The defence industry is changing fast. Across the UK and Europe, new threats and challenges mean that military systems must be smarter, faster, and more reliable. At the heart of this transformation is the powerful combination of IoT and advanced PCB technologies. If you’re involved in defence, you know that every detail matters, from the design of a single sensor to the reliability of a whole network. Let’s explore how printed circuit board manufacturers, IoT PCB design, and custom PCB assembly are driving the next generation of defence solutions.
Why IoT Matters in Defence
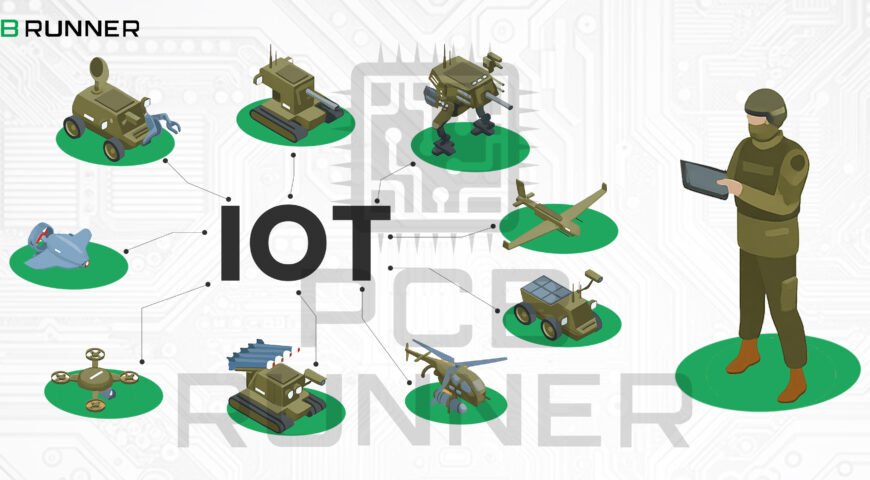
IoT, or the Internet of Things, means connecting devices so they can share data and work together. In defence, this is more than just a buzzword. IoT is already helping military teams track assets, monitor soldiers’ health, and manage complex operations in real time. Imagine a smart base where every piece of equipment, from vehicles to water pumps, reports its status automatically. Or a battlefield where sensors detect threats and share information instantly. This is possible because of reliable IoT PCB technology.
The Backbone: PCBs in Defence Applications
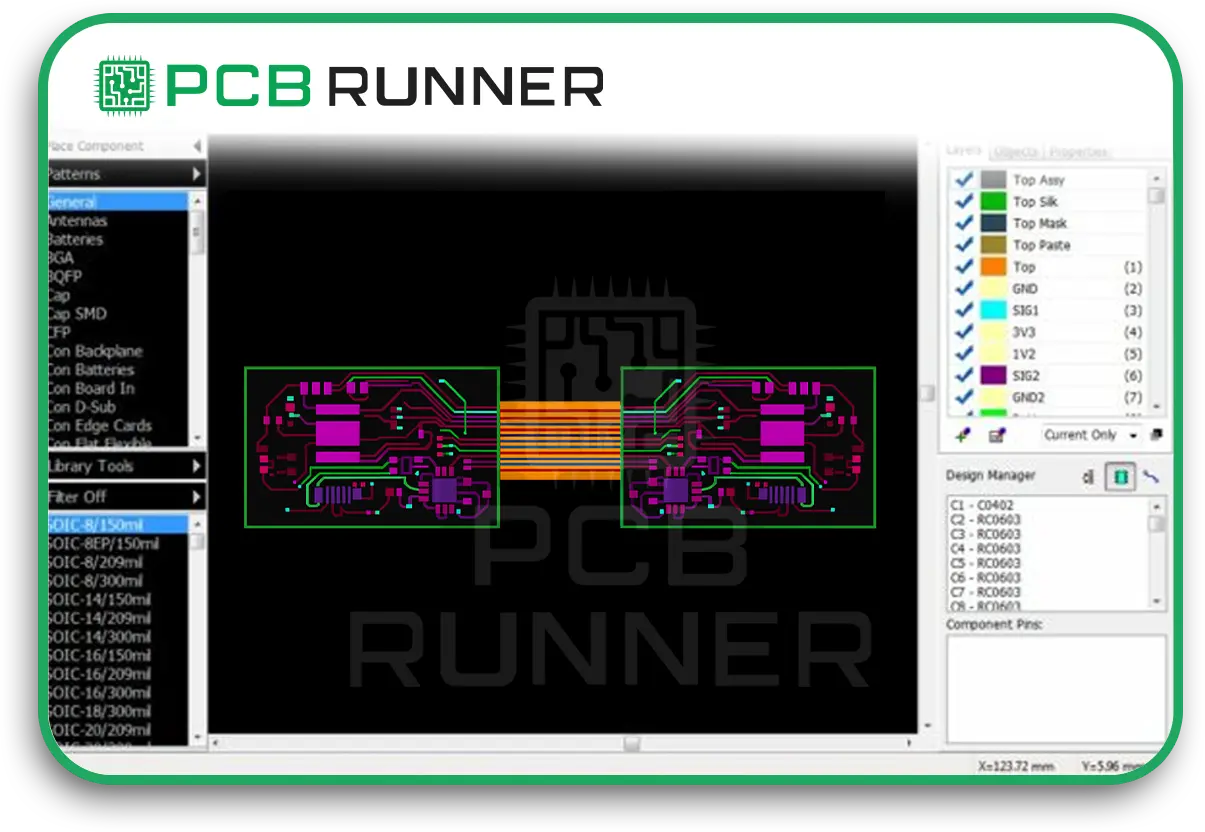
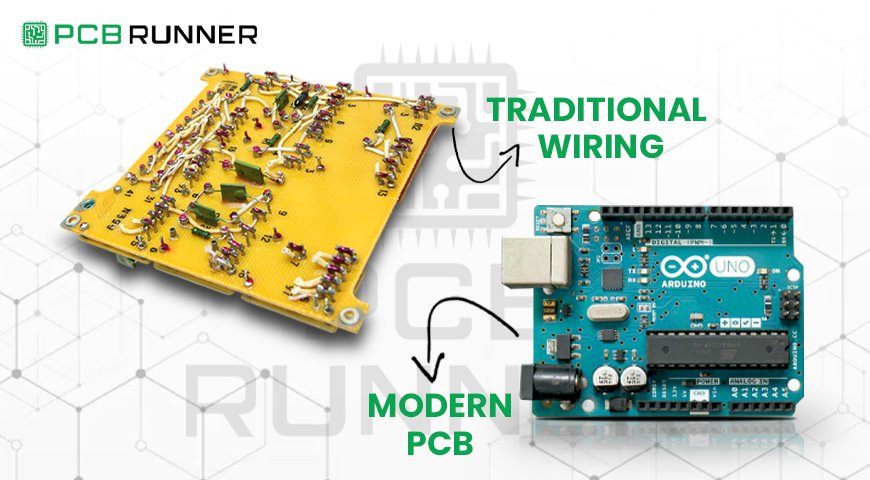
Printed circuit boards are the foundation of all modern electronics. In defence, they’re everywhere, from radios and radar systems to drones and missile guidance. Defence PCBs must be rigid, precise, and secure. They have to work in extreme temperatures, resist shock and vibration, and keep data safe. That’s why PCB manufacturing to defence standards is so important.
Key Roles of PCBs in Defence:
- Signal processing and secure data handling
- Power management for mission-critical systems
- Integrating sensors and communication modules
- Enabling advanced guidance, navigation, and targeting
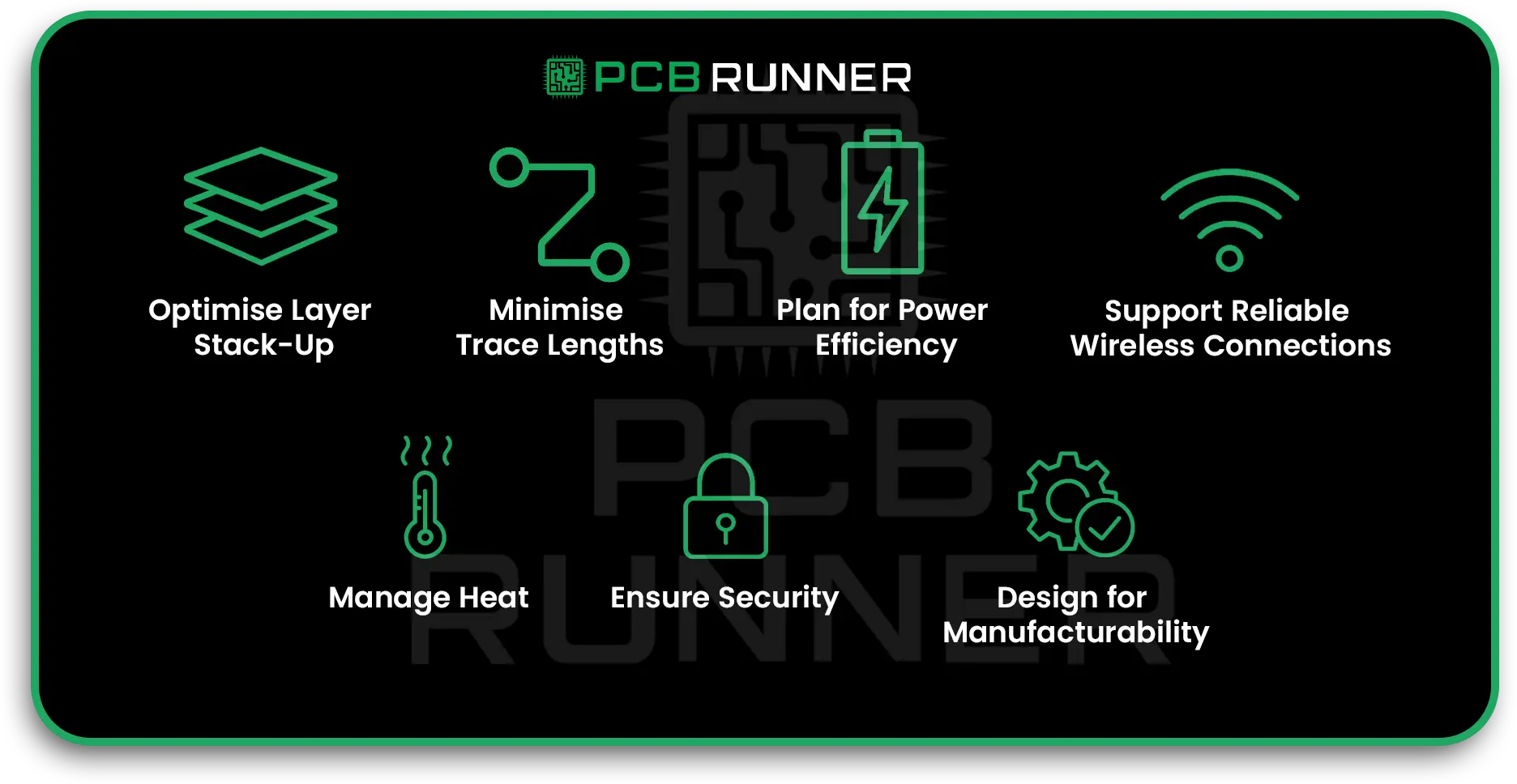
IoT PCB Design: Meeting Unique Defence Demands
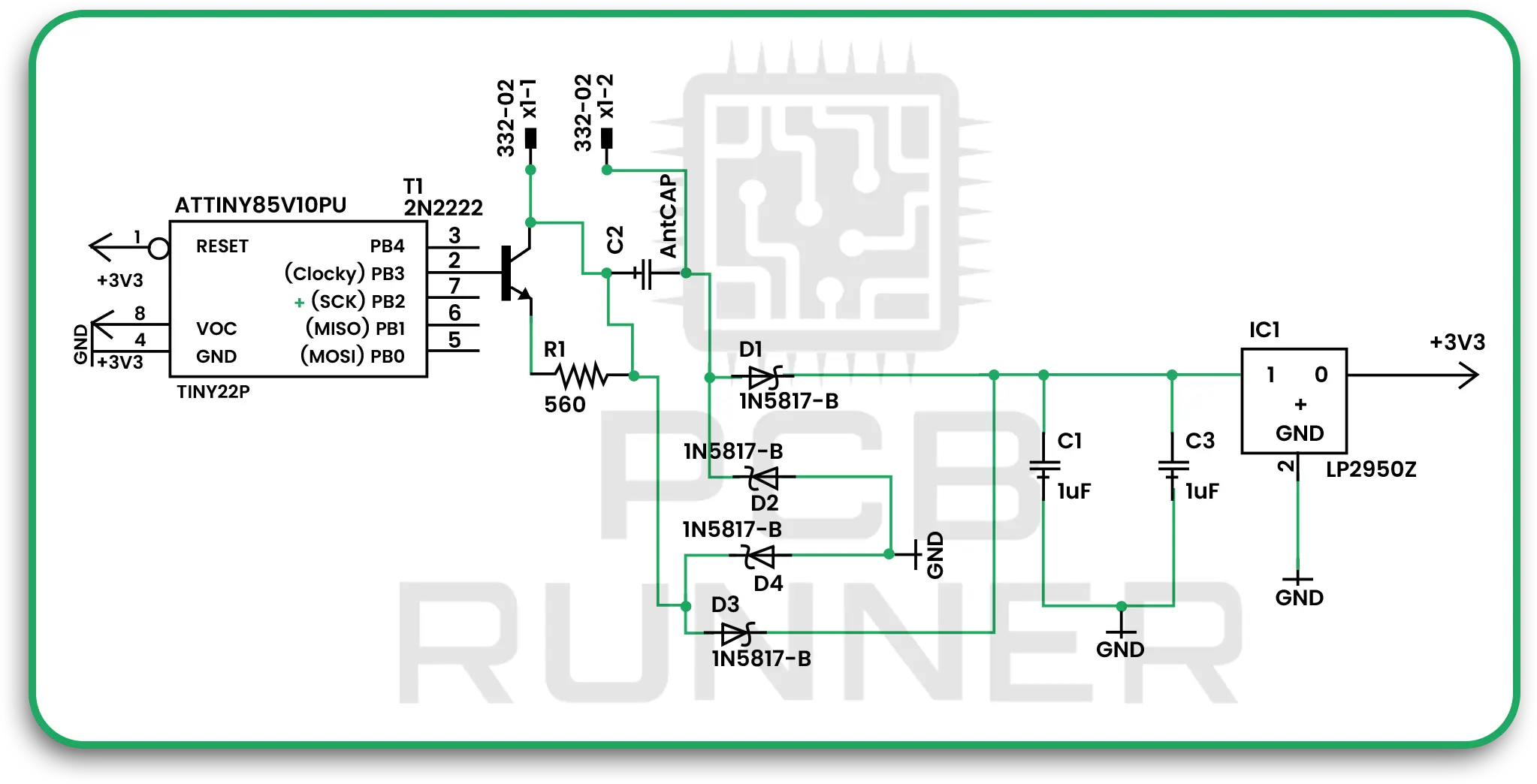
IoT devices in defence need special PCBs. These boards must be small, lightweight, and energy-efficient, ut also strong enough for harsh environments. IoT PCB design is all about balance, packing in more features without sacrificing reliability.
What Makes IoT PCBs Different?
- Miniaturisation: Defence systems need compact sensors and controllers. High-density PCB designs allow more connections in less space.
- Power efficiency: IoT devices often run on batteries. Low-power PCB layouts help them last longer in the field.
- Durability: IoT PCBs are coated and protected to survive dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
- Security: Defence IoT PCBs must protect against hacking and data leaks, sometimes with hardware-based encryption.
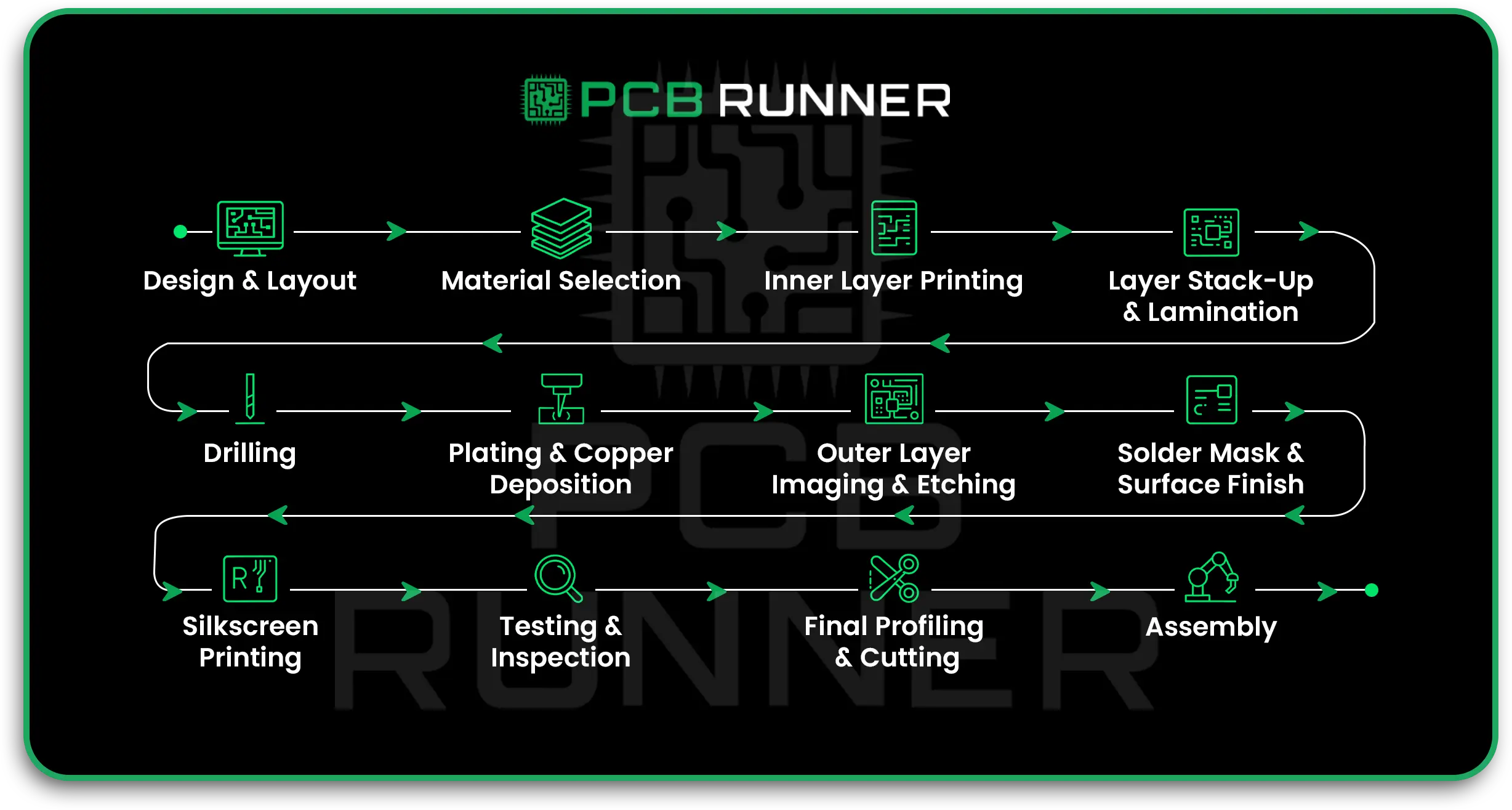
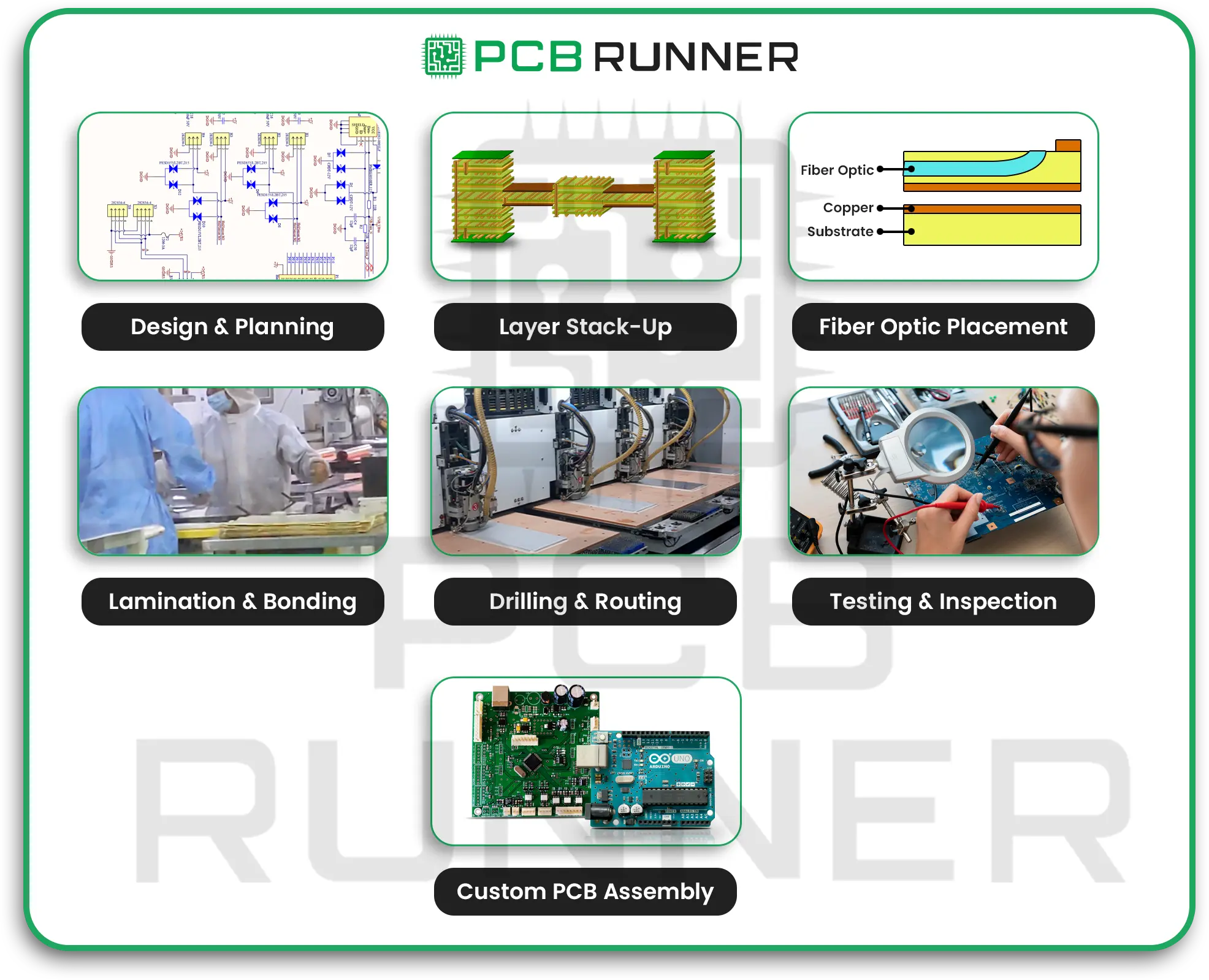
From Prototype to Production: The PCB Fabrication Journey
Every great defence device starts with a prototype. PCB prototype services let engineers test new ideas quickly. Once the design is proven, it moves to complete PCB fabrication in the UK or Europe. Here’s how it works:
- Design: Engineers create detailed IoT PCB designs, often using advanced simulation tools.
- Prototyping: Printed circuit board manufacturers build small batches for testing.
- Testing: Boards are checked for reliability, durability, and compliance with defence standards.
- Custom PCB Assembly: Once approved, the boards are assembled with components and prepared for deployment.
Choosing a partner with experience in PCB manufacture to defend standards is vital. They’ll understand the strict rules and quality checks needed for military use.
Custom PCB Assembly for Defence: Why It Matters
Defence projects rarely use off-the-shelf boards. Each mission has unique needs, from stealth drones to rugged vehicle controls. Custom PCB assembly lets you:
- Select materials that resist heat, shock, and moisture
- Add special coatings for electromagnetic shielding
- Integrate IoT modules for real-time data sharing
- Meet exact defence standards for safety and security
Real-World Applications: IoT and PCB Advancements in Action
Let’s look at how these technologies are making a difference:
Smart Bases
Military bases use networks of IoT sensors to monitor water, power, and security. Each sensor needs a reliable IoT PCB to collect and send data. If a water pump fails or a gate is left open, the system alerts staff immediately.
Asset and Shipment Tracking
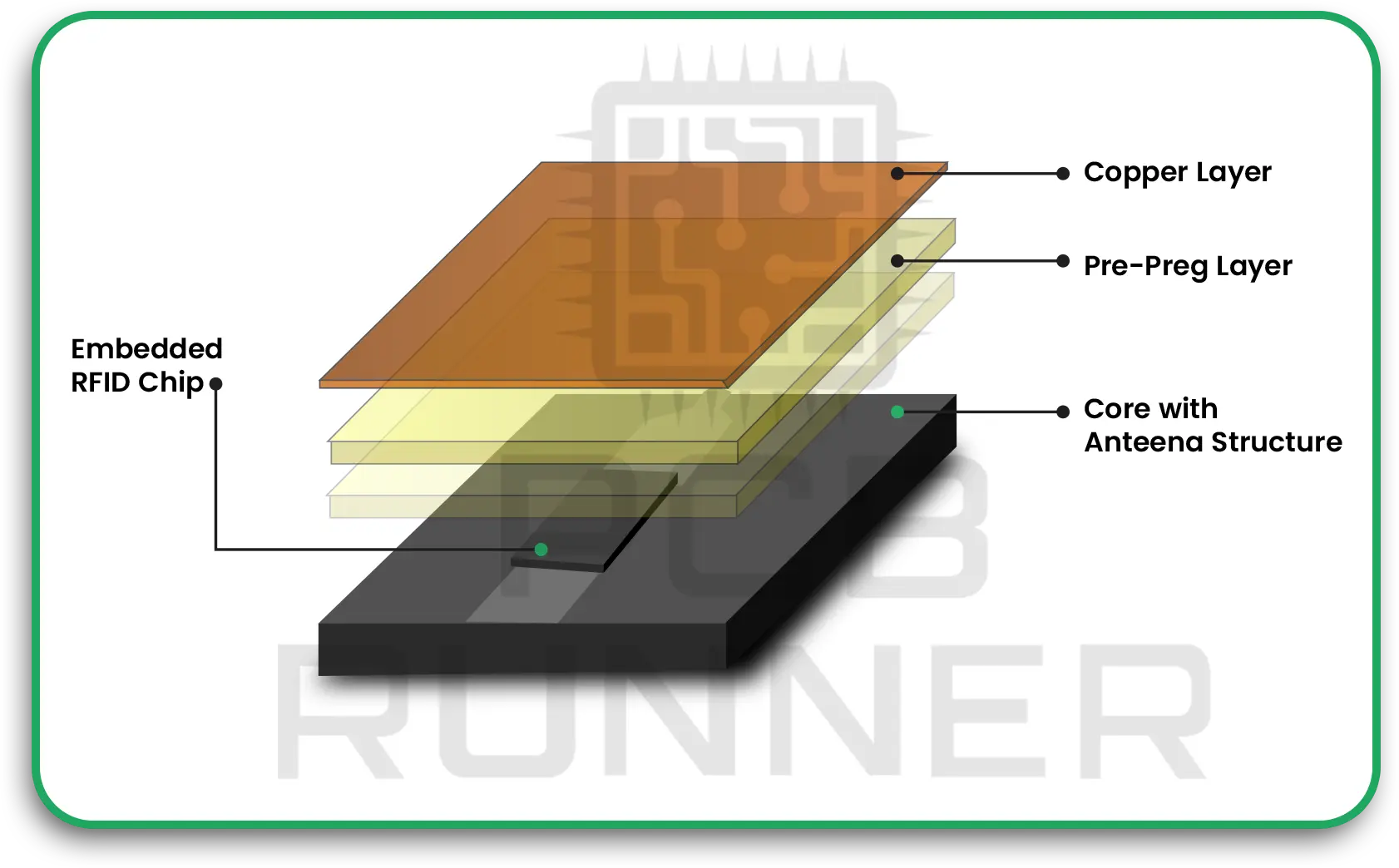
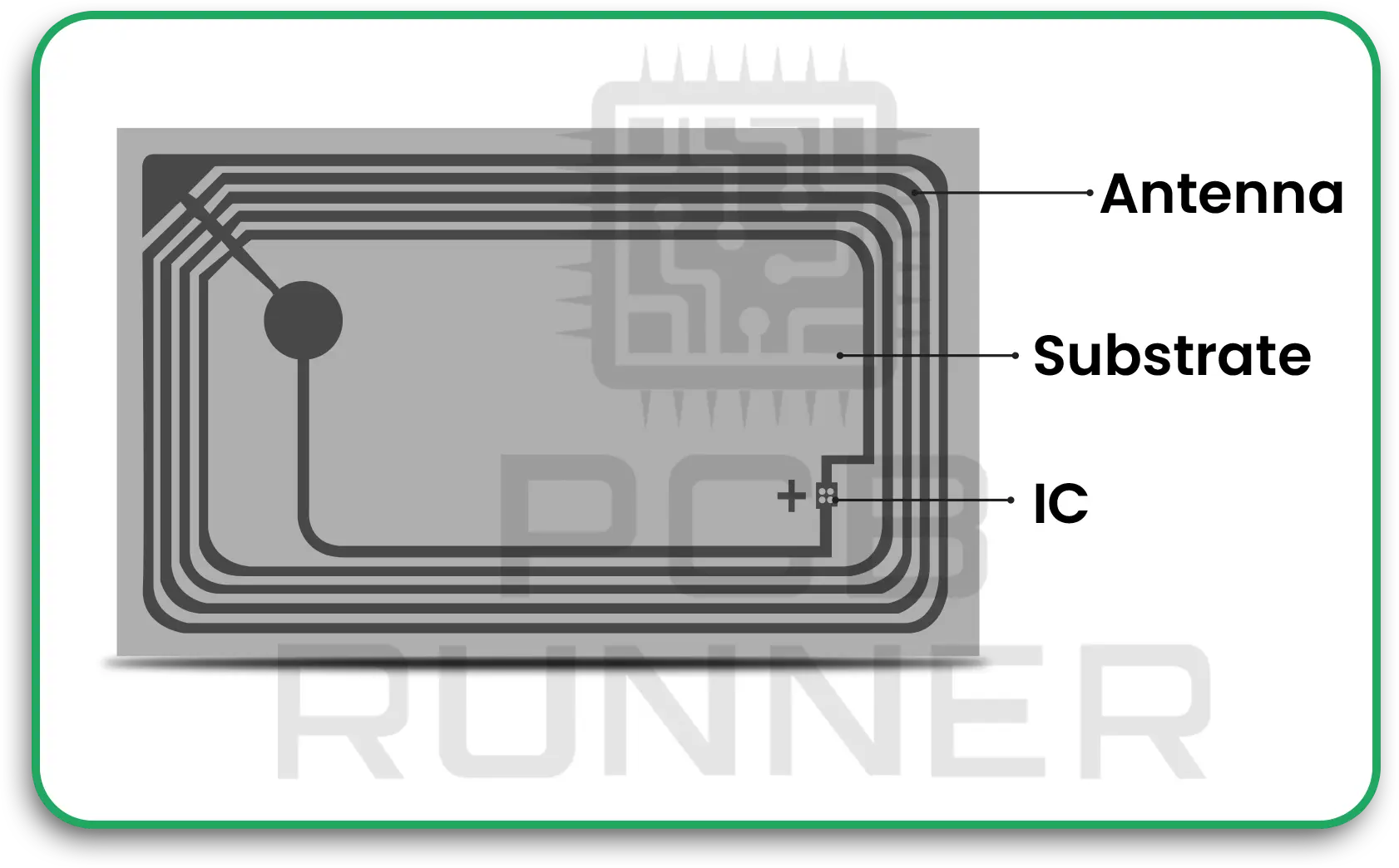
IoT PCBs in RFID tags and trackers help defence teams know exactly where weapons, vehicles, and supplies are at all times. This prevents loss and speeds up logistics.
Wearable Soldier Tech
Modern helmets and vests have built-in sensors to monitor health, location, and even stress levels. These wearables use miniaturised, ruggedised PCBs that can handle harsh conditions.
Advanced Weapon Systems
Guidance and targeting systems in missiles and drones depend on secure, high-performance PCBs. These boards process data from sensors, manage power, and keep communications safe from interference.
Meeting Defence Standards: What to Look For
Not all PCB fabrication is equal. Defence projects require boards that meet strict standards for quality, reliability, and security. When choosing a printed circuit board manufacturer for defence, check for:
- Experience with military projects
- Compliance with standards like MIL-STD-810
- Ability to deliver rapid PCB prototypes and scale up to mass production
- Custom PCB assembly with advanced testing and quality checks
Future Trends: Where IoT and PCB Technology Are Heading
The defence sector is constantly pushing the boundaries. Here’s what’s next:
- AI Integration: Future IoT PCBs will include chips for artificial intelligence, enabling real-time analysis and smarter decision-making.
- Flexible and Stretchable Boards: Wearable tech and conformal sensors will use flexible PCBs that bend and stretch with the user.
- Radiation-Hardened Boards: For space and nuclear applications, special PCBs will resist radiation and extreme environments.
- Sustainability: Defence agencies are looking for recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing to reduce their environmental impact5.
Actionable Insights for Defence Teams
If you’re planning a new defence project, here’s how to get the most from IoT and PCB advancements:
- Start with a clear goal: Know what you want your system to do, track assets, monitor health, or secure communications.
- Work with experts: Choose printed circuit board manufacturers with a track record in defence and IoT PCB design.
- Prototype early: Use PCB prototype services to test ideas quickly before moving to full production.
- Insist on quality: Demand boards that meet defence standards for reliability and security.
- Plan for the future: Design your systems so they can be upgraded as new IoT and PCB technologies emerge.
Final Thoughts
The strategic integration of IoT and PCB advancements is reshaping the defence industry across the UK and Europe. Reliable, secure, and innovative PCB technologies are the backbone of everything from smart bases to advanced weapon systems. By working with experienced partners in PCB Fabrication UK, focusing on IoT PCB design, and insisting on custom PCB assembly to defence standards, you can build systems that are ready for the challenges of tomorrow.
Whether you’re developing the next generation of wearable soldier tech or upgrading your base’s security network, remember: the right PCB makes all the difference. Choose wisely, and you’ll be ready for whatever comes next.