Have you ever wondered why some printed circuit boards last longer or work better in harsh environments? If you’re involved in PCB manufacture, PCB production in the UK, or even custom PCB design for electric vehicle charging station contractors, you’ve likely heard about selective coating. But what is it, and why does it matter for your PCB printed circuit board assembly or PCB board layout design? Let’s break it down in simple terms so that you can make better choices for your next project.
What Is Selective Coating in PCB Manufacturing?
Selective coating is a process where a protective layer is applied only to certain parts of a PCB, not the whole board. This coating shields sensitive areas from moisture, dust, chemicals, and other hazards. Instead of dipping or spraying the entire board, selective coating targets just the spots that need protection.
Why not coat the whole board? Some components, like connectors or test pads, shouldn’t be covered because they need to stay accessible. Selective coating lets you protect what matters without causing problems elsewhere.
Why Is Selective Coating Important?
Think about where your PCBs end up. In electric vehicle charging stations, for example, boards face rain, heat, and even road salt. Without protection, they can fail early. Selective coating helps your PCB printed circuit board assembly last longer and work better, especially in harsh places.
For custom PCB design, selective coating also means you can fine-tune your board’s durability. You decide which parts need extra care and which parts should stay open for connections or repairs.
How Does Selective Coating Work?
Let’s walk through the steps:
1. Preparation and Cleaning
Before coating, the board must be spotless. Any leftover flux, dust, or fingerprints can ruin the coating’s grip. Cleaning is done with special washes or vapour degreasers.
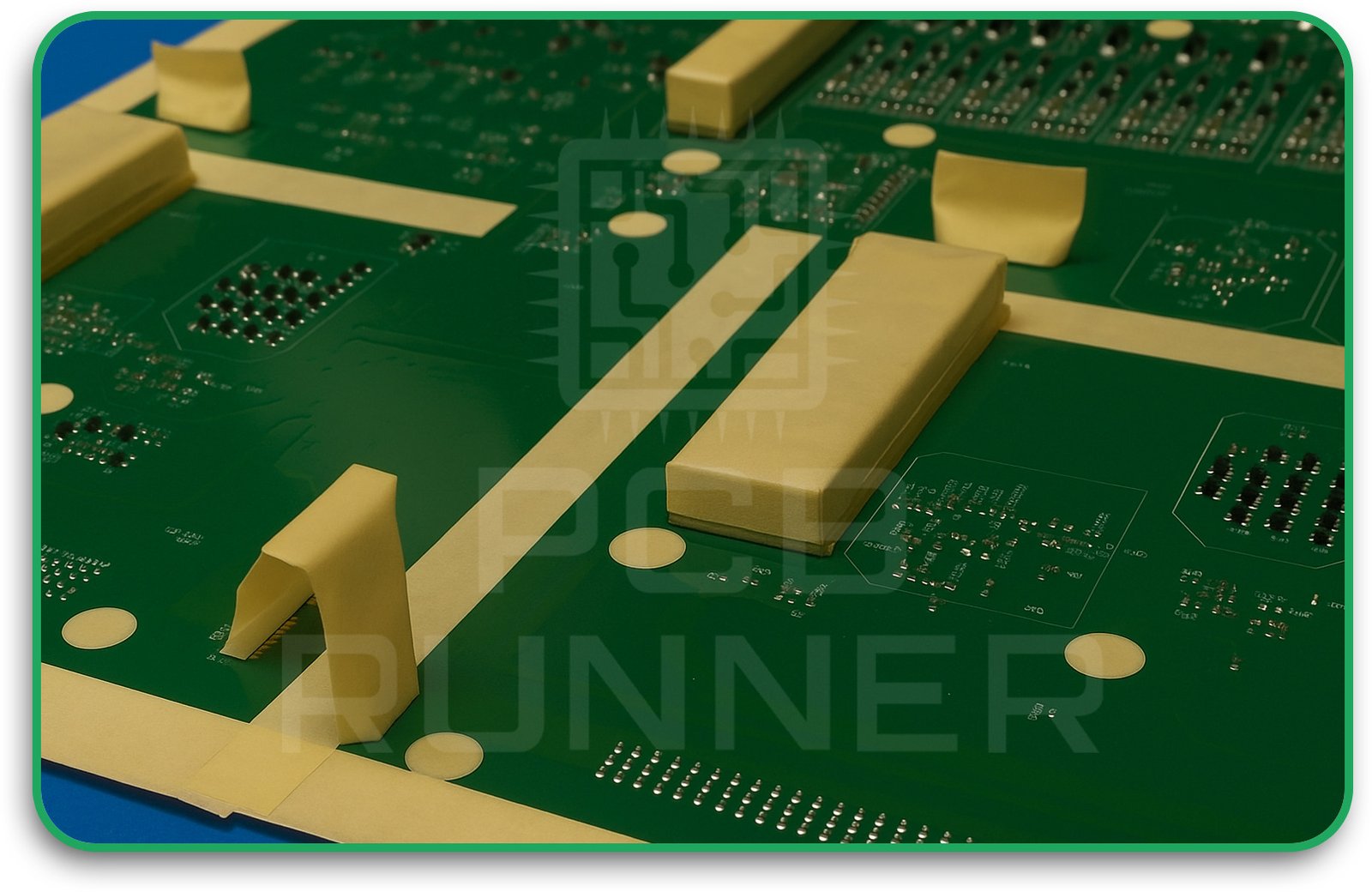
2. Masking
Not every part of the PCB should be coated. Connectors, test pads, and edge contacts are masked off using tape, boots, or peelable masks6. This step is crucial—if you miss it, you might coat something you shouldn’t.
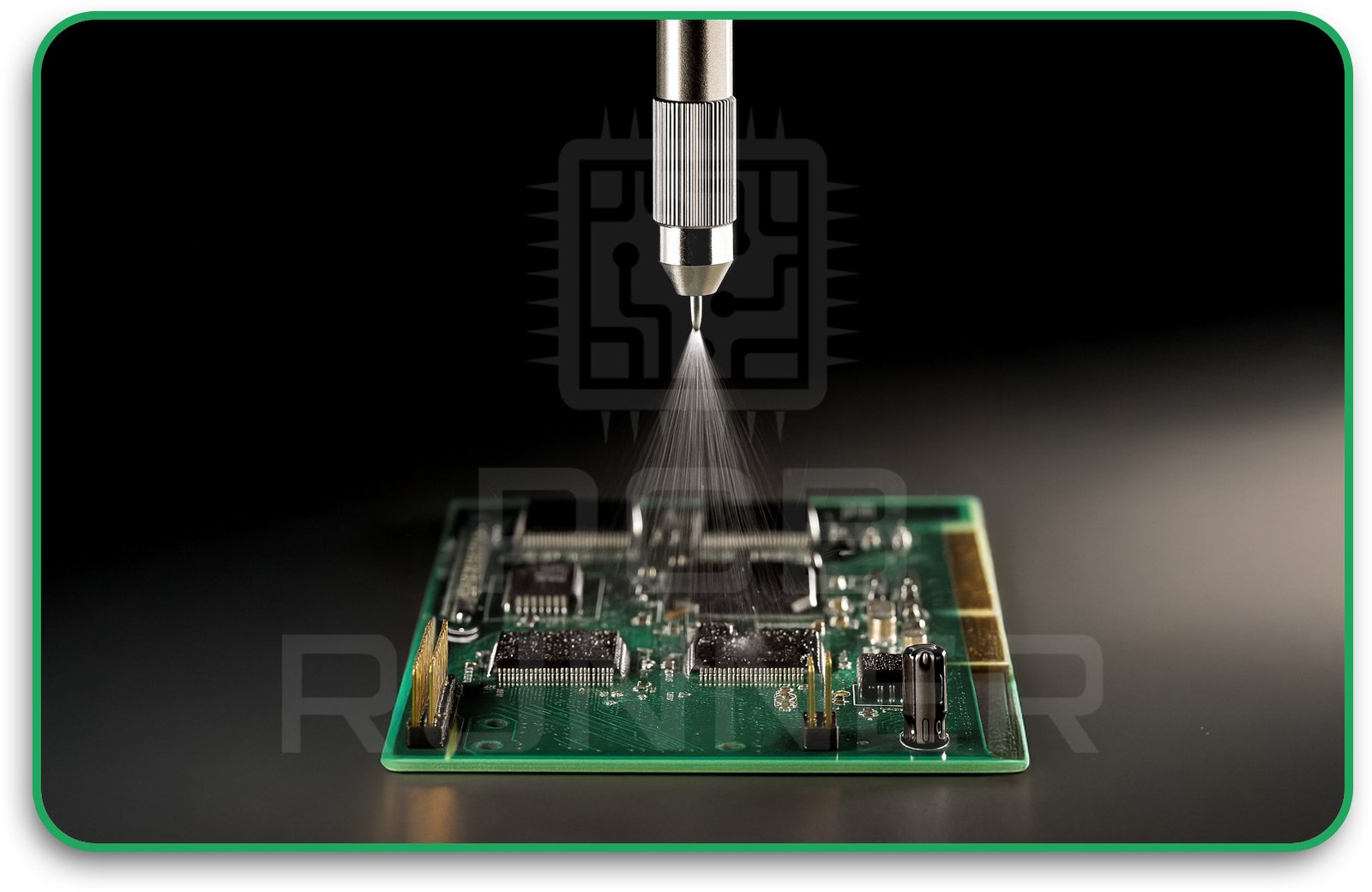
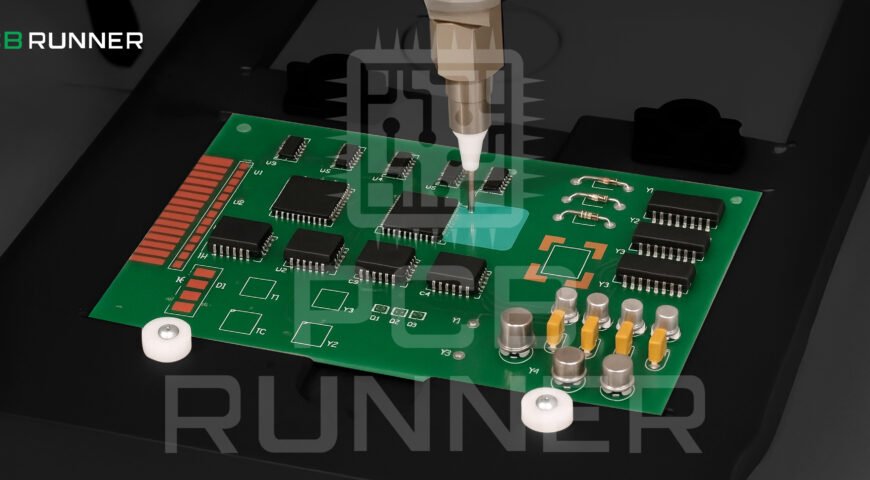
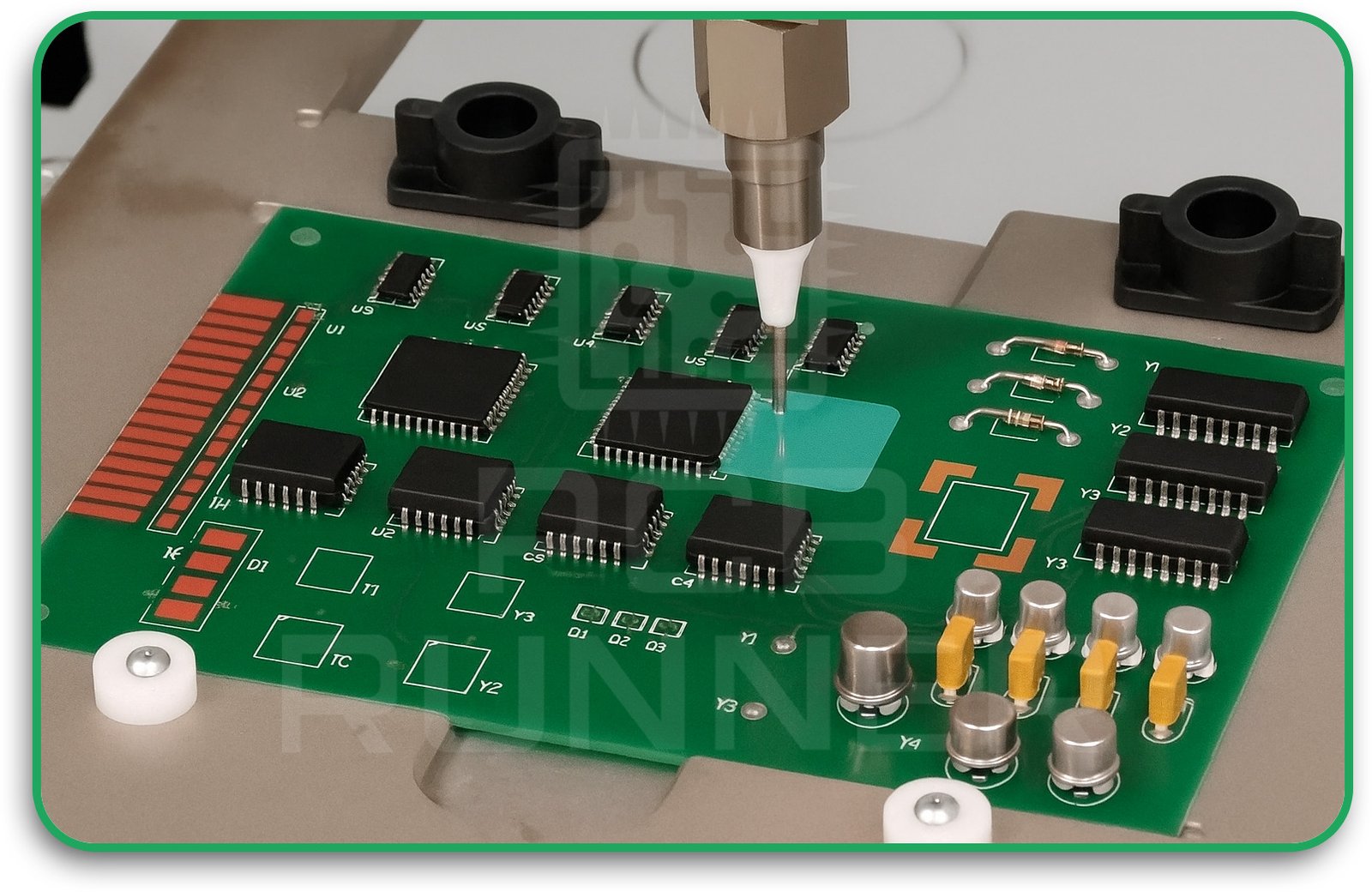
3. Programming the Coating Path
The modern selective coating uses robotic arms. You (or your engineer) create a digital map that tells the robot where to apply the coating, how thick it should be, and how fast to move. This ensures the coating is accurate and repeatable, even for complex PCB board layout designs.
4. Applying the Coating
The robot uses a needle or jet valve to apply the coating material only where needed. This is much more precise than old methods like spraying or dipping. It also saves material and reduces waste.
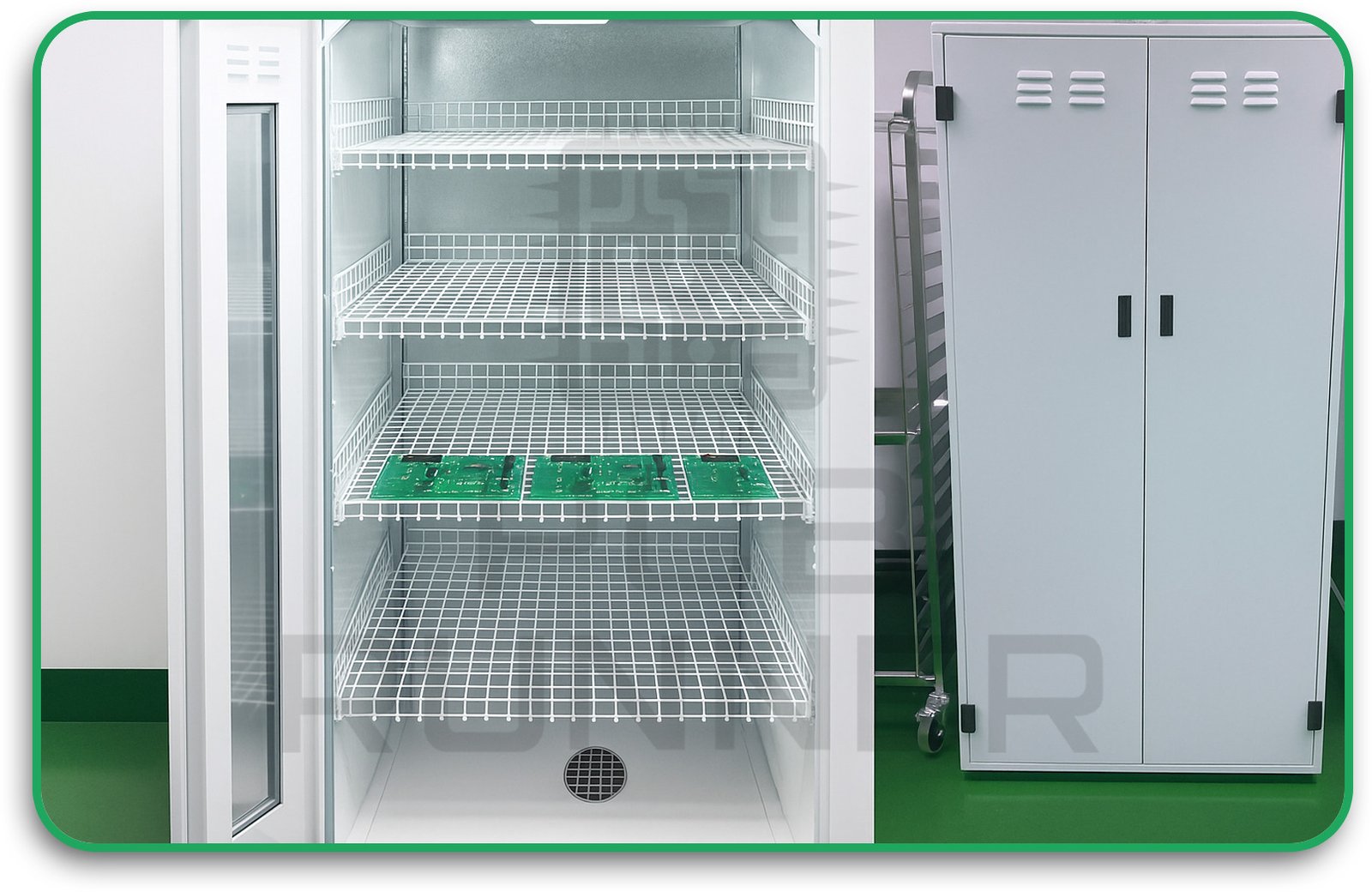
5. Curing
Once the coating is on, it needs to dry or “cure.” This can be done with heat, UV light, or even moisture, depending on the type of coating used. The curing process is carefully controlled to avoid bubbles or thin spots.
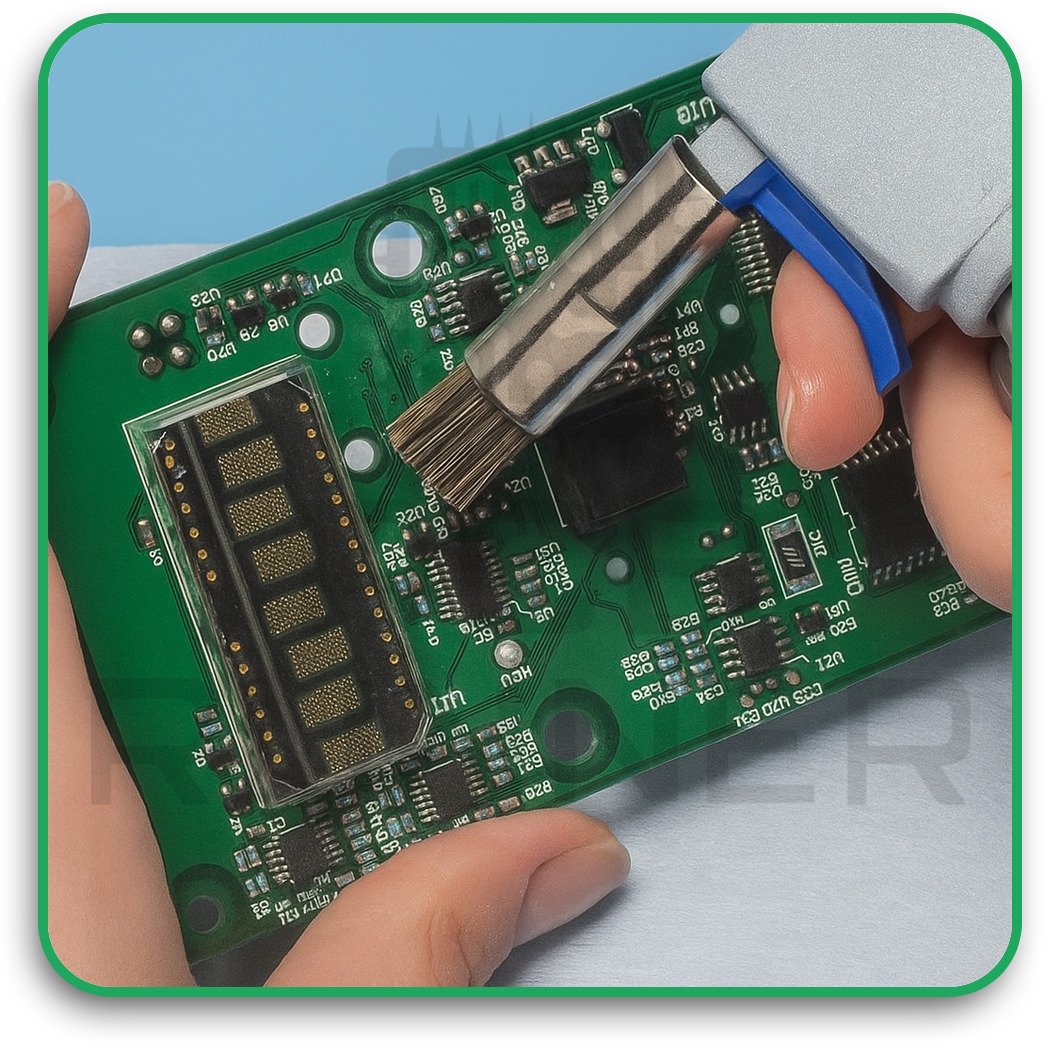
6. Inspection
After curing, the board is checked under visible and UV light to make sure the coating is even, with no gaps or defects. Some manufacturers also test how well the coating sticks and protects against electricity.
Types of Coating Materials
Different projects need different coatings. Here are the most common types:
- Acrylic: Easy to apply and remove, suitable for general use.
- Silicone: Handles high heat, great for automotive or EV charging station boards.
- Polyurethane: Tough and resistant to chemicals.
- Epoxy: Extremely hard but harder to remove for repairs.
Your choice depends on where your PCB will be used and what it needs to survive.
Benefits of Selective Coating for Your Project
1. Precision
Selective coating is very accurate. Robots can coat tiny areas without spilling over onto sensitive parts. This is perfect for custom PCB design where you have unique components or layouts.
2. Efficiency
You use less coating material, which saves money and reduces drying time. This is a big plus for PCB production uk, where cost and speed matter.
3. Better Performance
By protecting only what needs it, you avoid problems like blocked connectors or test points. Your pcb printed circuit board assembly stays easy to test and repair.
4. Consistency
Robots don’t get tired or make mistakes. Every board gets the same high-quality coating, which is essential for large-scale PCB manufacture.
Where Is Selective Coating Used?
Selective coating is everywhere, especially in industries where boards face harsh conditions:
- Electric Vehicle Charging Stations: Boards need to handle weather, temperature swings, and even vandalism.
- Automotive: Protects boards from oil, vibration, and heat.
- Telecom: Keeps moisture and dust away from sensitive circuits.
- Industrial Controls: Shields boards in factories from chemicals and grime.
If you’re an electric vehicle charging station contractor, using selective coating can help your installations last longer and reduce maintenance calls.
Tips for Better PCB Board Layout Design with Selective Coating
If you’re planning a custom PCB design, keep selective coating in mind from the start. Here’s how:
- Group sensitive parts: Place components that need coating together to make the process easier and faster.
- Keep connectors and test pads separate: This makes it simpler to mask them off before coating.
- Talk to your manufacturer early: Not all PCB production UK shops have the same coating options. Ask what they offer and what they recommend for your project.
What Happens If You Skip Selective Coating?
Skipping selective coating can lead to big problems:
- Short Circuits: Moisture or dust can cause electrical shorts.
- Corrosion: Chemicals or salt can eat away at copper traces.
- Early Failure: Your product might stop working sooner, leading to unhappy customers and costly repairs.
For electric vehicle charging station contractors, this could mean more service calls and a damaged reputation.
How to Choose the Right Selective Coating Partner
Not every PCB manufacturing shop offers selective coating, and not all do it well. When picking a partner, ask:
- Do they use robotic selective coating systems?
- Can they handle your board size and complexity?
- What coating materials do they offer?
- How do they inspect and test coated boards?
- Can they support your volume, from prototypes to full production?
Choosing the right partner in PCB production UK can save you time, money, and headaches down the road.
Action Steps for Your Next Project
- Review your PCB board layout design with coating in mind.
- Ask your manufacturer about selective coating options and materials.
- Decide which areas need protection and which should stay open.
- Request a sample or prototype to see the coating quality before full production.
- Inspect the finished boards to make sure the coating is even and covers the right spots.
Final Thoughts
Selective coating is a smart way to protect your PCBs without wasting material or blocking essential parts. It’s precise and efficient and helps your boards last longer in harsh environments. Whether you’re working on custom PCB design, PCB manufacture, or building electric vehicle charging stations, understanding selective coating can help you deliver better products and happier customers.
If you want your next PCB printed circuit board assembly to stand up to the real world, don’t overlook selective coating. Ask your PCB production UK partner about it today, and make sure your boards are ready for anything.