Have you ever wondered how PCBs (printed circuit boards) remain functional and are able to last long? The tiny copper traces on PCBs are well protected and do not corrode due to oxidation because of surface protection techniques. In this article, we will undertake a friendly, detailed exploration of PCB finishes, including what they are, their importance, and which might be most suitable for your project or learning.
Why do PCBs require Surface Protection?
Think about baking cookies and leaving them exposed to the open air. In no time, they become hard and stale. PCBs also contain copper and thus undergo a baking-like process. During the CNC milling process, oxidised copper will be challenging to use, similar to brown and oxidised apples stuck turning brown, which creates problems during the PCB printed circuit board assembly, as well as the final steps of assembly.
In order to make PCBs dependable and straightforward to assemble, manufacturers apply surface finishes or specialised coatings to PCBs, which reduce the chances of air, precipitation and other dangerous things, can severely damage their performance. Manufacturers try to use surface finishes that will add to the dependability of the PCBs.
How Does The Surface Finish Of A PCB Work?
Think about if your school locker had a shiny sticker on it that prevents it from rusting. Surface finishes on PCBs help to prevent copper from oxidising, aid in the soldering of parts onto the board, and help in the overall working of the board.
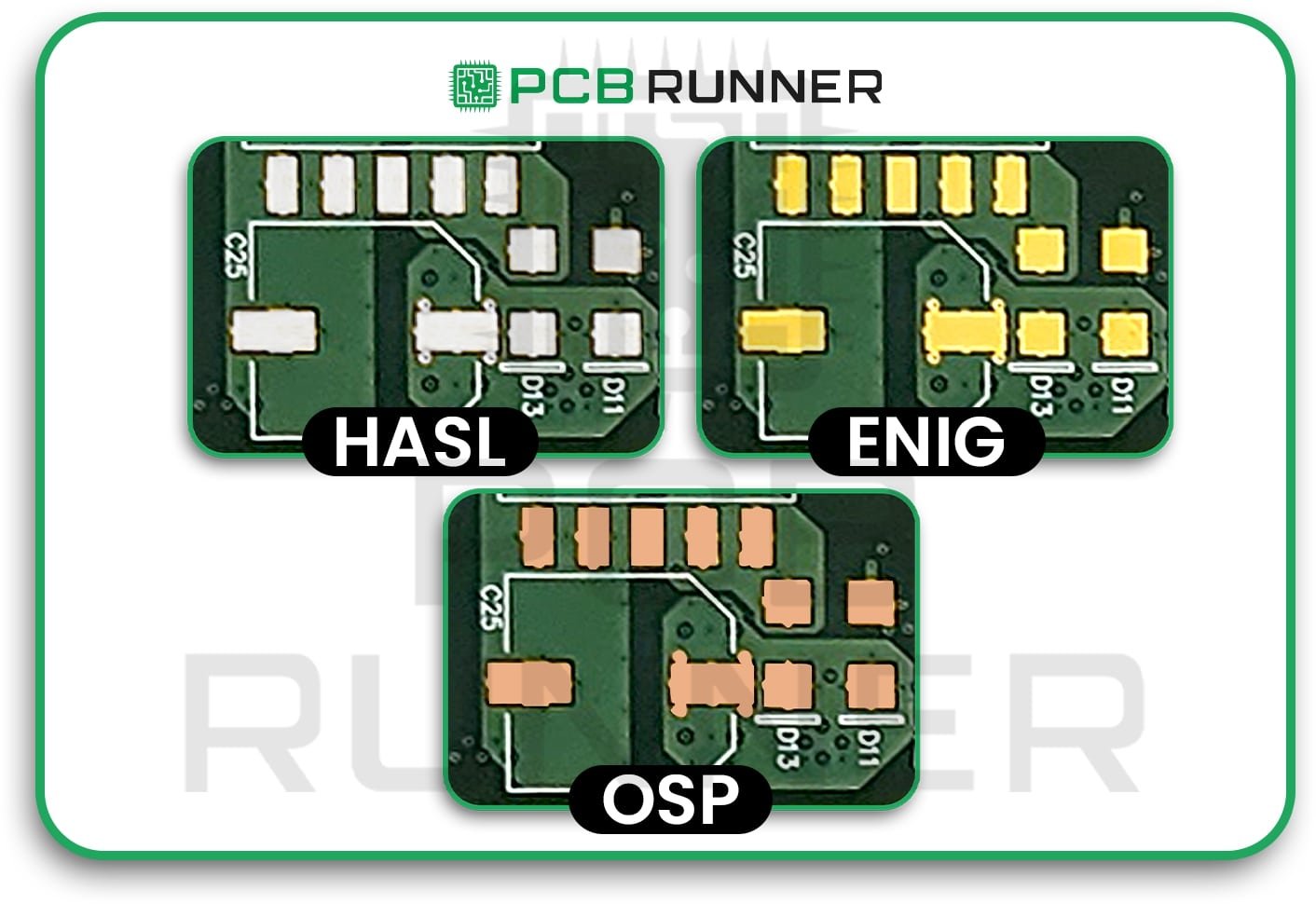
Three of the most common finishes you’ll hear about are ENIG, HASL, and OSP.
Exploring The Main Types Of Surface Finishes Used On PCBs
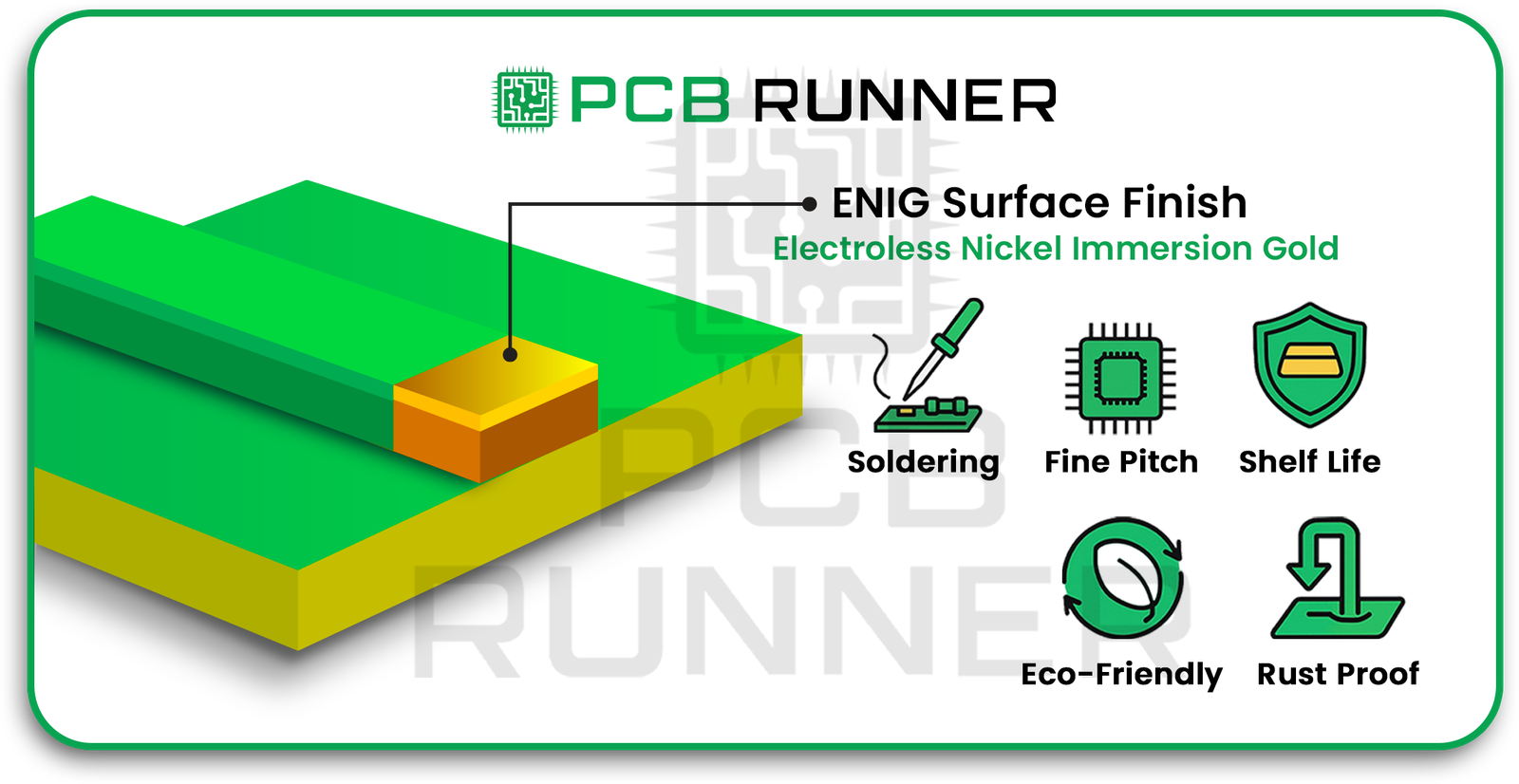
1. ENIG: Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold Surface Finish PCB
The surface finish ENIG is a flat surface finish of nickel and gold that is shiny and helps to waterproof a PCB. The surface is flat and shiny while also being very reliable.
Benefits:
- Parts soldered to the PCB will remain attached through the entire building process.
- Best for small spaces and parts, like in a smartphone and medical tools and equipment.
- The gold surface delays any rust for months, and in some cases, even up to a year.
- Good for the environment and products with strict safety standards.
- Flexible and helps in rust resistance.
Drawbacks:
- Cost: The finishing touch on a product with gold is prohibitive.
- Not always needed: The gold finishing touch provides needless protection on simple boards.
When to choose it?
ENIG is a good choice when you want to augment the durability and longevity of the circuit board, also if you want to solder small parts while being concerned with the safety of the circuit board and the electronics.
2. HASL: Hot Air Solder Levelling PCB Surface Finish
HASL is an older but still proper technique. It is akin to a PCB being dunked into a bath of solder. The PCB is then soldered with hot air to smooth the finish. The finishing touch can be leaded or non-leaded.
Benefits:
- Cost-effective: This is better for a project that needs to make and sell many boards.
- Electronic components’ protection: The copper parts of the circuit board are covered in solder, preventing rust.
- Error identification: The shiny sensor assists in looking for cracks and the mistakes that come along with it.
- Embraced for a long time: This has been used widely in areas such as automotive, industrial and many more industries.
Drawbacks:
- Not super smooth: The board’s surfaces, which have copper parts, can be covered in solder, preventing rust. Also, the copper components having a rough surface to them are not advantageous.
- Non-leaded option isn’t eco-friendly: This has left a mark on the current eco-friendly approach that many companies aim towards.
When is HASL most suitable?
For simple projects, bigger pieces, or when the budget is tight, HASL works best. PCB circuit board manufacturers typically prefer it due to its ease of application and consistency.
3. OSP: Organic Solderability Preservative PCB Surface Finish
OSP surface finish PCB applies a nearly invisible organic coating. It’s like applying an evident seal to your school books, protecting them from damage.
Advantages:
- Streamlined: Cheaper than using metallic finishes.
- Eco: Does not contain harsh chemicals or metals.
- Best for flat designs: The surface is even and smooth.
- Repairable: Parts can be unsoldered and re-soldered without much hassle.
Disadvantages:
- Limited lifespan: Protects the copper for only 6–12 months.
- Risk of damage: Can be easily scratched with improper handling.
- Hard to check off: Because it’s clear, flaws become difficult to check.
Best for:
The best fit for projects needing faster assembly or low-cost outsourcing with a strong focus on saving money and eco-impact.
How Surface Finishes of a PCB Change Real-Life Projects
Imagine a student crafting a model volcano for a science fair. If he doesn’t waterproof the model, it will get easily destroyed. Surface finish protects printed circuit boards the same way finishing a model volcano protects it. It helps to prevent damage, wear, and finish wear and ensures the circuit board survives thorough testing as well as use.
Whether it is computing, robotics, medical instruments, or toy designing, the relevant pcb surface finish will enable the device to perform optimally. This is precisely why engineers and PCB manufacturers put extra thought into every decision:
- Durability: Will the board need to endure harsh conditions for years?
- Solderability: Are you using parts that are smaller for the smart gadgets?
- Cost/ Eco-friendliness: Is the project a school project, or is it a heavy-duty industrial device?
- Ease of assembly: Will they need to fix or solder the board again?
Tips to help you choose the Right Surface Finish
- Check the complexity of the board: Small parts and intricate circuits call for the use of ENIG. Bigger and simpler components can use HASL or OSP.
- Keep the expense in mind: HASL is the next cheaper after OSP, and then ENIG.
- Think about the shelf life of your project: ENIG survives for the longest, and then HASL can survive for a few months. OSP survives the shortest.
- Think of these ENIG and OSP are eco-friendly, and they are prioritising the project directly helps the environment.
- Inspectability: Inspection of HASL is straightforward and visually accessible, while OSP is challenging to see.
FAQs
If no finish is applied to a PCB, what is the most likely outcome, and what is the gloss and matte finish for the identical PCB?
The risk is the same as an insufficient protective coating. Heating and ignoring protective etiquette risks failure. Assembly failure is like the breakdown of a bicycle left outside to rust.
Which of the described finishes has the most extended operational life, and what is the
difference between matte and gloss finishes?
Gloss finishes are generally valued for being visually appealing compared to matte. They are more prone to scratching, so their operational life will depend on the surface treatment of the substrate.
What do I do if a joint has to be reworked?
Finishes on OSP boards are the most permissive, and so they can be worked on repeatedly, allowing easy removal of the finish and addition of solder.
Easy Ways to Remember the Differences
- ENIG: “Gold standard”—best for tiny, long-lasting boards.
- HASL: “Budget pick”—classic, shiny, great for bigger, less-packed boards.
- OSP: “Green choice”—cheap, environmentally kind, but not for use after a long shelf life.
Wrapping It Up
In creating or configuring any device, safeguarding the PCB is as critical as deciding on its contours or the components it should house. Industry Standard Surface finishes ENIG, HASL, and OSP serve as the outer guard for the circuitry, making sure it is well protected, rugged, and ready for integration, regardless of what you intend to construct.
Depending on your expectations, expenditures, and timeline, the finish selection varies. ENIG caters best to high-density and high-end boards, HASL is beneficial to generic works, and OSP is the cheapest of the three and environment friendly.
The good thing is that knowing these protective methods enables you to engage meaningfully with PCB circuit board vendors or design and execute projects as a seasoned professional.
Keep in mind, every PCB, regardless of the complexity, merits the right protective finish for its intended voyage. PCB Runner stands by this philosophy, ensuring each board, regardless of its dimensions, contributes to a bright, dependable, and safe future for electronics.