Innovation in electronics often comes from subtle yet impactful design improvements. One such advancement is the multi-layer semi-flex PCB design, a hybrid solution that combines the rigidity of traditional boards with the flexibility needed for dynamic applications.
If you’ve worked with flex PCB production, you’ll know that semi-flex boards are designed for devices requiring controlled bending during assembly or operation.
They are useful in applications where space is limited and reliability is essential, such as in automotive electronics, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
What Exactly Is a Semi-Flex PCB?
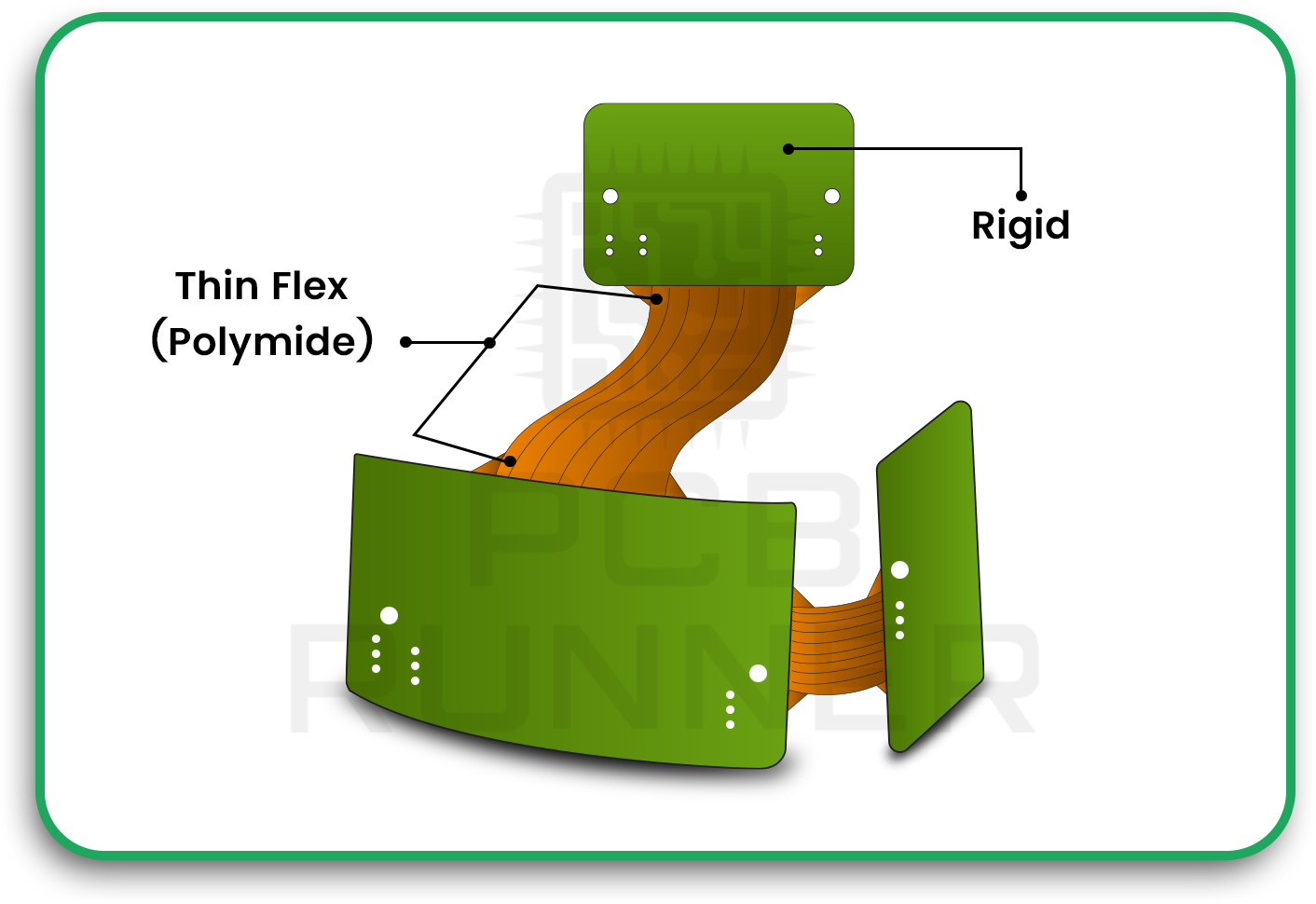
A semi-flex PCB is a rigid printed circuit board that includes the flex layers capable of bending. This is achieved by carefully stacking the thin flex Polyimide layers in targeted layer sequence to meet required bandability.
Unlike a fully flexible PCB, a semi-flex design does not require additional connectors or separate flexible layers. This simplifies the assembly process, reduces overall costs, and minimises potential points of failure. It strikes an ideal balance between flexibility and structural strength.
Looking to optimize your next flex PCB production project?
PCB Runner provides custom semi-flex PCB manufacturing with precise engineering and reliable turnaround times. Submit your design files at sales@pcbrunner.com for review and pricing
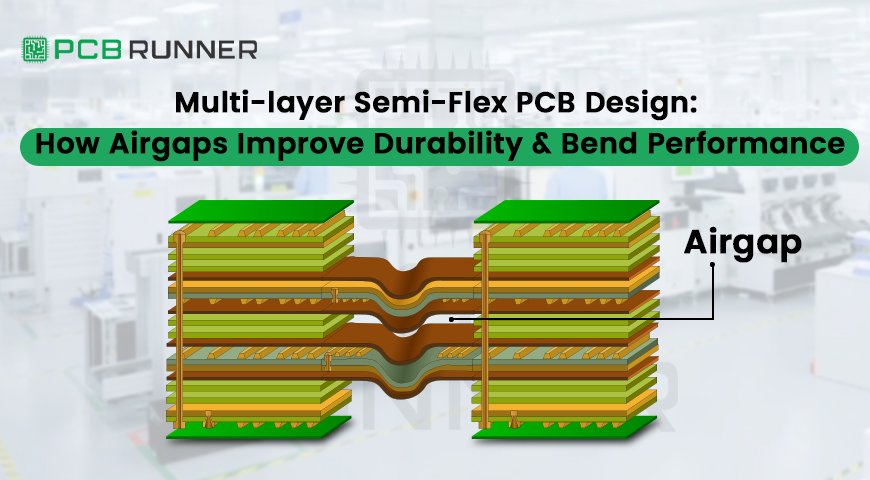
The Role of Airgaps in Semi-Flex PCB Design
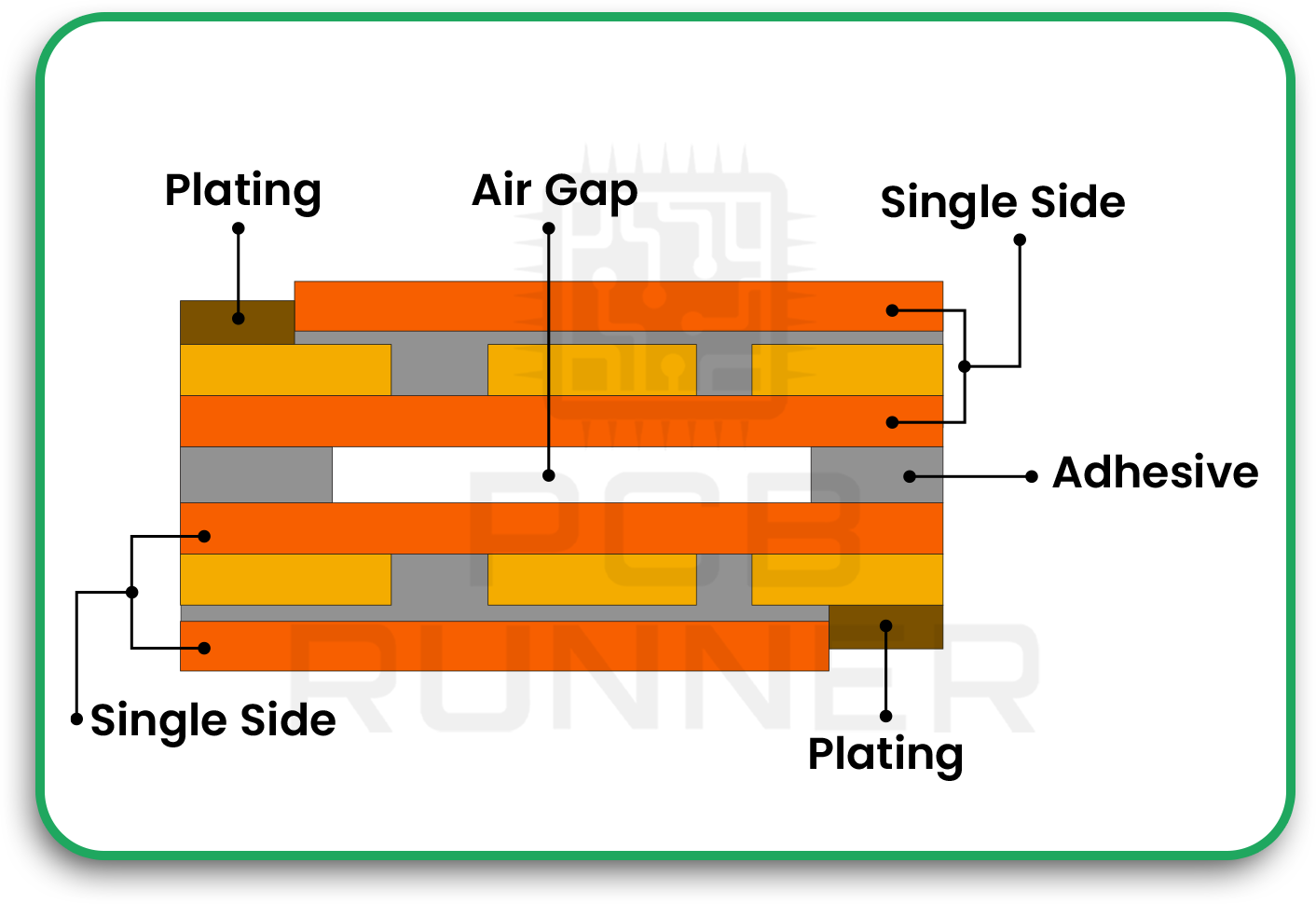
The inclusion of airgaps has significantly improved the performance and reliability of semi-flex PCBs. An airgap refers to a deliberate space left between selected layers in the PCB stack-up. This feature helps distribute stress evenly when the board bends, which enhances both its flexibility and durability.
When PCB Designers need to make m rigid flex PCB bends, The stress builds up in the center of flex outer layers, which can lead to stiff curves or crack.. By introducing an airgap, the inner airgap structure between flex can absorb strain more efficiently and allow more bendradius then stacked Flex multi layers, preventing material fatigue and extending the board’s lifespan. The air gap also contributes to better thermal balance and mechanical stability.
Benefits of Airgap Integration
Adding airgaps to a multi-layer PCB design can transform how the board performs under repeated movement or stress. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Improved bend reliability: Airgaps allow smoother bending and reduce stress concentration in the copper and dielectric layers.
- Enhanced lifespan: Boards with air gaps can endure more bending cycles, maintaining consistent electrical performance.
- Better thermal management: The air pocket helps dissipate heat efficiently, preventing localised expansion or damage.
- Lower risk of delamination: By absorbing internal stress, air gaps help maintain adhesion between layers.
This innovation makes semi-flexible boards suitable for applications that require repeated movement without compromising electrical integrity.
Talk to our PCB engineering experts at PCB Runner to explore rigid flex PCB manufacturing options that match your specifications. Contact Us
Design Considerations for Semi-Flex PCBs
Designing a semi-flex PCB with airgaps requires precise engineering. Factors such as material selection, copper thickness, and the placement of flexible zones all affect how well the board performs.
Engineers typically use polyimide or specially treated FR4 materials to balance flexibility and mechanical strength. The bend radius must also be carefully calculated; a smaller radius increases strain, while a larger one can reduce compactness.
Working with a reliable rigid flex PCB manufacturer ensures that these aspects are optimised during production. Manufacturers can simulate mechanical stress prior to fabrication, allowing them to predict how the board will perform under real-world conditions.
Applications of Multi-layer Semi-Flex PCBs
Semi-flex technology is becoming increasingly popular across industries that demand compactness and dependability. Some notable uses include:
- Automotive systems: Used in dashboards, LED modules, and sensor connections where limited flexibility is required.
- Medical equipment: Ideal for compact diagnostic tools that need to handle repeated movement.
- Consumer electronics: Found in foldable devices, cameras, and wearable gadgets.
- Industrial automation: Perfect for control panels and robotic systems with moving parts.
Semi-flex PCBs reduce the need for connectors and separate flexible circuits, simplifying design and assembly.
Understanding the Rigid Flex with Airgap Concept
Another important innovation in PCB engineering is the rigid flex with airgap design. This method combines the advantages of rigid-flex technology with the structural benefits of airgaps.
By introducing small spaces between certain layers, the design reduces mechanical fatigue in flexible sections. This makes the pcb more resistant to bending stress while preserving its electrical performance. Engineers often use this design in high-reliability applications such as aerospace, medical devices and defence electronics.
How Flex Airgap PCBs Enhance Performance
A flex airgap PCB offers additional versatility by providing controlled flexibility where needed without compromising stability elsewhere. The air gap helps ensure that the bending area maintains its structural integrity, allowing repeated motion without cracking or delamination.
This type of PCB is particularly valuable in designs where lightweight and compact construction are essential. For example, in portable medical devices or compact industrial controllers, the air gap ensures long-term durability even under constant mechanical stress.
The Role of Stackup Engineering
In advanced designs, engineers often use a Rigidflex airgap stackup, which involves carefully layering rigid and flexible materials with integrated airgaps. The goal is to balance electrical performance, heat dissipation, and mechanical strength.
Every layer in this stackup is placed strategically to maintain signal integrity and avoid excessive stress in the bending zones. This method makes it easier to produce PCBs that are dependable and built to last, even in tough conditions.
Industry Trends and Evolving Design Practices
With electronics becoming more compact and sophisticated, designers are constantly exploring ways to combine flexibility, strength, and cost efficiency. Airgap technology is a key part of this evolution, offering better control over board mechanics without requiring exotic materials or complex assembly processes.
As manufacturing capabilities improve, semi-flex PCBs are becoming more accessible across industries. Companies like PCB Runner are continually refining techniques that ensure consistent quality, predictable performance, and long-term reliability.
As PCB Runner continues to innovate, we help clients across industries implement multi-layer semi-flex designs that deliver high performance, predictable reliability, and scalable manufacturability.
Conclusion: The Future of Semi-Flex PCB Engineering
The multi-layer semi-flex PCB design represents the next step in achieving flexible, durable, and compact electronic assemblies. Engineers can greatly improve a board’s bending performance, heat stability, and mechanical strength by incorporating air gaps. Designers looking for efficient, flexible, and reliable solutions should consider air gap integration as a better and cost-effective option.
Partnering with experienced manufacturers such as PCB Runner helps ensure every design meets precise technical standards while maintaining consistent quality throughout production.
FAQs
- What is a semi-flex PCB?
A semi-flex PCB is a rigid board with certain areas engineered to bend, offering flexibility without the need for separate connectors or cables.
- How do air gaps improve durability?
It reduces internal stress during bending, preventing cracks, delamination, and other mechanical failures.
- What materials are used in semi-flex PCBs?
Engineers commonly use modified FR4 or polyimide materials that balance flexibility and strength.
- What is a Rigidflex airgap stackup?
It’s a structure combining rigid and flexible PCB layers with integrated airgaps to improve mechanical reliability.
- Why are semi-flex boards preferred for modern electronics?
They reduce space, improve reliability, and simplify assembly compared to traditional rigid or fully flexible boards.