Runners, we specialize in high-performance PCB fabrication and assembly, delivering custom solutions tailored to your needs. Contact us today for a free quote and experience cutting-edge PCB manufacturing!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an ultra-multilayer PCB?
An ultra-multilayer PCB is a circuit board with more than 10 layers designed for high-speed, high-density electronic applications.
2. How are multilayer PCBs different from single-layer PCBs?
Multilayer PCBs have multiple copper layers, offering better performance, increased routing capability, and enhanced thermal management compared to single-layer PCBs.
3. What industries use ultra-multilayer PCBs?
Industries such as telecommunications, aerospace, medical devices, automotive, and consumer electronics rely on multilayer PCBs for complex electronic systems.
4. What materials are used in multilayer PCB fabrication?
Common materials include FR-4, PTFE, polyimide, high-Tg laminates, and ceramic-based substrates.
5. How do I choose a reliable multilayer PCB manufacturer?
Look for certifications, manufacturing experience, quality control measures, and customer reviews when selecting a PCB manufacturer.