Change is the only constant in technology and electronics. There are many remarkable advancements in the design of printed circuit boards (PCBs); one of them is Surface Mount Technology (SMT). SMT changed the design and machines used to assemble and manufacture PCBs. Knowing how SMT operates and its effects on PCB design will help you understand the reason why it is known as the “game changer” of electronics.
Let us tell you more about what Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is, how it evolved PCB design and its advantages for PCB circuit board manufacturers and designers.
What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Before there was Surface Mount Technology (SMT), printed circuit boards (PCBs) used to be assembled using a method called through-hole technology. This method uses holes drilled into a board, where electronic components are placed and attached using solder on the opposing side. This technique works, but the large and heavy components required and assembling them was very tedious.
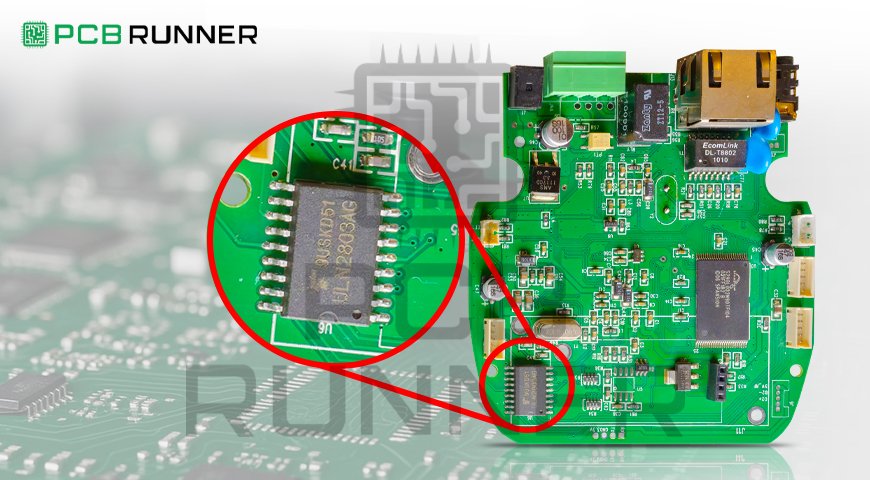
In contrast with SMT (Surface Mount Technology), through mounting techniques, the components are mounted onto the surface of the printed circuit board instead of routed through holes. The elements, referred to as Surface Mounted Devices (SMDs), are smaller in size and are meant to be placed on the top surface of the board. This enables the design of more compact and sophisticated assemblages, leading to adoption by almost all PCB board manufacturers.
How SMT Changed PCB Design
The impact of SMT on PCB design has been transformative, improving speed dramatically and efficiency and making space for more complex circuits. Below are just a few examples of how the landscape has changed:
1. More powerful miniature devices
SMT has a greater impact, which is the decrease in the size of components. Through-hole, components were big and bulky, which took a lot of space on the PCB, but with SMT, components are relatively more minor in size, which means more components can be fitted onto a single PCB. This not only led to the development of miniaturized and robust devices like smartphones, too, but also widened the scope of medical equipment.
For manufacturers of PCB circuits, this allows them to produce compact boards that are efficient and advanced in contemporary electronics technology. Also, they save space and material costs.
2. Faster and More Efficient Assembly Process
An improvement in one particular area of PCB assembly is SMT surface mounting technology, which is faster compared to previous techniques. Through-hole assembly, traditionally, every piece was painstakingly inserted into a hole and then soldered individually, which was a tedious and painstaking process.
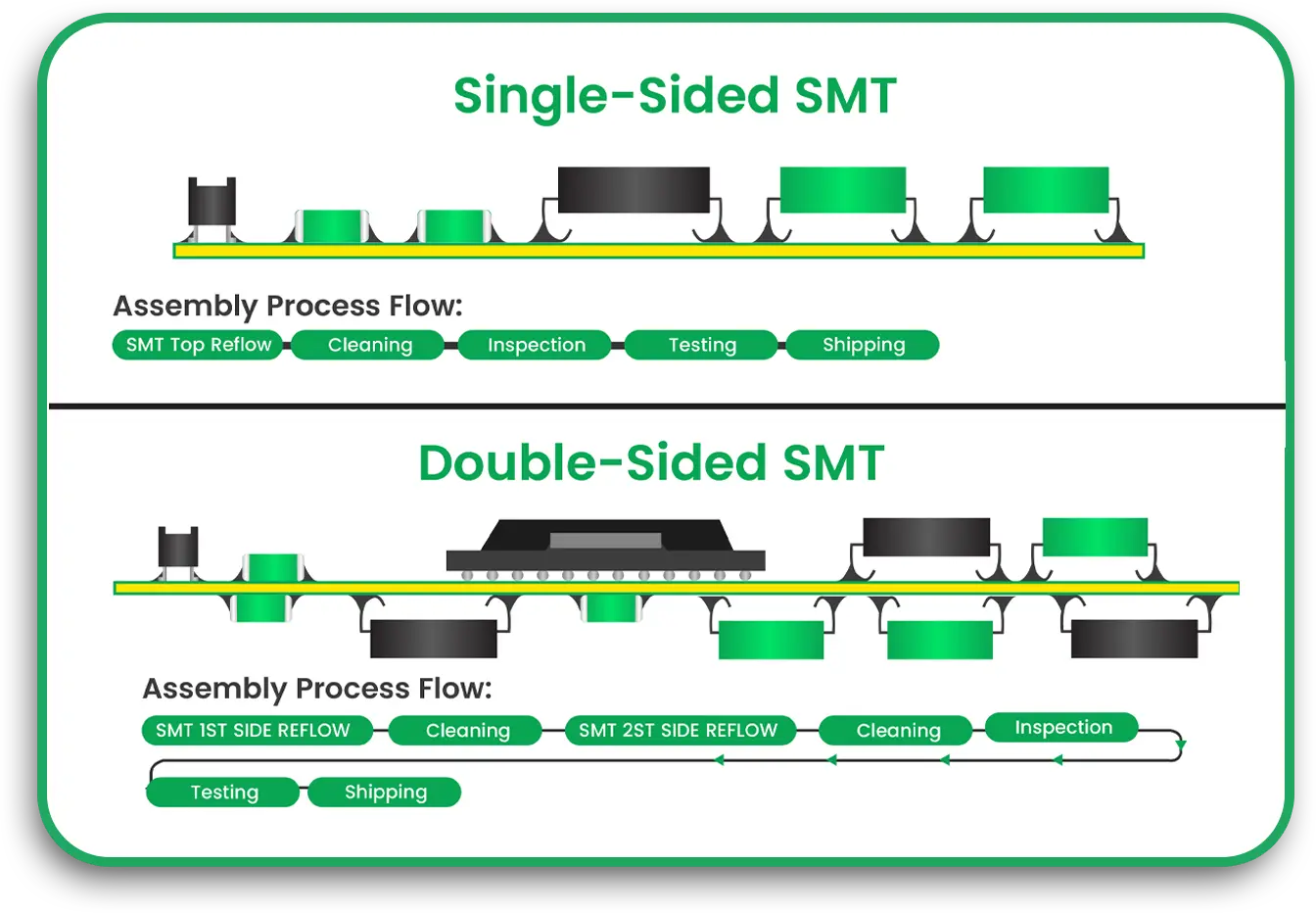
SMT, on the other hand, utilizes automated machines that place the components on the surface of the PCB and not on the holes. Components are held in place by soldering them in a process called reflow soldering wherein the board is heated in a furnace, thus softening the solder paste and adhering the pieces in place. This approach diminishes the amount of manual work required, expedites the fabrication, and enhances the reliability of the results.
Because of the automation potential for PCB customization, custom printed circuit board suppliers experience increased productivity alongside reduced costs.
3. Better Performance and Reliability
The small size of SMDs and their precise placement on the board automatically enhances the degree of reliability and performance. SMT components are more robust because they have fewer mechanical parts (like leads) that can be subject to wear and tear. Furthermore, the solder joints created by SMT surface mounting technology are more reliable because they tend to have better electrical connections, which strengthens the bond.
Surface mount devices contribute to an overall decrease in the size and weight of the PCB, thus relieving the stress placed on the board and increasing its mechanical durability. This reduces the likelihood of suffering from failure due to extreme stress.
4. Increased Component Density
The use of SMT enables PCB designers to integrate more components onto the board as sufficed with higher component density. In through-hole designs, components were spaced further apart owing to their larger size. However, with SMT, components can be placed closer to one another, translating to more functionality available in a given space.
This is extremely useful in the telecommunications industry, where high-density boards are needed. PCB circuit board manufacturers are able to design PCBs using SMT, incorporating more components while keeping the size manageable in view of the powerful and compact devices designed.
5. Cost Efficiency
Smaller size and faster assembly add cost savings due to the use of SMT surface mounting technology. PCB board manufacturers can accomplish more in less time, resulting in decreased labour and material expenses. In addition, smaller components are usually less expensive than their through-hole counterparts, lowering costs even more.
Moreover, the use of automated pick-and-place machines means the manufacturer can reduce the use of human hand work in the production process, enhancing resource efficiency and lowering costs. This results in decreased overhead for the production of each board.
6. Design Flexibility and Innovation
The invention of SMT has permitted greater flexibility in design. Engineers can custom print circuit boards without as many restrictions as before. The availability of smaller and densely packed components allows for innovative printed circuit board designs which are not feasible with through-hole technology.
This flexibility enables the production of a broader range of products, from consumer electronics to automotive systems. For PCB board manufacturers, this flexibility means greater challenging designs that can be tailored to client needs.
7. Enhanced Testing and Inspection Capabilities
The Innovations made in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has also improved the methods used in Testing and inspection of PCBs. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems can effectively and rapidly find errors in surface mount devices. This guarantees that only good and defectless boards come to the higher stage of production.
Moreover, the Standardized geometry and small size of SMDs also facilitate inspection during the production process. This improves yield and decreases the number of defective boards, which benefits PC board manufacturers in the form of savings and increased customer satisfaction.
Key Components of SMT
To analyze the implications of SMT, it is essential to learn the fundamental constituents of SMT surface mounting technology first:
Surface Mount Devices (SMDs): These are the Electronic components that are mounted on the surface of the PCB. Resistors, capacitors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs) are some common examples of SMDs.
Reflow Soldering: This refers to the process of melting solder and affixing the SMDs onto the board by heating the PCB.
Pick and place machines: These are mechanical devices that position the SMDs on the board in advance of the reflow soldering phase.
Conclusion
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a game-changer because it enhances the efficiency of PCB design, reduces costs, improves manufacturing precision, and enables the development of smaller and more powerful devices. Physically Smaller parts, quicker assembly, and better component placement enables the electronics design innovation due to SMT.
For manufacturers of PCB circuit boards, the adoption of SMT surface mounting technology results in more advanced, cost-effective, high-performance PCBs. SMT is now central in fulfilling the requirements of modern technology design for consumer electronics and industrial devices due to the compact, reliable, and efficient design it enables.
SMT will continue to serve as the backbone for advancements in custom printed circuit boards across myriad applications in future and will help professional designers address the challenges of tomorrow.