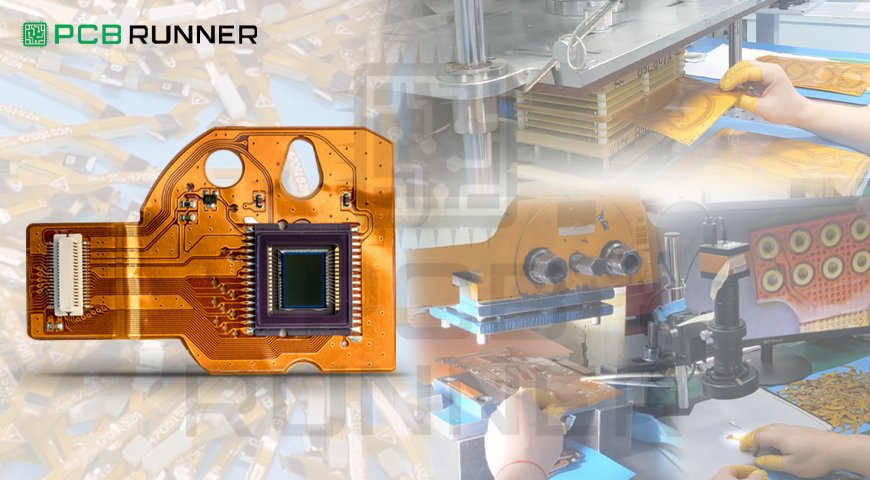
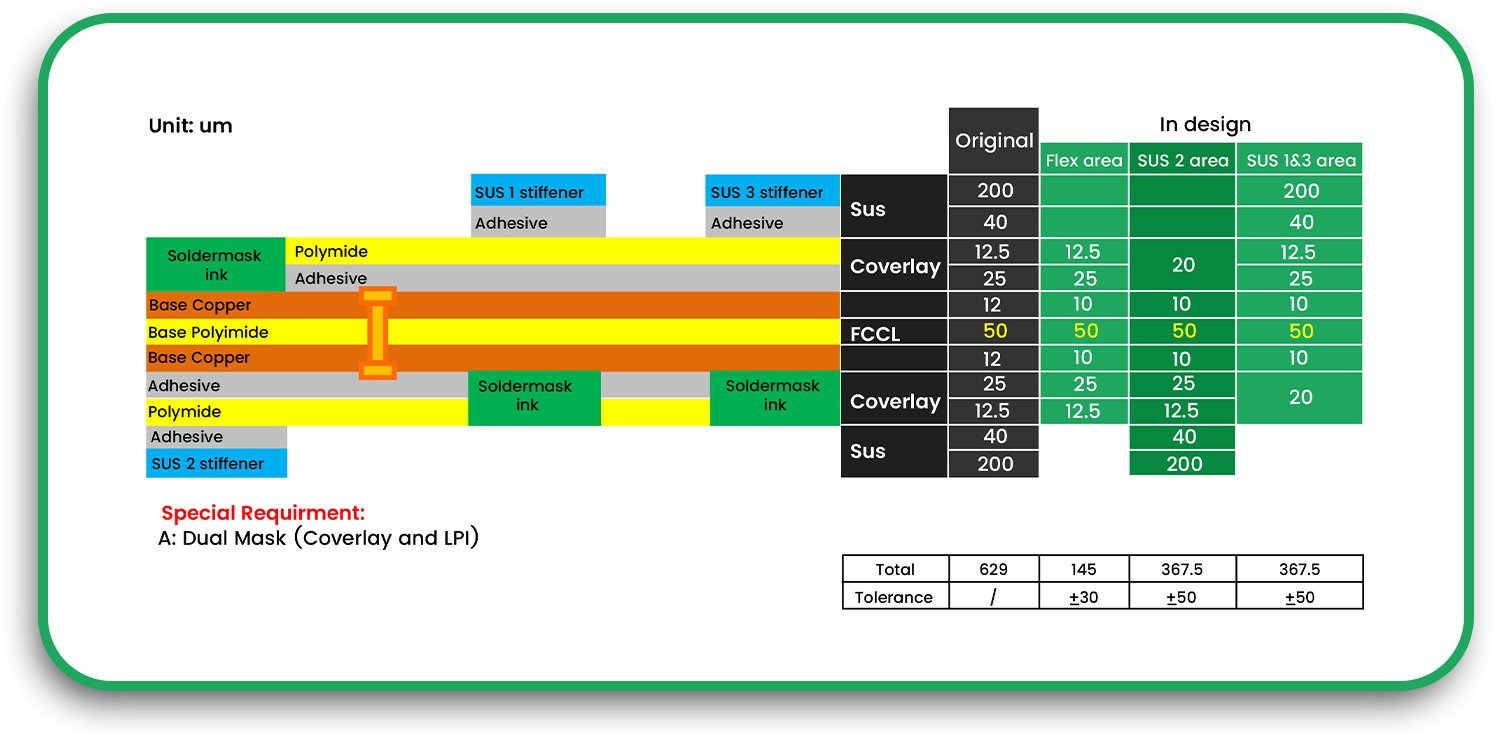
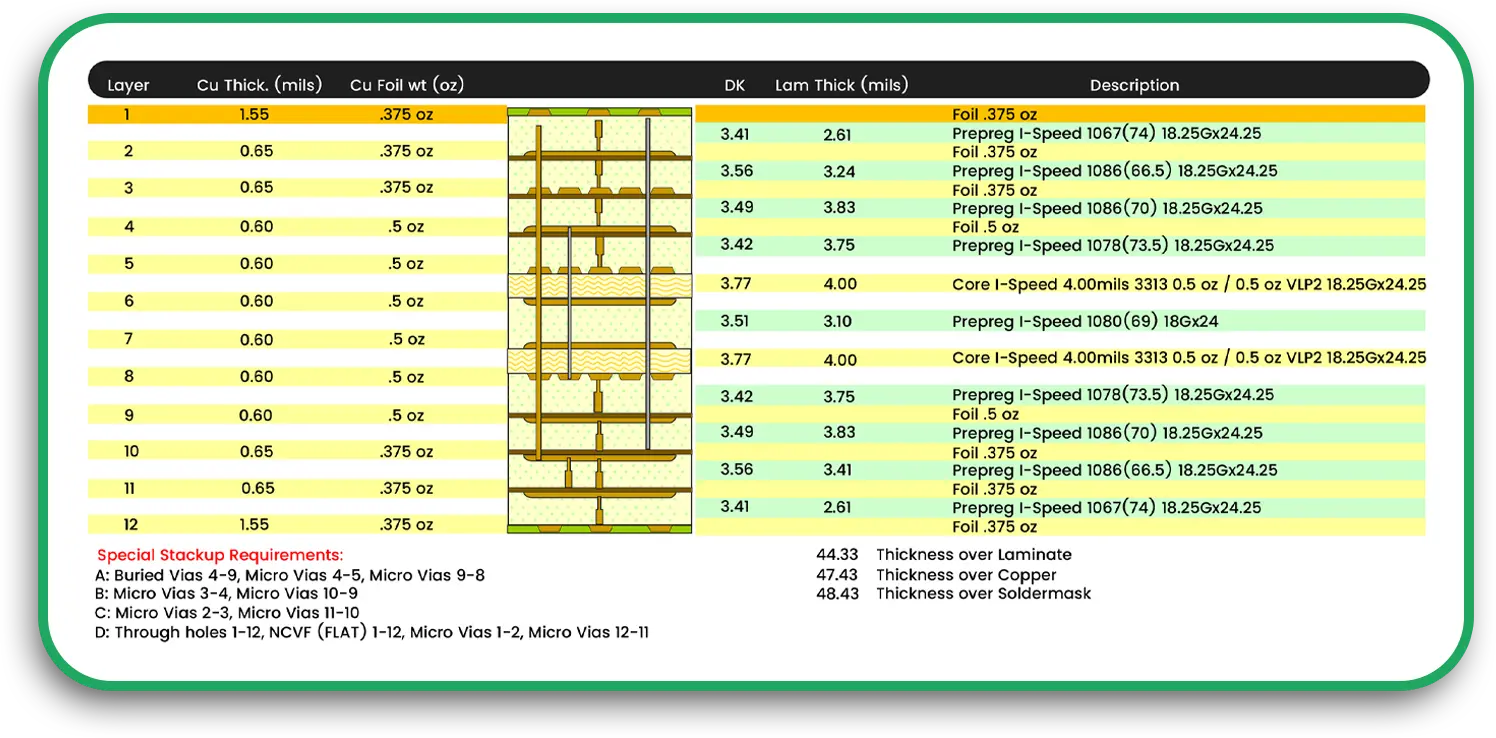
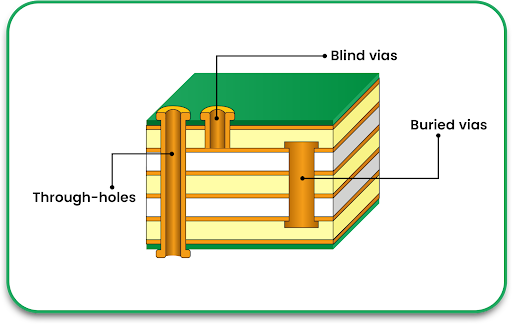
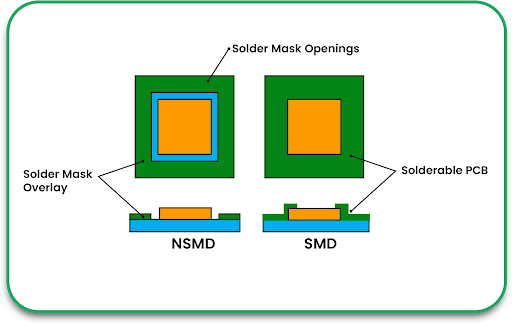
Electronics are getting smaller, lighter, and more complex. With this evolution, traditional rigid circuit boards are sometimes not the best solution. Flexible circuits offer a more durable, space-saving alternative that can withstand bending, twisting, and harsh environments.
For engineers and manufacturers, electronic PCB design must focus on durability and reliability. Whether used in wearables, medical devices, automotive electronics, or industrial applications, flexible circuits provide a significant advantage. PCB circuit board manufacturers are now integrating flexible PCBs into designs to enhance performance and longevity.
This blog will discuss how flexible circuits improve durability in electronics and why they are becoming a go-to solution in electronic PCB manufacturing.
What Are Flexible Circuits?
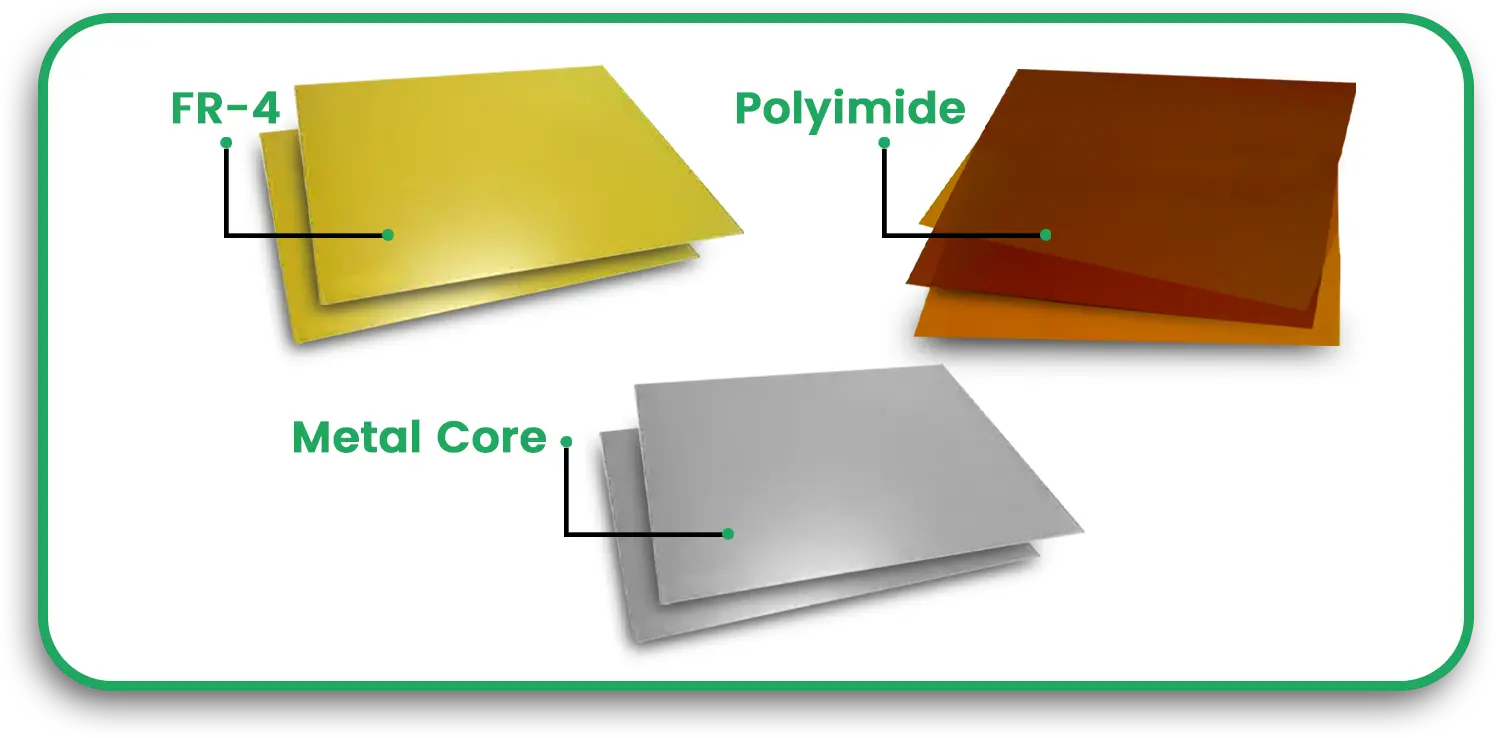
A flexible circuit, also called a flex PCB, is a type of printed circuit board that can bend, twist, and fold without breaking. Unlike traditional rigid multilayer PCBs, these circuits use thin, flexible materials such as polyimide or PET film instead of FR-4. These circuits allow for better space utilisation, improved shock resistance, and increased mechanical durability. They are widely used in electronic PCB circuits for applications where flexibility, weight reduction, and reliability are essential.
Why Durability Matters in Electronics
1. Reducing Mechanical Stress
In rigid circuit boards, repeated vibrations or impacts can cause solder joints to crack, leading to device failure. Flexible circuits, however, are designed to absorb stress, making them perfect for electronic assembly PCBs used in automotive and aerospace applications.
2. Resistance to Environmental Factors
Flexible PCBs are often coated with protective layers that make them resistant to moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. This feature is critical for electronic PCB manufacturing in industries like medical electronics and outdoor sensor devices.
3. Extended Lifespan
Because flexible circuits eliminate the need for bulky connectors and reduce the number of solder joints, they have fewer failure points, leading to longer-lasting electronic devices.
How Flexible Circuits Improve Durability in Electronics
1. Withstand Repeated Bending and Flexing
Unlike traditional multilayer PCBs, which can crack under repeated stress, flexible circuits can handle thousands of bending cycles without damage. This durability makes them ideal for wearable technology, foldable devices, and medical implants.
2. Enhanced Shock and Vibration Resistance
Electronics used in automotive, aerospace, and military applications experience high levels of vibration. Flexible circuits are designed to withstand these conditions, making them ideal for mission-critical systems.
3. High-Temperature Resistance
Polyimide-based flexible circuits have excellent heat resistance, which makes them suitable for harsh industrial environments where temperature fluctuations can cause traditional PCBs to fail.
4. Reduced Weight and Thickness
Because flexible circuits are thinner and lighter than traditional PCBs, they allow for compact electronic PCB design, making them perfect for portable medical devices, drones, and smartphones.
Materials Used in Flexible Circuit Fabrication
To achieve durability and flexibility, PCB circuit board manufacturers use specialised materials in electronic PCB manufacturing.
1. Substrates
- Polyimide (PI): The most common material used for flexible circuits, offering high heat resistance and durability.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Used in lower-cost applications, offering moderate flexibility but lower heat resistance.
2. Conductive Layers
- Copper Foil: Standard choice for conducting layers in flexible circuits.
- Silver Ink: Used in low-cost, low-power applications.
3. Protective Layers
- Solder Mask Material: Prevents oxidation and short circuits.
- Conformal Coating: Adds a protective barrier against moisture and dust.
Key Applications of Flexible Circuits in Electronics
1. Wearable Electronics
From fitness trackers to smart glasses, flexible circuits make it possible to design compact, lightweight devices that can be worn comfortably while withstanding everyday wear and tear.
2. Medical Devices
Many medical implants and diagnostic devices require highly durable and biocompatible electronic circuits. Flexible PCBs help ensure these devices function reliably over long periods.
3. Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles rely on electronic assembly PCBs for navigation systems, sensors, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Flexible circuits improve reliability in high-vibration environments.
4. Aerospace and Military Applications
Satellites, aircraft, and defence equipment require multilayer PCBs that can survive extreme conditions. Flexible circuits provide durability and weight savings in these applications.
5. Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, laptops, and cameras use flexible circuits for improved space efficiency and device longevity.
How to Optimise Flexible Circuit Design for Durability
1. Choose the Right Material
Selecting high-quality polyimide or PET substrates ensures better flexibility and temperature resistance.
2. Use Reinforced Traces
Adding copper plating or protective coatings helps prevent cracks and improves durability.
3. Optimise Bending Areas
Design circuits with curved, gradual bends rather than sharp angles to prevent stress fractures.
4. Minimise Connectors and Solder Joints
Reducing the number of connectors eliminates potential failure points, making electronic PCB circuits more reliable.
5. Implement Stress-Relief Features
Adding strain relief structures in key areas prevents excessive mechanical stress on the circuit. For example, using anchor pads at solder joints can help distribute mechanical load more evenly.
6. Use Protective Coatings
Applying solder mask material or conformal coatings can protect the electronic PCB circuit from environmental damage, such as moisture, dust, and chemicals.
7. Optimise Trace Width and Spacing
Ensuring the proper trace width and spacing prevents overheating and signal interference, which is especially important in high-density multilayer PCB designs.
Flexible Circuit vs. Traditional Rigid PCB: A Durability Comparison
| Feature | Flexible Circuit | Rigid PCB |
| Bendability | Highly flexible, can bend repeatedly | Cannot bend, will break under stress |
| Shock Resistance | Absorbs vibrations and impact | Susceptible to cracks and fractures |
| Weight & Thickness | Lighter and thinner | Bulkier and heavier |
| Temperature Resistance | Withstands high and low temperatures | Can degrade in extreme conditions |
| Durability in Harsh Environments | High | Moderate |
While rigid PCBs are ideal for applications requiring structural strength, flexible circuits offer superior durability and versatility in demanding environments.
Manufacturing Challenges and Solutions for Flexible Circuits
Although flexible circuits provide many benefits, their manufacturing process comes with certain challenges. Here’s how PCB circuit board manufacturers address them:
1. Handling Thin Substrates
Flexible PCBs use ultra-thin substrates that can wrinkle or tear. Solution: Using supporting carriers during fabrication prevents damage.
2. Achieving Consistent Plating
Because flexible circuits bend, ensuring even copper plating can be difficult. Solution: Advanced plating techniques and controlled chemical baths improve consistency.
3. Preventing Signal Interference
High-speed electronic PCB circuits require proper shielding to avoid electromagnetic interference (EMI). Solution: Using ground planes and shielding layers improves signal integrity.
4. Optimising Assembly Process
Flexible PCBs require careful handling during circuit board assembly to avoid misalignment or damage. Solution: Automated precision equipment ensures accurate component placement.
Future Trends in Flexible PCB Technology
1. Increasing Use of High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs
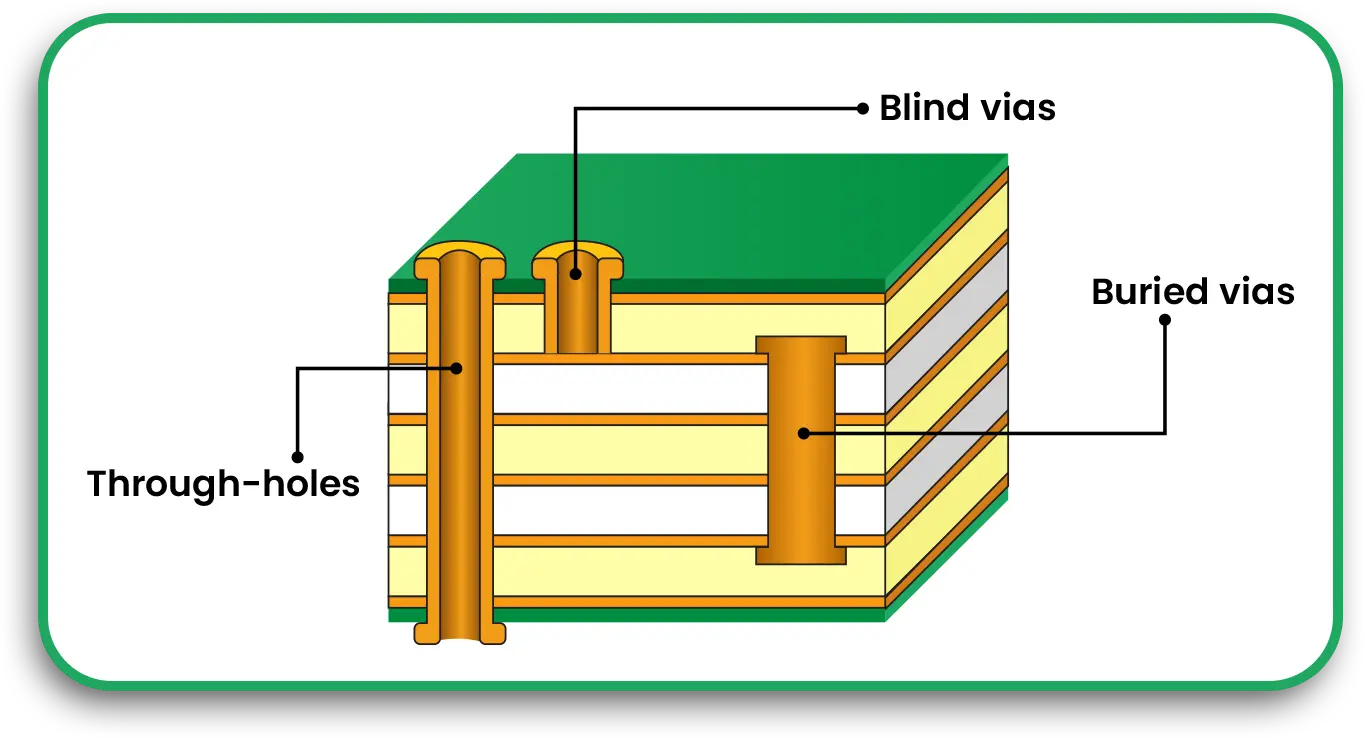
As electronics continue to shrink, HDI multilayer PCBs with microvias and ultra-fine traces will be essential for next-generation devices.
2. Printed Electronics and Conductive Inks
Innovations in conductive ink technology are enabling flexible hybrid electronics, where printed circuits replace traditional copper traces.
3. Stretchable Electronics
Next-gen stretchable PCBs will revolutionise wearables and medical implants, offering even greater durability and adaptability.
4. Enhanced Materials for Extreme Environments
Future flexible circuits will use advanced polymers and nanomaterials to withstand higher temperatures and radiation exposure in aerospace and industrial applications.
Conclusion
Flexible circuits are transforming the electronics industry by offering unmatched durability, lightweight designs, and improved reliability. Whether for wearable technology, medical devices, or aerospace systems, these circuits provide a long-lasting and space-saving solution. As electronic PCB manufacturing continues to evolve, flexible PCBs will play an even bigger role in high-performance applications. If you need custom printed circuit boards that prioritise durability and efficiency, flexible circuits are the way to go.
Looking for Reliable Flexible PCB Solutions?
At PCB Runners, we specialise in high-quality PCB fabrication for flexible circuits, multilayer PCBs, and custom designs. Contact us today to get started on your next circuit board assembly project.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What makes flexible PCBs more durable than rigid PCBs?
Flexible PCBs can bend and absorb stress, making them more resistant to mechanical damage and environmental factors like heat and moisture.
2. Can flexible circuits replace traditional rigid PCBs?
In some applications, yes. Flexible circuits are ideal for wearables, medical devices, and aerospace, but rigid PCBs are still necessary for high-structural integrity applications.
3. What are the common materials used in flexible PCB manufacturing?
Flexible PCBs use polyimide (PI), PET film, and conductive copper layers to ensure durability and flexibility.
4. How can I ensure my flexible PCB lasts longer?
Use high-quality materials, apply protective coatings, minimise stress points, and follow best practices in electronic PCB design.
5. Are flexible circuits more expensive than rigid PCBs?
Initially, flexible circuits may cost more due to specialised materials and processes, but they reduce overall costs by eliminating connectors and improving reliability.